Identity Security
In today's interconnected world, protecting our personal information has become more crucial than ever. With the rise of cybercrime and data breaches, ensuring identity security has become a paramount concern for individuals and organizations alike. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of identity security, common threats to our identities, and practical steps to safeguard our personal information.
Identity security refers to the protection of our personal information from unauthorized access, use, or theft. It encompasses various aspects such as safeguarding our Social Security numbers, bank account details, credit card information, and online credentials. By maintaining a robust identity security, we can mitigate the risks of identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities that can have severe consequences on our personal and financial well-being.
There are a number of common threats that jeopardize our identity security. Cybercriminals employ various tactics such as phishing, malware, and social engineering to gain unauthorized access to our personal information. They exploit vulnerabilities in our online behavior, weak passwords, and outdated security measures. It is essential to be aware of these threats and take proactive measures to protect ourselves.
Now that we understand the importance of identity security and the threats we face, let's explore practical steps to fortify our defenses. This section will provide actionable tips, including:
Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Creating unique, complex passwords and enabling two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to our online accounts.
Secure Internet Connections: Avoiding public Wi-Fi networks and using VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) when accessing sensitive information can help prevent unauthorized access to our data.
Regular Software Updates: Keeping our operating systems, applications, and antivirus software up to date is crucial to patch security vulnerabilities.
Practicing Safe Online Behavior: Being cautious while clicking on links or downloading attachments, avoiding suspicious websites, and being mindful of sharing personal information online are essential habits to develop.
Matt Conran
Highlights: Identity Security
The Importance of Identity Security
Identity security safeguards your personal information from unauthorized access, fraud, and identity theft. With the increasing prevalence of data breaches and online scams, it is essential to comprehend the significance of protecting your digital identity. Doing so can mitigate potential risks and maintain control over your sensitive data. Identity theft is a pervasive issue that can have devastating consequences.
Cybercriminals employ various techniques to obtain personal information, such as phishing, hacking, and data breaches. Once they access your identity, they can wreak havoc on your financial and personal life. It is essential to understand the gravity of this threat and take necessary precautions.
Required – Identity Security:
– Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: One fundamental aspect of identity security is creating strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts. Avoid using common passwords or personal information that can be easily guessed. Implementing two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of protection by requiring a verification code or biometric confirmation in addition to your password.
– Regularly Update and Secure Your Devices: Keeping your devices updated with the latest software and security patches is vital for identity security. Manufacturers periodically release updates to address vulnerabilities and strengthen defenses against potential threats. Additionally, consider installing reputable antivirus software and firewalls to protect against malware and other malicious attacks.
– Be Mindful of Phishing Attempts: Phishing is a common tactic used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into revealing their personal information. Be cautious when clicking on links or providing sensitive data, especially in emails or messages from unknown sources. Verify the legitimacy of websites and communicate directly with trusted organizations to avoid falling victim to phishing scams.
Zero-Trust Identity Management
Zero-trust identity management involves continuously verifying users and devices to ensure access and privileges are granted only when needed. The backbone of zero-trust identity security starts by assuming that any human or machine identity with access to your applications and systems may have been compromised.
The “assume breach” mentality requires vigilance and a Zero Trust approach to security centered on securing identities. With identity security as the backbone of a zero-trust process, teams can focus on identifying, isolating, and stopping threats from compromising identities and gaining privilege before they can harm.
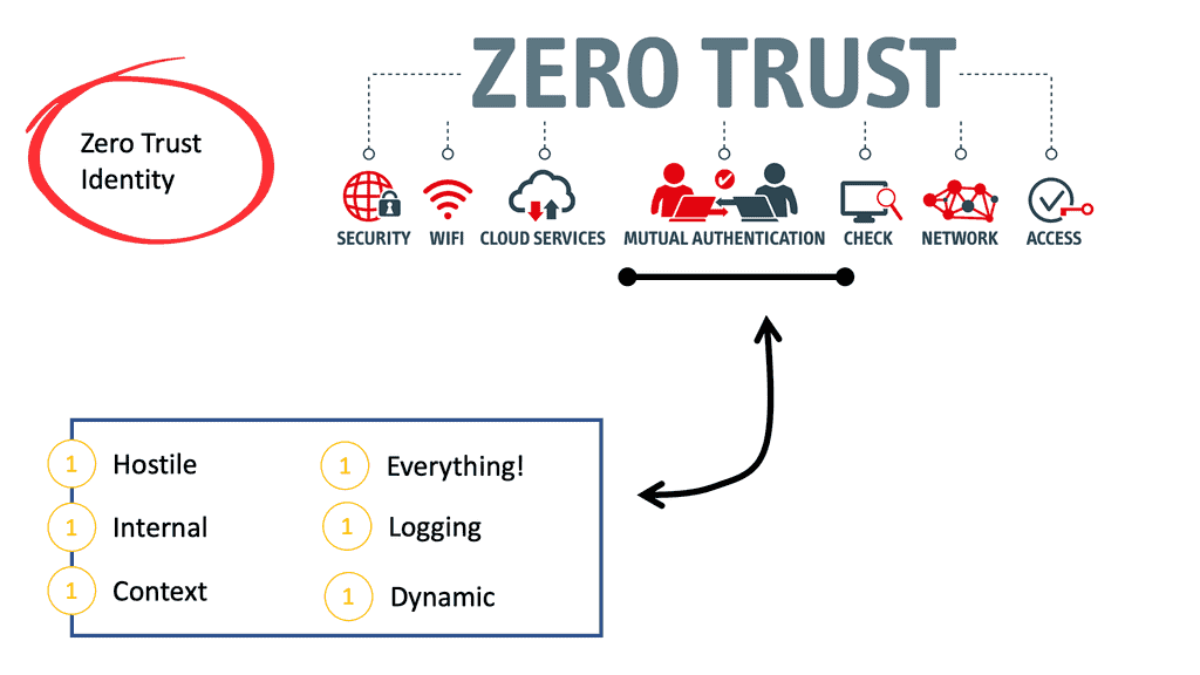
Zero Trust Authentication
The identity-centric focus of zero trust authentication uses an approach to security to ensure that every person and every device granted access is who and what they say they are. It achieves this authentication by focusing on the following key components:
- The network is always assumed to be hostile.
- External and internal threats always exist on the network.
- Network locality needs to be more sufficient to decide trust in a network. As discussed, other contextual factors must also be taken into account.
- Every device, user, and network flow is authenticated and authorized. All of this must be logged.
- Security policies must be dynamic and calculated from as many data sources as possible.
Zero Trust Identity: Validate Every Device
Not just the user: Validate every device. While user verification adds a level of security, more is needed. We must ensure that the devices are authenticated and associated with verified users, not just the users.
Risk-based access: Risk-based access intelligence should reduce the attack surface after a device has been validated and verified as belonging to an authorized user. This allows aspects of the security posture of endpoints, like device location, a device certificate, OS, browser, and time, to be used for further access validation.
Device Validation: Reduce the attack surface
While device validation helps limit the attack surface, it is only as reliable as the endpoint’s security. Antivirus software to secure endpoint devices will only get you so far. We need additional tools and mechanisms to tighten security even further.
Identity Security – Google Cloud
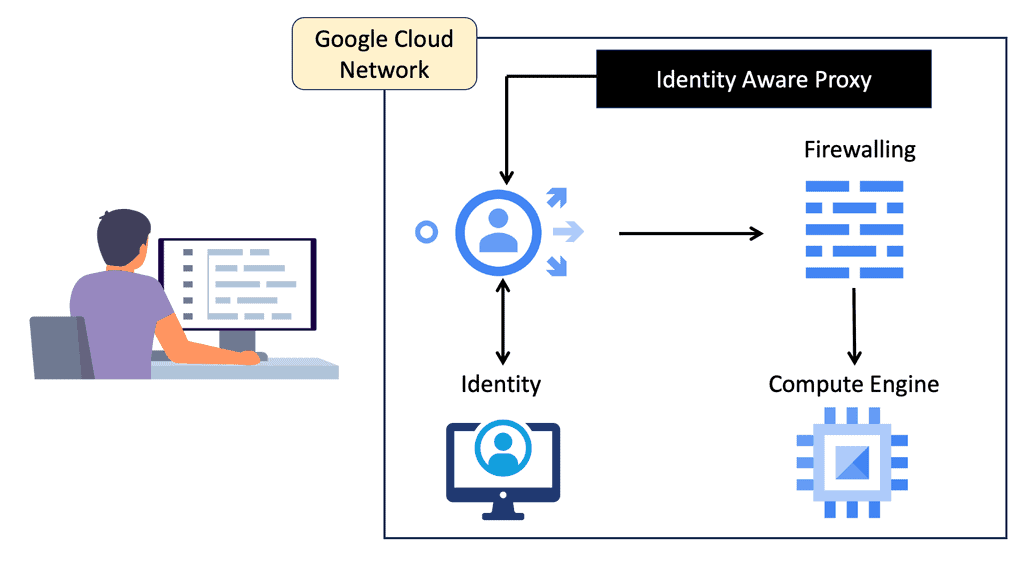
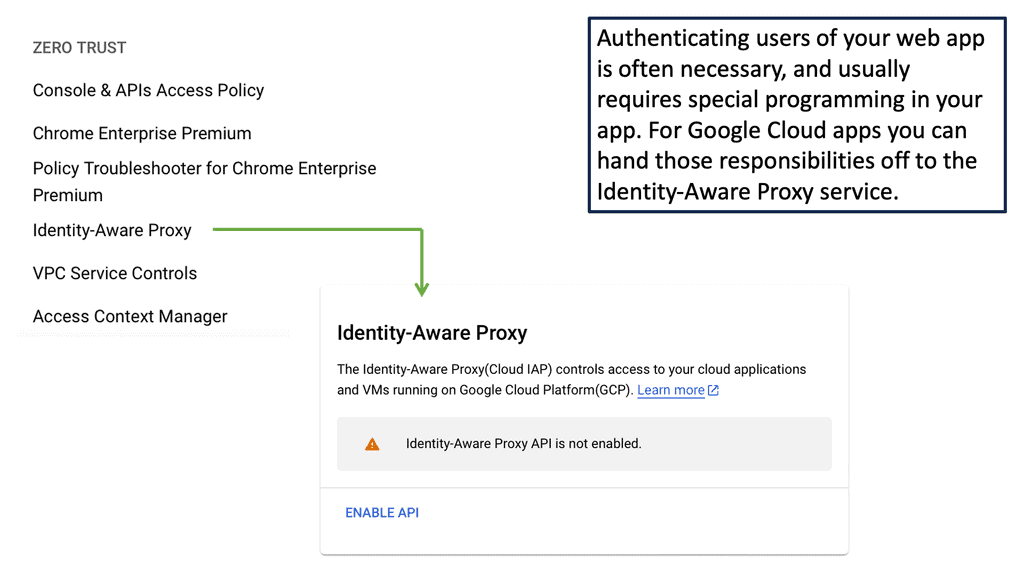
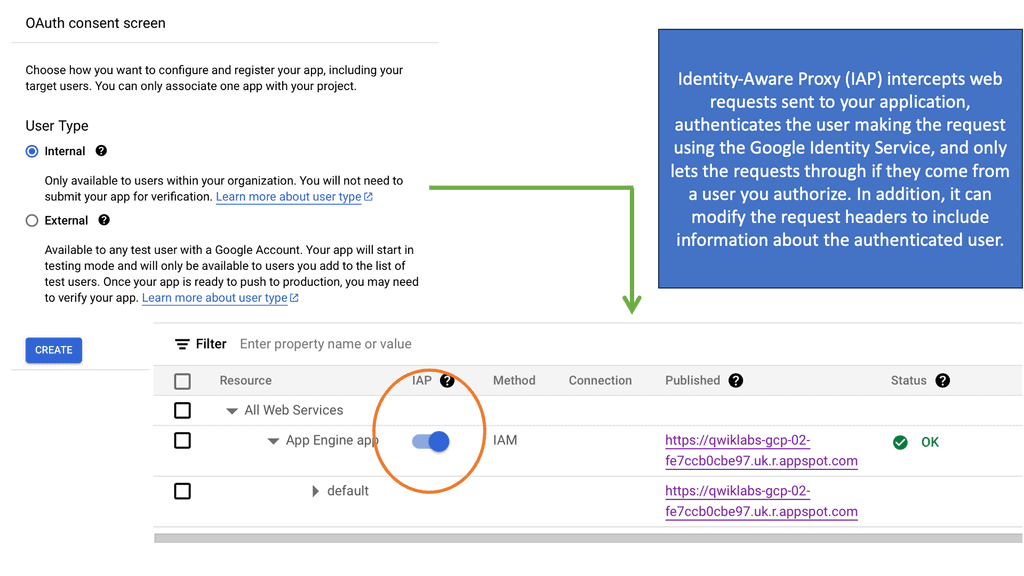
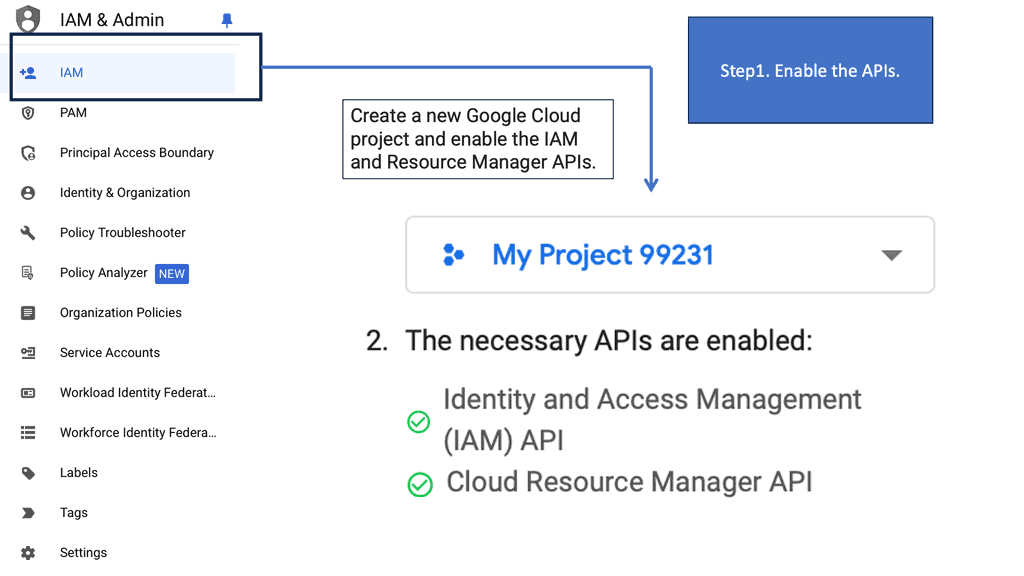
### What is Identity-Aware Proxy?
Identity-Aware Proxy is a security feature that ensures only authenticated users can access your applications and resources. Unlike traditional security models that rely on network-based access controls, IAP uses user identity and contextual information to allow or deny access. This approach allows organizations to implement a zero-trust security model, where the focus is on verifying the user and their context rather than the network they are connecting from.
### Benefits of Using Identity-Aware Proxy
Implementing IAP comes with a range of benefits that can significantly enhance an organization’s security posture:
1. **Improved Security**: By enforcing access based on user identity and context, IAP reduces the risk of unauthorized access. It ensures that only legitimate users can access sensitive applications and data.
2. **Simplified Access Management**: IAP centralizes access control management, allowing administrators to easily define and enforce access policies that are consistent across all applications and services.
3. **Scalability**: As organizations grow, so do their security needs. IAP scales effortlessly with your infrastructure, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
4. **Enhanced User Experience**: With IAP, users can access applications seamlessly without the need for a VPN or additional authentication layers, improving productivity and satisfaction.
### Integration with Google Cloud
Google Cloud’s Identity-Aware Proxy is a robust solution for securing application access. It integrates seamlessly with Google Cloud services, allowing organizations to leverage Google’s powerful infrastructure for managing and securing their applications. Google Cloud IAP supports a wide range of applications, including those hosted on Google Kubernetes Engine, Compute Engine, and App Engine. By using Google Cloud IAP, organizations can take advantage of features such as single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and detailed access logging.
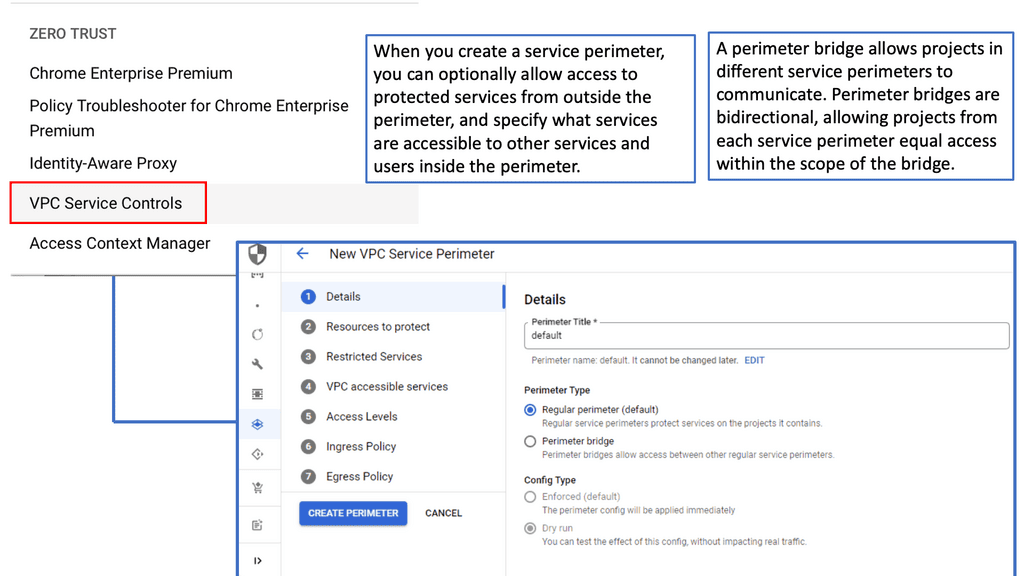
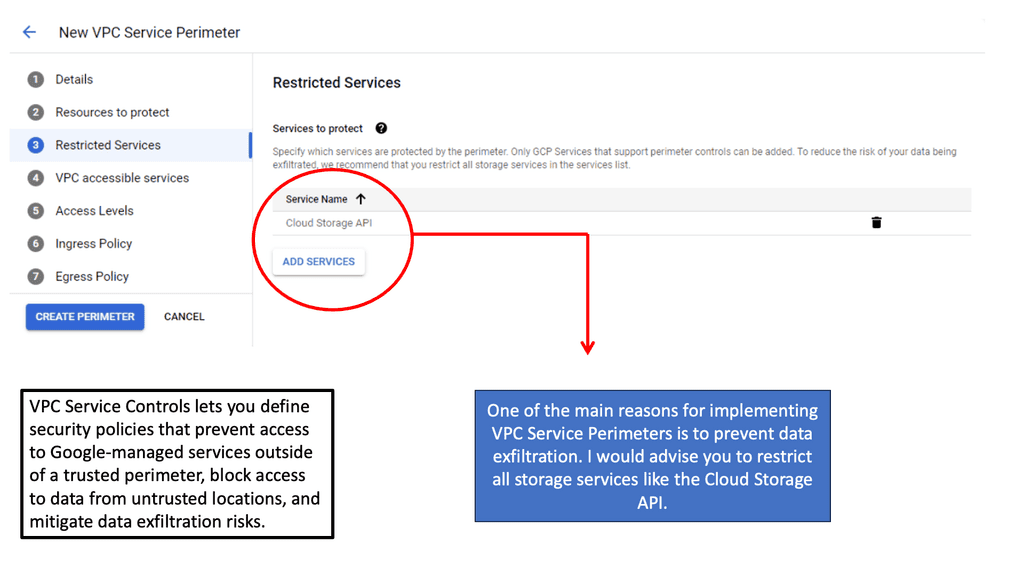
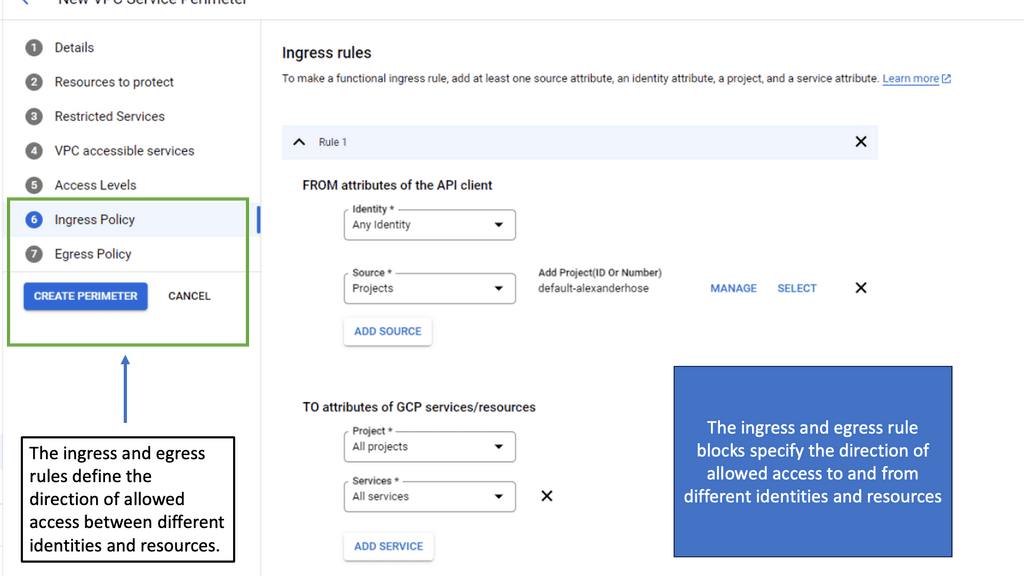
### What are VPC Service Controls?
VPC Service Controls provide a security perimeter around Google Cloud services, adding an extra layer of protection against data exfiltration. With VPC Service Controls, organizations can define security policies that restrict access to their data based on the source and destination of network traffic, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure even in a highly distributed environment. This feature is particularly beneficial for businesses dealing with sensitive data, as it provides a robust mechanism to control data access and movement.
### Enhancing Identity Security
Identity security is a critical component of any cloud security strategy. VPC Service Controls play a pivotal role in this aspect by allowing organizations to manage and secure identities across their cloud infrastructure. By defining policies that specify which identities can access particular services, organizations can minimize the risk of unauthorized data access. This level of control is crucial for maintaining compliance with regulatory standards and safeguarding sensitive information.
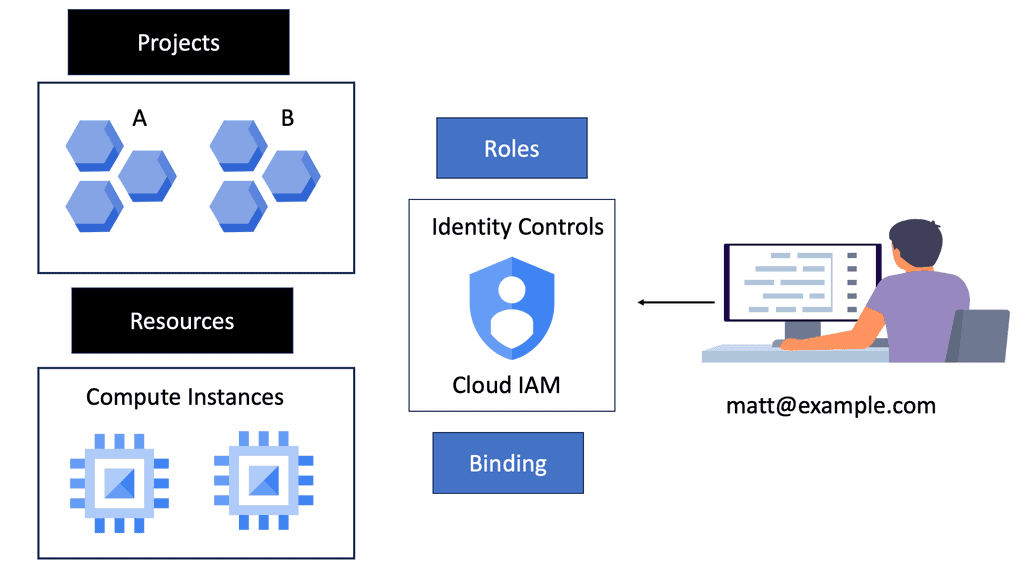
Cloud IAM **The Pillars of Identity Security**
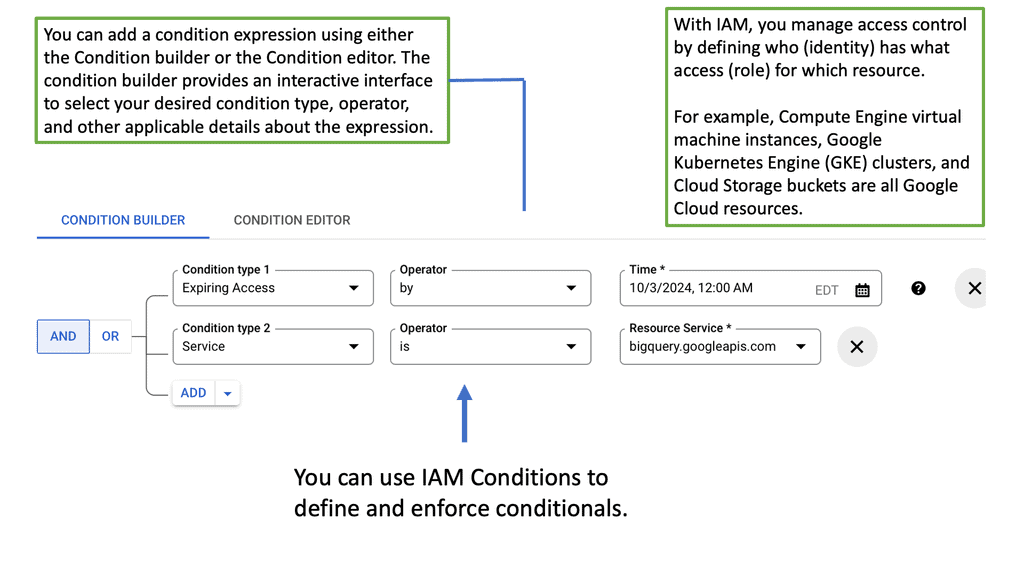
Identity security is more than just controlling access; it’s about safeguarding digital identities across the board. Google Cloud IAM offers robust identity security by employing the principle of least privilege, allowing users to access only what they need to perform their jobs. This minimizes potential attack surfaces and reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Additionally, IAM integrates seamlessly with Google Cloud’s security tools, providing a comprehensive security posture. This integration ensures that identity-related threats are quickly identified and mitigated, enhancing the overall security of your digital ecosystem.
**Streamlining Access Management**
Managing access is a dynamic challenge, especially in organizations where roles and responsibilities are constantly evolving. Google Cloud IAM simplifies this process by offering predefined roles and custom roles that can be tailored to specific needs. This flexibility allows administrators to define precise access controls, ensuring that users have the necessary permissions without overexposing sensitive data. Furthermore, IAM’s audit logs provide transparency and accountability, allowing administrators to track access and identify any anomalies.
**Enhancing Collaboration Through Secure Access**
In today’s interconnected world, collaboration is key. Google Cloud IAM facilitates secure collaboration by allowing organizations to manage and share resources efficiently across teams, partners, and clients. By leveraging IAM, organizations can create a seamless and secure environment where collaboration does not compromise security. Multi-factor authentication and context-aware access further enhance this security, ensuring that access is granted based on real-time conditions and user behavior.
**Unveiling the Vault**
**Introduction: Understanding the Basics**
In today’s digital landscape, securing sensitive data and ensuring only the right individuals have access to particular resources is paramount. This is where the concepts of authentication, authorization, and identity come into play, and tools like Vault become indispensable. Whether you’re a developer, systems administrator, or security professional, understanding how Vault manages these critical aspects can significantly enhance your security posture.
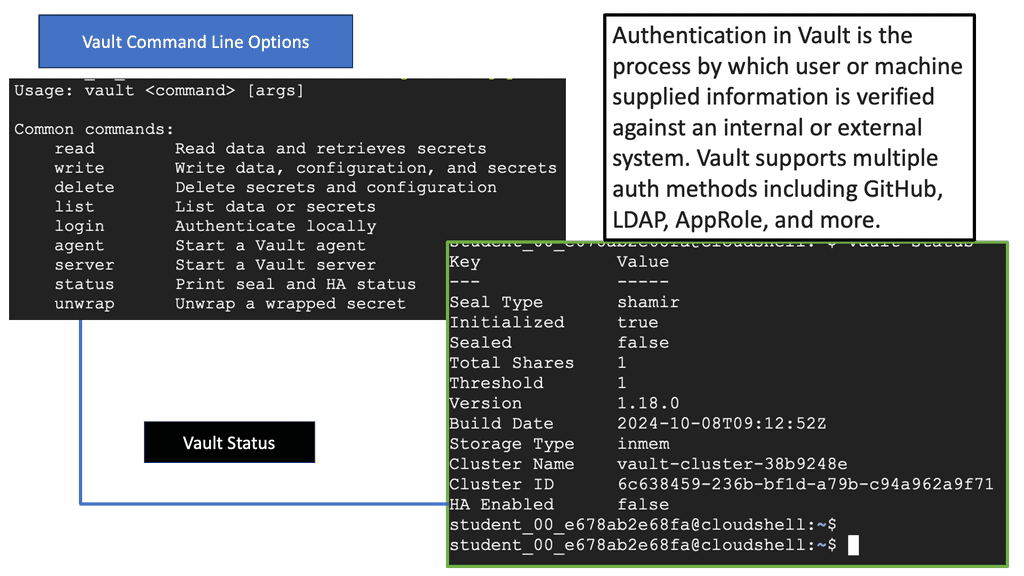
**Authentication: The First Line of Defense**
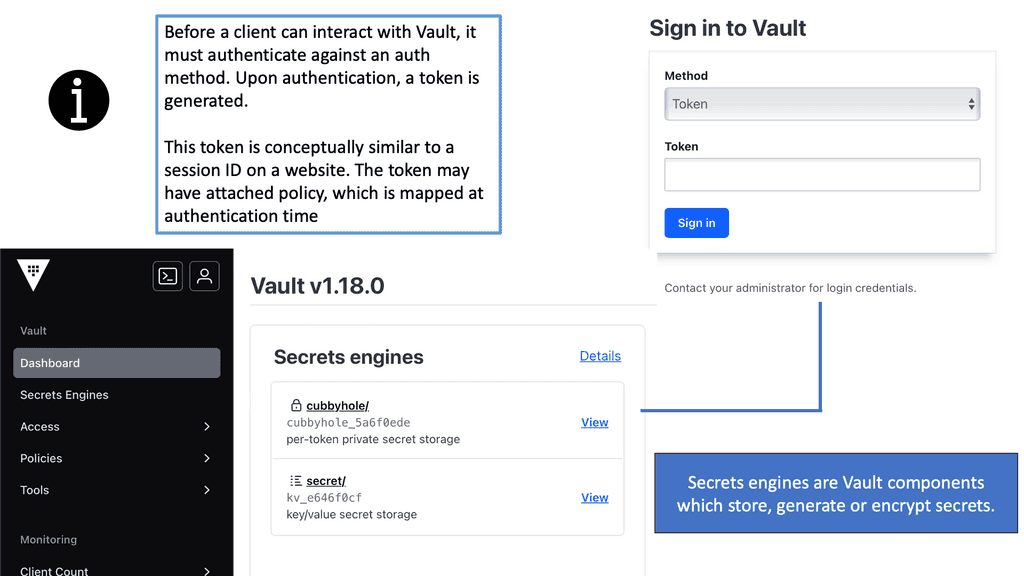
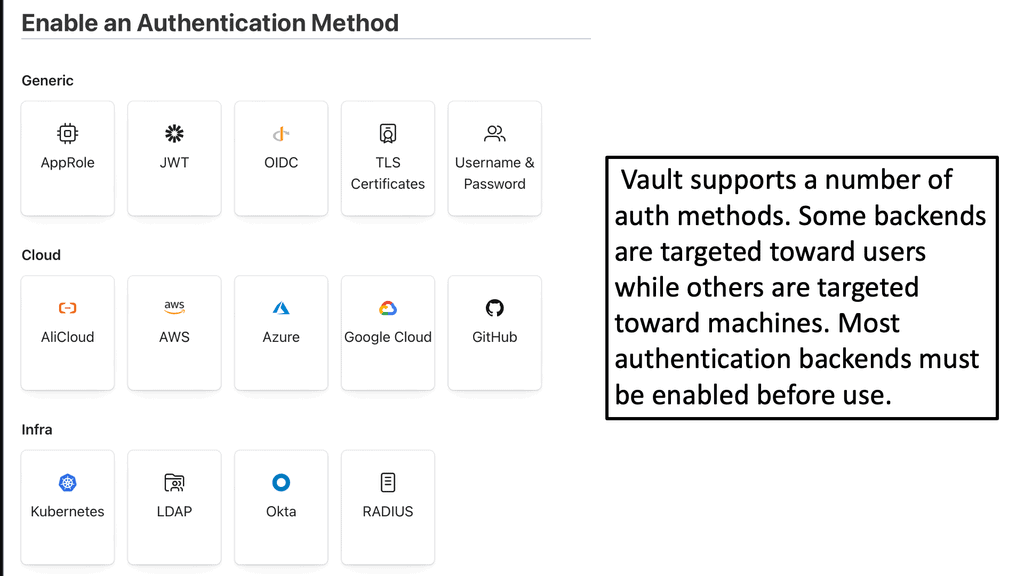
Authentication is the process of verifying who someone is. In the context of Vault, it involves ensuring that the entity (user or machine) trying to access a particular resource is who it claims to be. Vault supports a variety of authentication methods, including token-based, username and password, and more advanced methods like AWS IAM roles or Kubernetes service accounts. By providing multiple authentication paths, Vault offers flexibility and security to meet diverse organizational needs.
**Authorization: Granting the Right Permissions**
Once an entity’s identity is verified, the next step is to determine what they’re allowed to do. This is where authorization comes in, dictating the actions an authenticated user can perform. Vault uses policies to manage authorization. These policies are written in HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) and define precise control over what data and operations a user or system can access. With Vault, administrators can ensure that users have just enough permissions to perform their job, reducing the risk of data breaches or misuse.
**Identity: The Core of Secure Access Management**
Identity management is crucial for maintaining a secure environment, especially in complex, multi-cloud architectures. Vault’s identity framework allows organizations to unify users’ identities and manage them seamlessly. By integrating with external identity providers, Vault makes it easy to map the identities of various users and systems to Vault’s internal policies. This integration not only streamlines access management but also enhances overall security by ensuring consistent identity verification across platforms.
**Security Scanning: Potential Identity Threats**
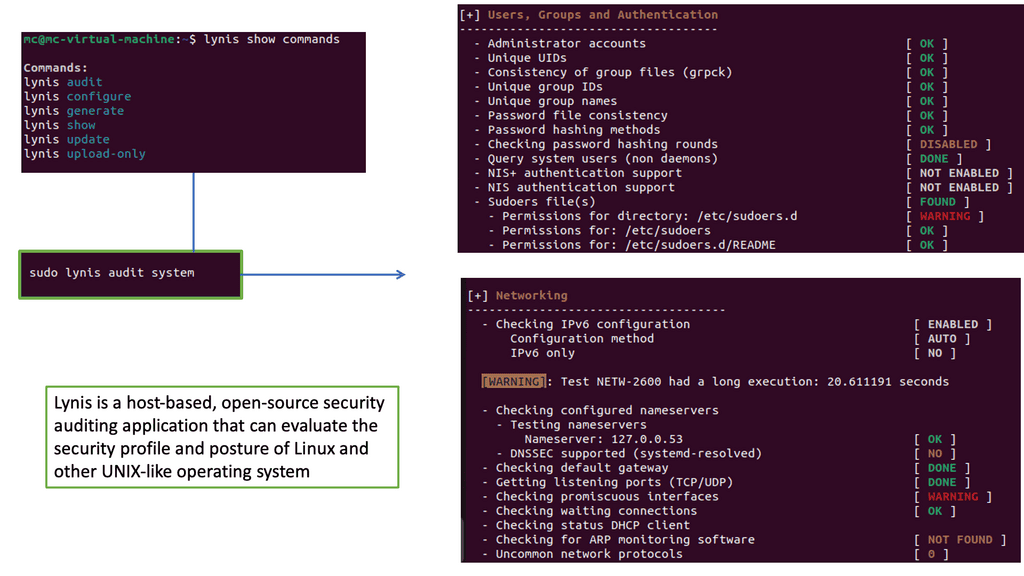
Example: Security Scan with Lynis
Lynis Security Scan is a powerful open-source security auditing tool that helps you identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your system. It comprehensively assesses your system’s security configuration, scanning various aspects such as file permissions, user accounts, network settings, and more. Lynis provides valuable insights into your system’s security status by leveraging various tests and checks.
**New Attack Surface, New Technologies**
Identity security has pushed authentication to a new, more secure landscape, reacting to improved technologies and sophisticated attacks. The need for more accessible and secure authentication has led to the wide adoption of zero-trust identity management zero trust authentication technologies like risk-based authentication (RBA), fast identity online (FIDO2), and just-in-time (JIT) techniques.
**Challenge: Visibility Gaps**
If you examine our identities, applications, and devices, you will see that they are in the crosshairs of bad actors, making them probable threat vectors. In addition, we are challenged by the sophistication of our infrastructure, which increases our attack surface and creates gaps in our visibility. Controlling access and the holes created by complexity is the basis of all healthy security.
**Challenge: Social Engineering**
Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into performing actions or divulging confidential information. Attackers may impersonate someone in a position of authority or use emotional manipulation to gain trust. By collecting personal data from social media platforms or other online sources, criminals can create convincing personas to deceive unsuspecting victims.
Hackers, fraudsters, and cybercriminals employ phishing, pretexting, and baiting tactics to achieve their nefarious goals.
Common Social Engineering Techniques
- Phishing: One of the most prevalent techniques involves sending fraudulent emails disguised as legitimate ones to trick recipients into divulging sensitive information.
- Pretexting: This technique involves creating a fabricated scenario and impersonating someone trustworthy to extract valuable information.
- Baiting: Baiting lures victims with enticing offers or rewards, often through physical media like infected USB drives or fake promotional materials.
Popular Attack Vectors: Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticated and deceptive. Cybercriminals create fake emails, websites, or messages that closely resemble legitimate organizations to trick users into revealing sensitive information. These attacks often prey on human psychology, exploiting trust and urgency to manipulate victims into divulging personal data.
Phishers employ various tactics to manipulate their targets and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. One common tactic is creating emails or messages that appear to be from reputable organizations, enticing recipients to click on malicious links or download harmful attachments. Another technique involves masquerading as a trusted individual, such as a colleague or a friend, to deceive the target into sharing confidential details.
Starting with Endpoint Security
Endpoint security protects endpoints like laptops, desktops, servers, and mobile devices.
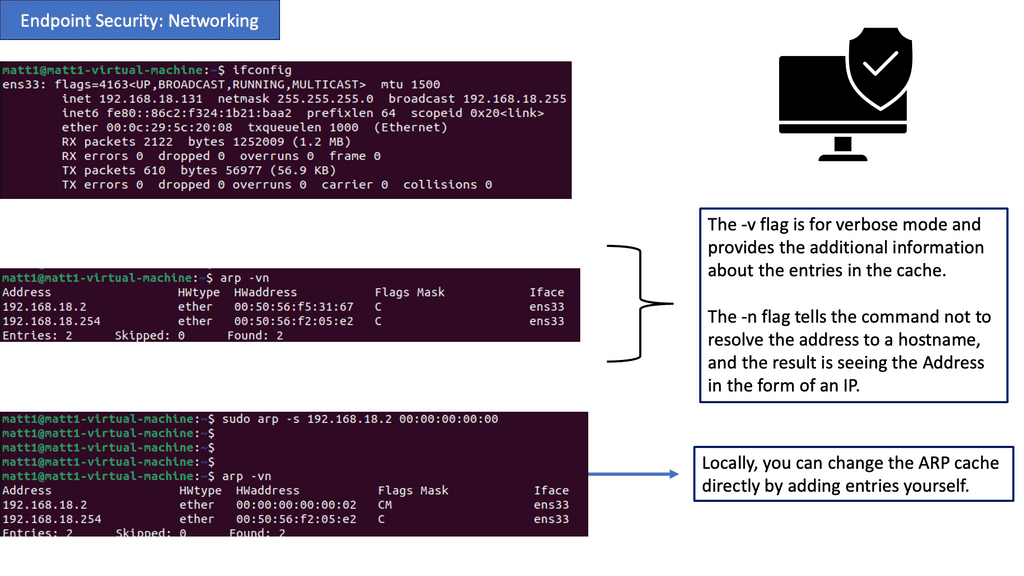
ARP Security: The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is vulnerable to various attacks, such as ARP spoofing, which can lead to network breaches. Implementing ARP security measures, such as ARP cache monitoring and strict ARP validation, can help protect against these attacks and ensure the integrity of your network.
Secure Routing: Securing your network’s routing protocols is essential to prevent unauthorized access and route manipulation. Implementing secure routing techniques, such as using encrypted protocols (e.g., BGP over IPsec) and implementing access control lists (ACLs) on routers, can enhance the overall security of your network.
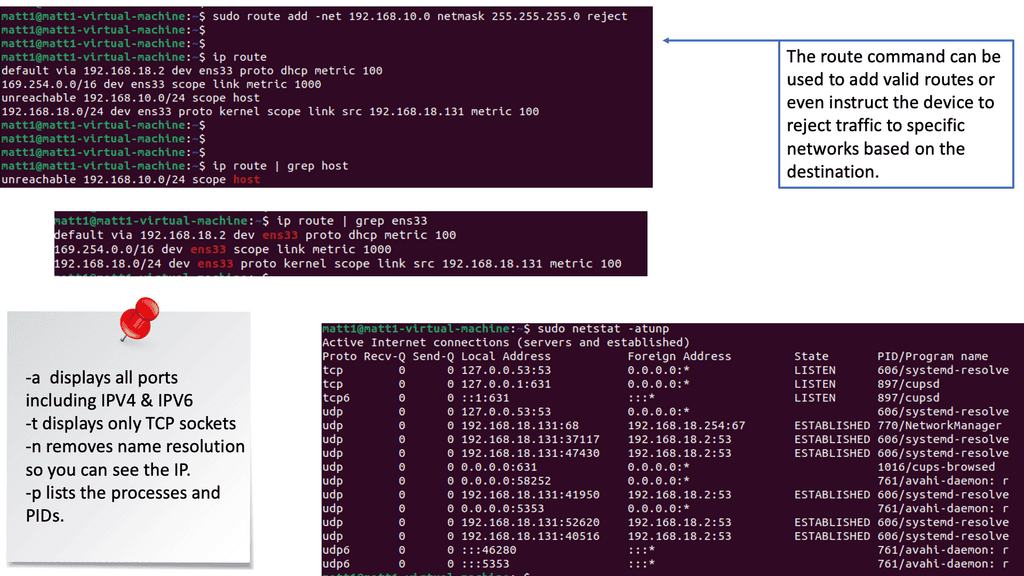
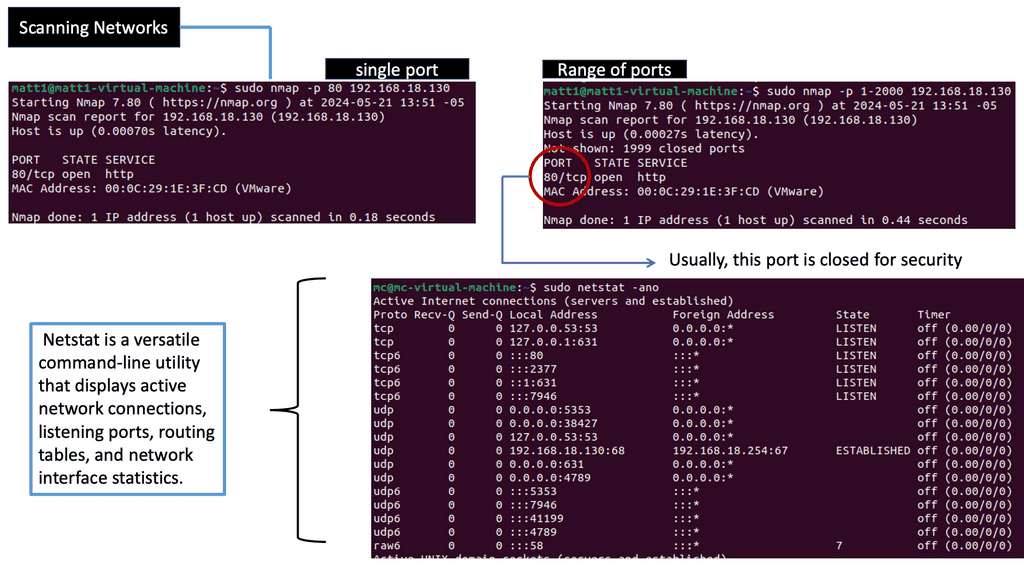
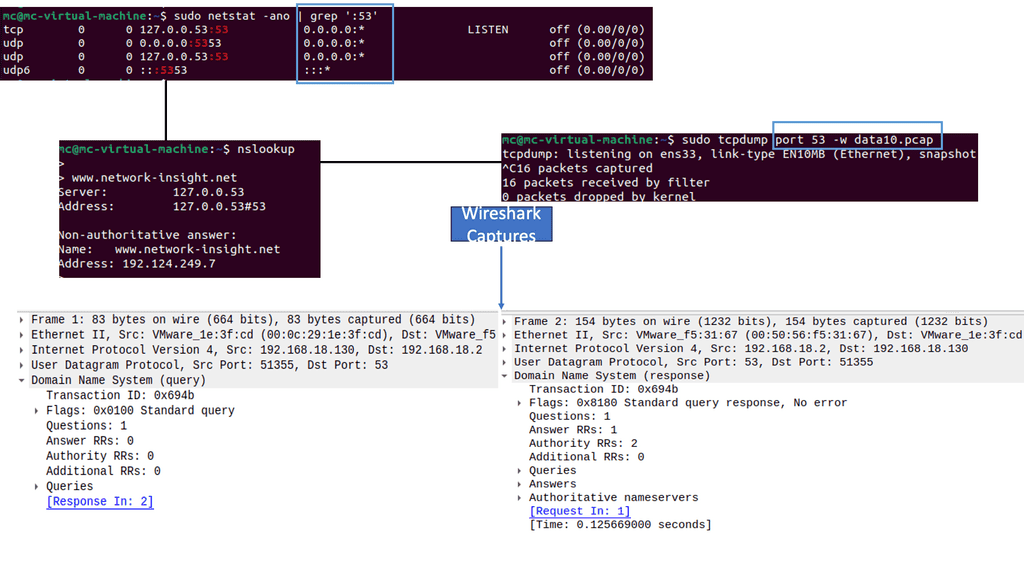
Network Monitoring with Netstat: Netstat is a powerful command-line tool for monitoring network connections, open ports, and active endpoint sessions. By regularly using netstat, you can identify suspicious connections or unauthorized access attempts and take appropriate action to mitigate potential threats.
Identity Security with Linux
Strong User Authentication
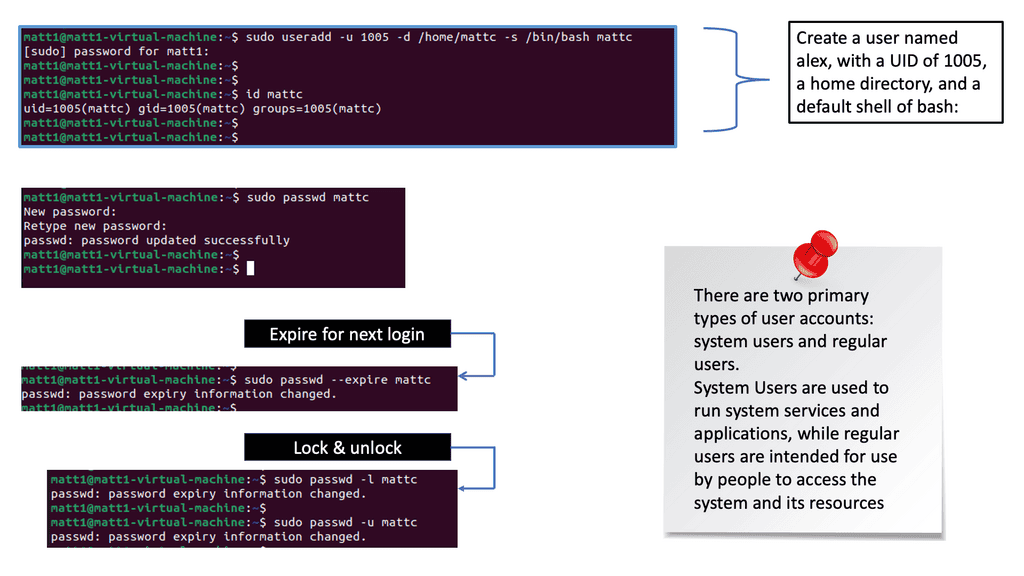
User authentication forms the first line of defense in securing identity. Implementing solid passwords, enforcing password policies, and utilizing multi-factor authentication (MFA) mechanisms are essential to enhance Linux security.
Efficient user account management plays a crucial role in identity security. Regularly reviewing and auditing user accounts, disabling unnecessary accounts, and implementing proper access controls ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
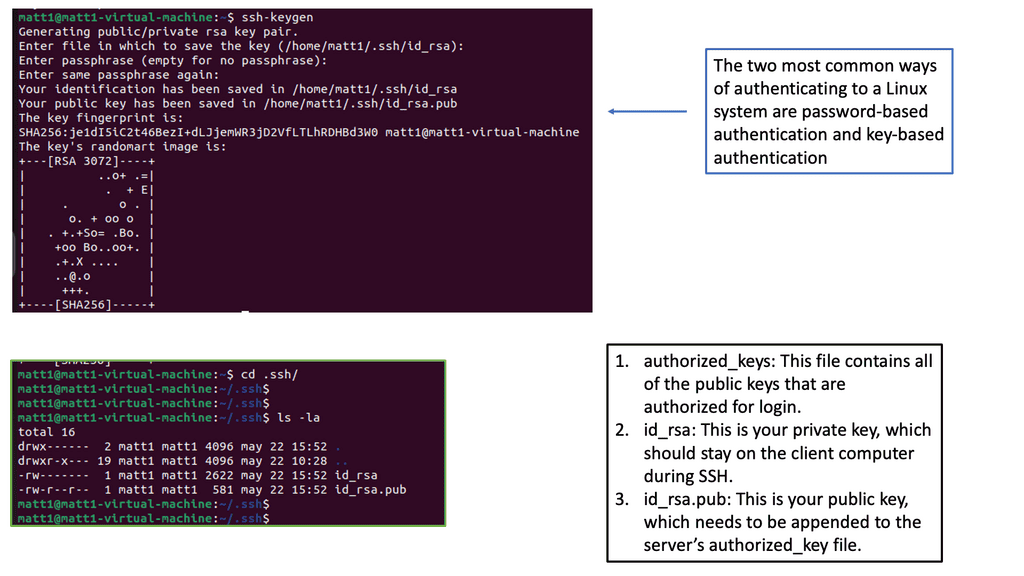
Securing communication channels is vital to protect identity during data transmission. Encrypted protocols such as SSH (Secure Shell) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) ensure that sensitive information remains confidential and protected from eavesdropping or tampering.
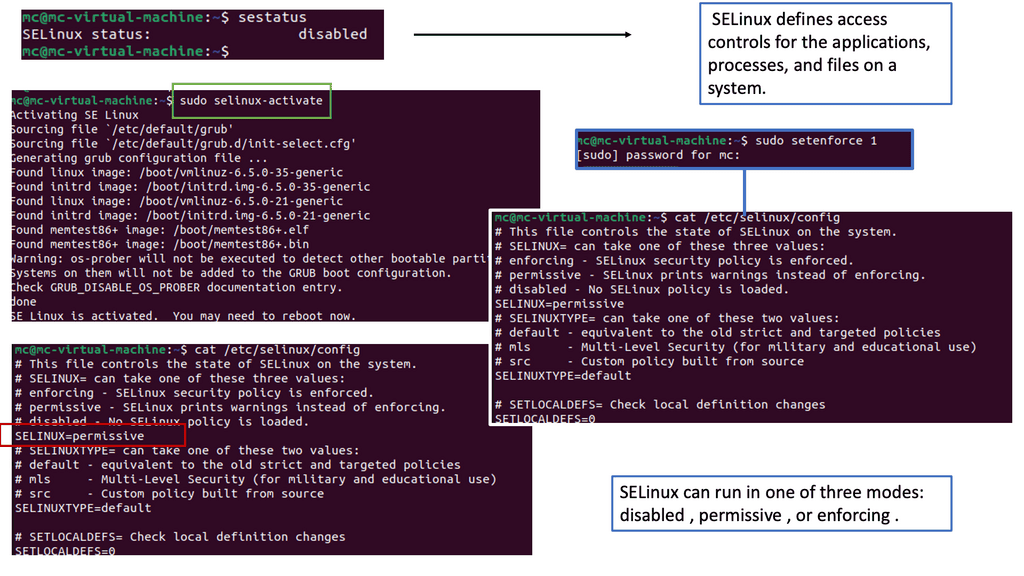
Understanding SELinux
SELinux, or Security-Enhanced Linux, is a security module integrated into the Linux kernel. It provides fine-grained access control policies and enhances the system’s overall security posture. Unlike traditional access control mechanisms, SELinux operates on the principle of least privilege, ensuring that only authorized actions are allowed.
Zero-trust endpoint protection is a security model that assumes no implicit trust in any user or device, regardless of location within or outside the network. It emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls to mitigate potential threats. Organizations can bolster their security measures by incorporating SELinux into a zero-trust framework by enforcing granular policies on every endpoint.
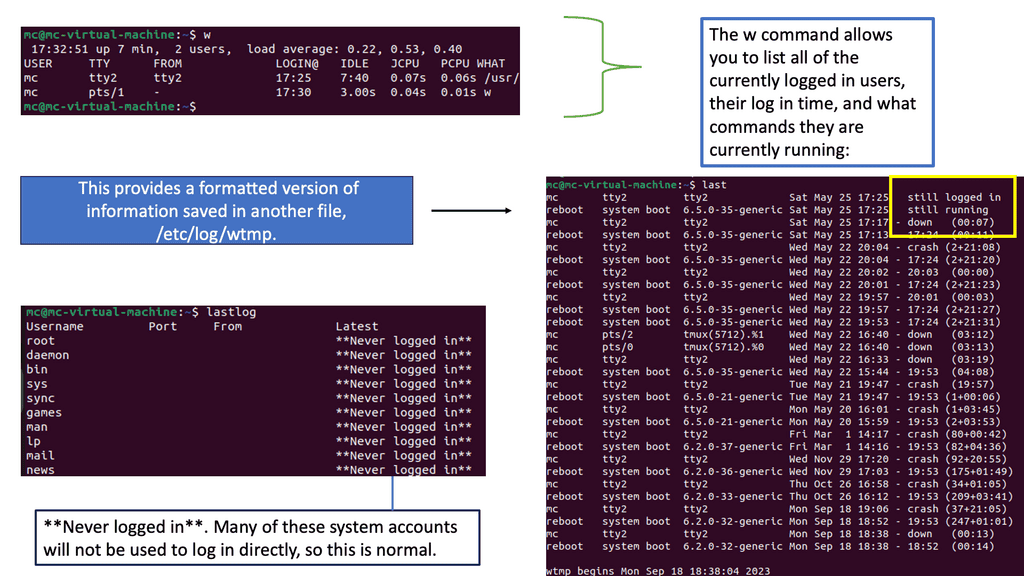
Detecting Identity Threats in Logs
The Power of Logs
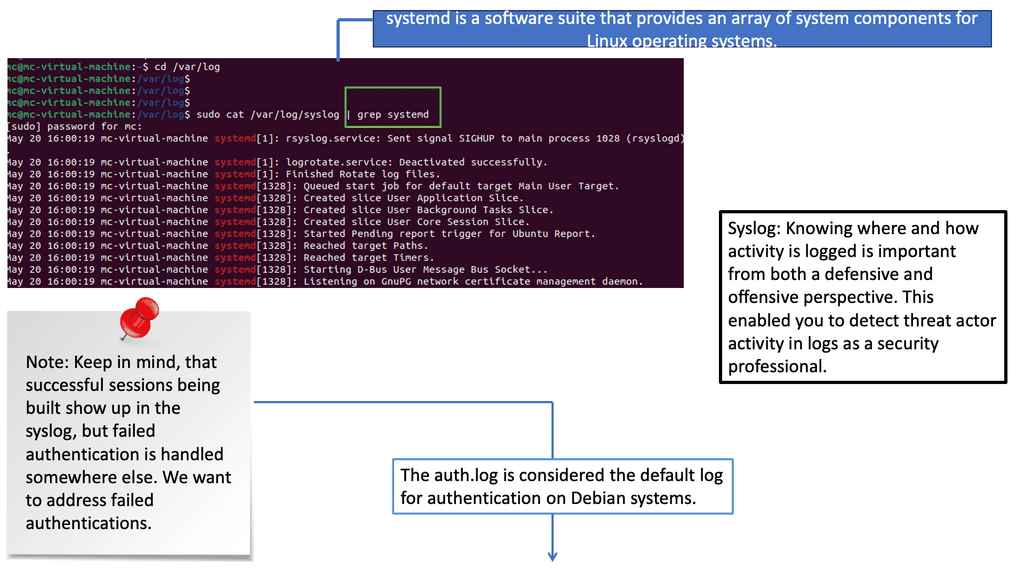
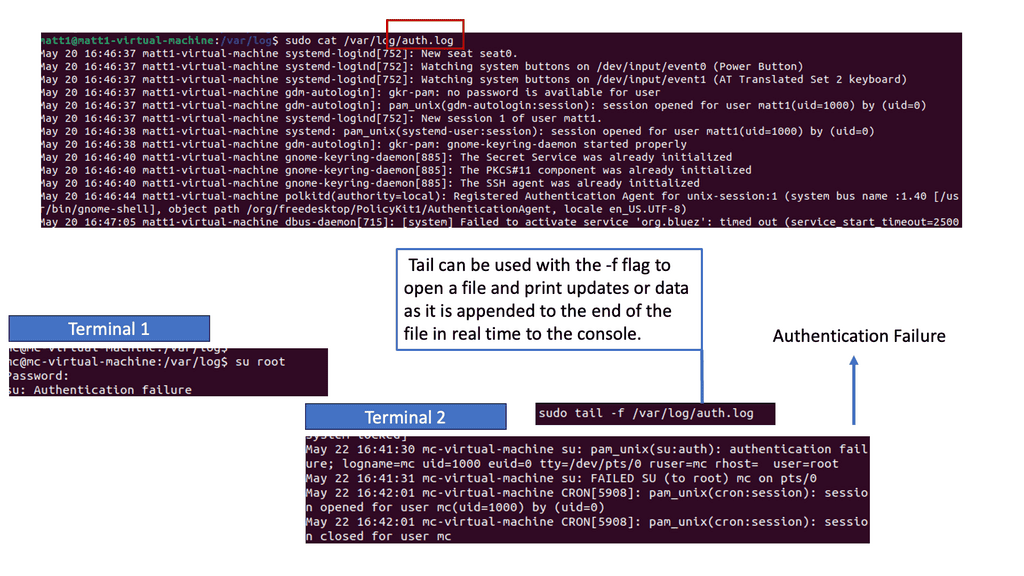
Logs serve as a digital footprint, capturing a wide range of activities and events within a system. They act as silent witnesses, recording valuable information to aid security analysis and incident response. Syslog and auth.log are two types of logs critical in security event detection.
Syslog is a standardized protocol for message logging, allowing various devices and applications to send log messages to a central repository. It offers a wealth of information, including system events, errors, warnings, etc. Understanding the structure and content of syslog entries is essential for effective security event detection.
Auth.log, short for authentication log, records authentication-related activities within a system. It tracks successful and failed login attempts, user authentication methods, and other relevant information. By analyzing auth.log entries, security professionals can swiftly identify potential breaches and unauthorized access attempts.
Example Identity Product: Understanding Cisco ISE
Cisco ISE is a comprehensive security policy management platform that enables organizations to enforce security policies across the network infrastructure. It provides granular control over user access and device authentication, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can connect to the network. By integrating with existing network infrastructure such as switches, routers, and firewalls, Cisco ISE simplifies the management of access control policies and strengthens network security.
Cisco ISE offers a wide range of features that enhance network security. These include:
1. Identity-Based Access Control: Cisco ISE allows organizations to define policies based on user identities rather than IP addresses. This enables more granular control over access permissions and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Device Profiling: With Cisco ISE, organizations can identify and profile devices connecting to the network. This helps detect and block unauthorized or suspicious devices, preventing potential security breaches.
3. Guest Access Management: Cisco ISE simplifies guest access management by providing a self-service portal for guest users. It allows organizations to define guest policies, control access duration, and monitor guest activities, ensuring a secure guest access experience.
Related: Before you proceed, you may find the following posts helpful
Identity Security: The Workflow
Identity Security: The Concept
The concept of identity security is straightforward and follows a standard workflow that can be understood and secured. First, a user logs into their employee desktop and is authenticated as an individual who should have access to this network segment. This is the authentication stage.
They have appropriate permissions assigned so they can navigate to the required assets (such as an application or file servers) and are authorized as someone who should have access to this application. This is the authorization stage.
As they move across the network to carry out their day-to-day duties, all of this movement is logged, and all access information is captured and analyzed for auditing purposes. Anything outside of normal behavior is flagged. Splunk UEBA has good features here.
- Stage of Authentication: You must accurately authenticate every human and non-human identity. After an identity is authenticated to confirm who it is, it only gets a free one for some to access the system with impunity.
- Stage of Re-Authentication: Identities should be re-authenticated if the system detects suspicious behavior or before completing tasks and accessing data that is deemed to be highly sensitive. If we have an identity that acts outside of normal baseline behavior, they must re-authenticate.
- Stage of Authorization: Then we need to move to authorization. We need to authorize the user to ensure they’re allowed access to the asset only when required and only with the permissions they need to do their job. So we have authorized each identity on the network with the proper permissions so they can access what they need and not more.
- Stage of Access: Then, we look into Access: Provide structured access to authorized assets for that identity. How can appropriate access be given to the person/user/device/bot/script/account and nothing else? Follow the practices of zero-trust identity management and least privilege. Ideally, access is granted to microsegments instead of significant VLANs based on traditional zone-based networking.
- Stage of Audit: All identity activity must be audited or accounted for. Auditing allows insight and evidence that Identity Security policies are working as intended. How do you monitor identity activities? How do you reconstruct and analyze an identity’s actions? An auditing capability ensures visibility into an identity’s activities, provides context for the identity’s usage and behavior, and enables analytics that identify risk and provide insights to make smarter decisions about access.
Scanning Networks
The Importance of Network Scanning
Network scanning systematically examines a network to identify its vulnerabilities, open ports, and active devices. Network administrators can gain valuable insights into their security posture using specialized tools and techniques. Understanding the fundamentals of network scanning is crucial for effectively securing network infrastructures.
There are several network scanning techniques, each serving a specific purpose. Port scanning, for example, involves probing network ports to identify potential entry points for attackers. Vulnerability scanning, on the other hand, focuses on identifying known vulnerabilities within network devices and applications. Organizations can adopt a comprehensive approach to network security by exploring these different types of network scanning.
Starting Zero Trust Identity Management
Now, we have an identity as the new perimeter compounded by identity being the latest target. Any identity is a target. Looking at the modern enterprise landscape, it’s easy to see why. Every employee has multiple identities and uses several devices.
What makes this worse is that security teams’ primary issue is that identity-driven attacks are hard to detect. For example, how do you know if a bad actor or a sys admin uses the privilege controls? As a result, security teams must find a reliable way to monitor suspicious user behavior to determine the signs of compromised identities.
We now have identity sprawl, which may be acceptable if only one of those identities has user access. However, it doesn’t, and it most likely has privileged access. All these widen the attack surface by creating additional human and machine identities that can gain privileged access under certain conditions, establishing new pathways for bad actors.
We must adopt a different approach to secure our identities regardless of where they may be. Here, we can look for a zero-trust identity management approach based on identity security. Next, I’d like to discuss your common challenges when adopting identity security.
Challenge 1: Zero trust identity management and privilege credential compromise
Current environments may result in anonymous access to privileged accounts and sensitive information. Unsurprisingly, 80% of breaches start with compromised privilege credentials. If left unsecured, attackers can compromise these valuable secrets and credentials to gain possession of privileged accounts and perform advanced attacks or use them to exfiltrate data.
Challenge 2: Zero trust identity management and exploiting privileged accounts
We have two types of bad actors. First, there are external attackers and malicious insiders who can exploit privileged accounts to orchestrate a variety of attacks. Privileged accounts are used in nearly every cyber attack. With privileged access, bad actors can disable systems, take control of IT infrastructure, and gain access to sensitive data. So, we face several challenges when securing identities, namely protecting, controlling, and monitoring privileged access.
Challenge 3: Zero trust identity management and lateral movements
Lateral movements will happen. A bad actor has to move throughout the network. They will never land directly on a database or important file server. The initial entry point into the network could be an unsecured IoT device, which does not hold sensitive data. As a result, bad actors need to pivot across the network.
They will laterally move throughout the network with these privileged accounts, looking for high-value targets. They then use their elevated privileges to steal confidential information and exfiltrate data. There are many ways to exfiltrate data, with DNS being a common vector that often goes unmonitored. How do you know a bad actor is moving laterally with admin credentials using admin tools built into standard Windows desktops?
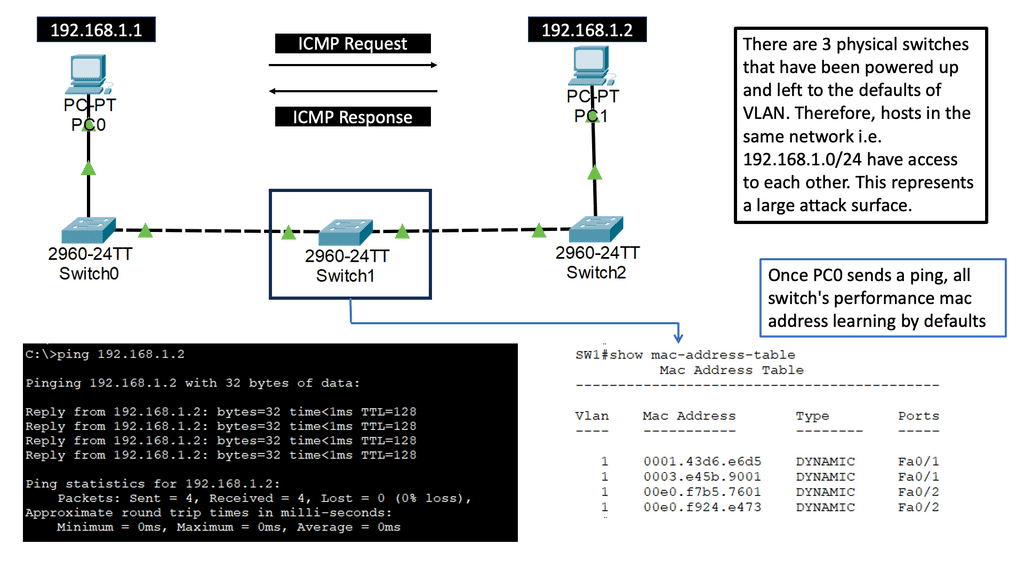
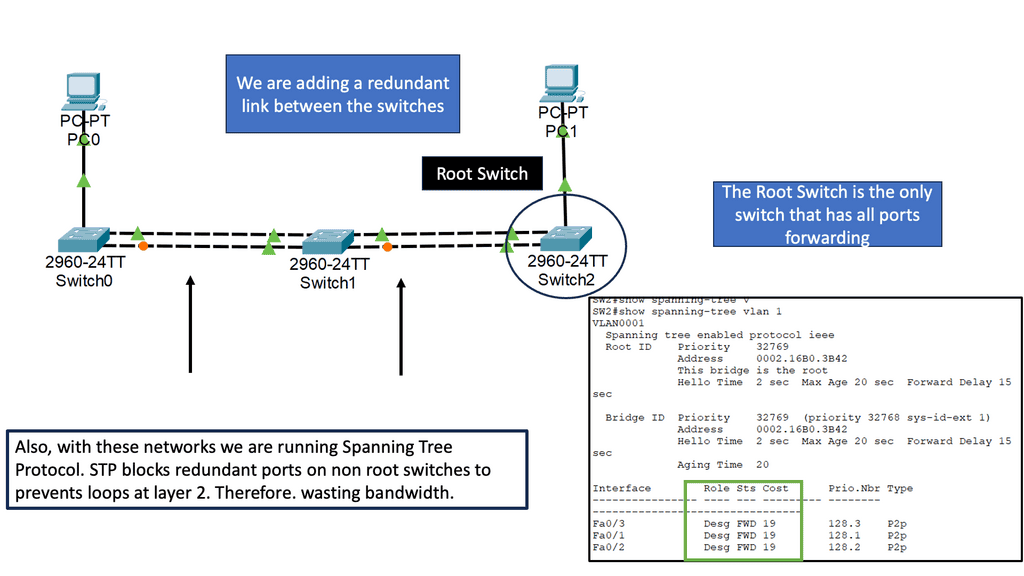
The issue with VLAN-based segmentation is large broadcast domains with free-for-all access. This represents a larger attack surface where lateral movements can take place. Below is a standard VLAN-based network running Spanning Tree Protocol ( STP ).
Example: Issues with VLAN based segmentation
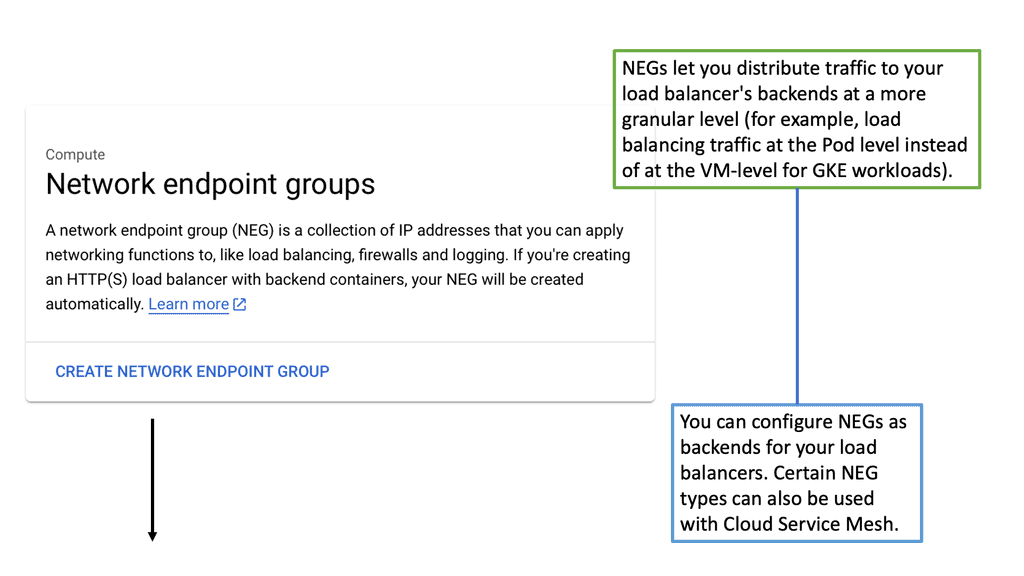
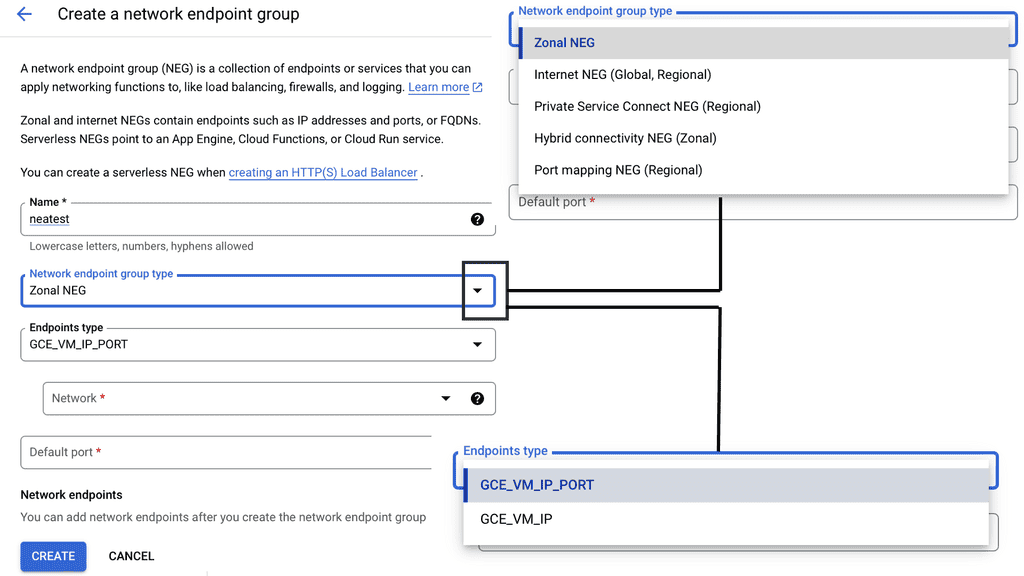
Example: Improved Segmentation with Network Endpoint Groups (NEGs)
Challenge 4: Zero trust identity management and distributed attacks
These attacks are distributed, and there will be many dots to connect to understand threats on the network. Could you look at ransomware? Enrolling the malware needs elevated privilege, and it’s better to detect this before the encryption starts. Some ransomware families perform partial encryption quickly. Once encryption starts, it’s game over. You need to detect this early in the kill chain in the detect phase.
The best approach to zero-trust authentication is to know who accesses the data, ensure they are the users they claim to be, and operate on the trusted endpoint that meets compliance. There are plenty of ways to authenticate to the network; many claim password-based authentication is weak.
The core of identity security is understanding that passwords can be phished; essentially, using a password is sharing. So, we need to add multifactor authentication (MFA). MFA gives a big lift but needs to be done well. You can get breached even if you have an MFA solution in place.
Knowledge Check: Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
More than simple passwords are needed for healthy security. A password is a single authentication factor – anyone with it can use it. No matter how strong it is, keeping information private is useless if lost or stolen. You must use a different secondary authentication factor to secure your data appropriately.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
•Two-factor authentication: This method uses two-factor classes to provide authentication. It is also known as ‘2FA’ and ‘TFA.’
•Multi-factor authentication: use of two or more factor classes to provide authentication. This is also represented as ‘MFA.’
•Two-step verification: This authentication method involves two independent steps but does not necessarily require two separate factor classes. It is also known as ‘2SV’.
•Strong authentication: authentication beyond simply a password. It may be represented by the usage of ‘security questions’ or layered security like two-factor authentication.
The Move For Zero Trust Authentication
No MFA solution is an island. Every MFA solution is just one part of multiple components, relationships, and dependencies. Each piece is an additional area where an exploitable vulnerability can occur. Essentially, any element in the MFA’s life cycle, from provisioning to de-provisioning and everything in between, is subject to exploitable vulnerabilities and hacking. And like the proverbial chain, it’s only as strong as its weakest link.
Zero trust authentication: Two or More Hacking Methods Used
Many MFA attacks use two or more of the leading hacking methods. Often, social engineering is used to start the attack and get the victim to click on a link or to activate a process, which then uses one of the other methods to accomplish the necessary technical hacking.
For example, a user may receive a phishing email directing them to a fake website, which accomplishes a man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack and steals credential secrets. Alternatively, a hardware token may be physically stolen and forensically examined to find the stored authentication secrets. MFA hacking requires using two or all of these main hacking methods.
You Can’t Rely On MFA Alone
You can’t rely on MFA alone; you must validate privileged users with context-aware Adaptive Multifactor Authentication and secure access to business resources with Single Sign-On. Unfortunately, credential theft remains the No. 1 area of risk. And bad actors are getting better at bypassing MFA using a variety of vectors and techniques.
For example, a bad actor can be tricked into accepting a push notification to their smartphone to grant access in the context of getting admission. You are still acceptable to man-in-the-middle attacks. This is why MFA and IDP vendors introduce risk-based authentication and step-up authentication. These techniques limited the attack surface, which we will talk about soon.
**Considerations for Zero Trust Authentication**
- Think like a bad actor.
By thinking like a bad actor, we can attempt to identify suspicious activity, restrict lateral movement, and contain threats. Try envisioning what you would look for if you were a bad external actor or malicious insider. For example, are you looking to steal sensitive data to sell it to competitors, start Ransomware binaries, or use your infrastructure for illicit crypto mining?
- Attacks with happen
The harsh reality is that attacks will happen, and you can only partially secure some of their applications and infrastructure wherever they exist. So it’s not a matter of ‘if’ but a concern of’ when.’ Protection from all the various methods that attackers use is virtually impossible, and there will occasionally be day 0 attacks. So, they will eventually get in; it’s all about what they can do once they are in.
- The first action is to protect Identities.
Therefore, you must first protect their identities and prioritize what matters most—privileged access. Infrastructure and critical data are only fully protected if privileged accounts, credentials, and secrets are secured and protected.
- The bad actor needs privileged access.
We know that about 80% of breaches tied to hacking involve using lost or stolen credentials. Compromised identities are the common denominator in virtually every severe attack. The reason is apparent:
The bad actor needs privileged access to the network infrastructure to steal data. However, without privileged access, an attacker is severely limited in what they can do. Furthermore, without privileged access, they may be unable to pivot from one machine to another. And the chances of landing on a high-value target are doubtful.
- The malware requires admin access
The malware used to pivot and requires admin access to gain persistence; privileged access without vigilant management creates an ever-growing attack surface around privileged accounts.
**Adopting Zero Trust Authentication**
Where can you start identity security with all of this? Firstly, we can look at a zero-trust authentication protocol. We need an authentication protocol that can be phishing-resistant. This is FIDO2, known as Fast Identity Online (FIDO2), built on two protocols that effectively remove any blind protocols. FIDO authentication Fast Identity Online (FIDO) is a challenge-response protocol that uses public-key cryptography. Rather than using certificates, it manages keys automatically and beneath the covers.
**Technology with Fast Identity Online (FIDO2)**
FIDO2 uses two standards. The Client to Authenticator Protocol (CTAP) describes how a browser or operating system establishes a connection to a FIDO authenticator. The WebAuthn protocol is built into browsers and provides an API that JavaScript from a web service can use to register a FIDO key, send a challenge to the authenticator, and receive a response to the challenge.
So, there is an application the user wants to go to, and then we have the client, which is often the system’s browser, but it can be an application that can speak and understand WebAuthn. FIDO provides a secure and convenient way to authenticate users without using passwords, SMS codes, or TOTP authenticator applications. Modern computers, smartphones, and most mainstream browsers understand FIDO natively.
FIDO2 addresses phishing by cryptographically proving that the end-user has a physical position over the authentication. There are two types of authenticators: a local authenticator, such as a USB device, and a roaming authenticator, such as a mobile device. These need to be certified FIDO2 vendors.
The other is a platform authenticator such as Touch ID or Windows Hello. While roaming authenticators are available, for most use cases, platform authenticators are sufficient. This makes FIDO an easy, inexpensive way for people to authenticate. The biggest impediment to its widespread use is that people won’t believe something so easy is secure.
**Risk-based authentication**
Risk is not a static attribute, and it needs to be re-calculated and re-evaluated so you can make intelligent decisions for step-up and user authentication. We have Cisco DUO that reacts to risk-based signals at the point of authentication.
These risk signals are processed in real-time to detect signs of known account takeout signals. These signals may include Push Bombs, Push Sprays, and Fatigue attacks. Also, a change of location can signal high risk. Risk-based authentication (RBA) is usually coupled with step-up authentication.
For example, let’s say your employees are under attack. RBA can detect this attack as a stuffing attack and move from a classic authentication approach to a more secure verified PUSH approach than the standard PUSH.
This would add more friction but result in better security, such as adding three to six digital display keys at your location/devices, and you need to enter this key in your application. This eliminates fatigue attacks. This verified PUSH approach can be enabled at an enterprise level or just for a group of users.
**Conditional Access**
Then, we move towards conditional access, a step beyond authentication. Conditional access examines the context and risk of each access attempt. For example, contextual factors may include consecutive login failures, geo-location, type of user account, or device IP to either grant or deny access. Based on those contextual factors, access may be granted only to specific network segments.
Risk-based decisions and recommended capabilities
The identity security solution should be configurable to allow SSO access, challenge the user with MFA, or block access based on predefined conditions set by policy. It would help if you looked for a solution that can offer a broad range of shapes, such as IP range, day of the week, time of day, time range, device O/S, browser type, country, and user risk level.
These context-based access policies should be enforceable across users, applications, workstations, mobile devices, servers, network devices, and VPNs. A key question is whether the solution makes risk-based access decisions using a behavior profile calculated for each user.
**Technology with JIT techniques**
Secure privileged access and manage entitlements. For this reason, many enterprises employ a least privilege approach, where access is restricted to the resources necessary for the end-user to complete their job responsibilities with no extra permission. A standard technology here would be Just in Time (JIT). Implementing JIT ensures that identities have only the appropriate privileges, when necessary, as quickly as possible and for the least time required.
JIT techniques that dynamically elevate rights only when needed are a technology to enforce the least privilege. The solution allows for JIT elevation and access on a “by request” basis for a predefined period, with a full audit of privileged activities. Full administrative rights or application-level access can be granted, time-limited, and revoked.
Summary: Identity Security
In today’s interconnected digital world, protecting our identities online has become more critical than ever. From personal information to financial data, our digital identities are vulnerable to various threats. This blog post aimed to shed light on the significance of identity security and provide practical tips to enhance your online safety.
Understanding Identity Security
Identity security is the measure to safeguard personal information and prevent unauthorized access. It encompasses protecting sensitive data such as login credentials, financial details, and personal identification information (PII). Individuals can mitigate the risks of identity theft, fraud, and privacy breaches by ensuring robust identity security.
Common Threats to Identity Security
In this section, we’ll explore some of the most prevalent threats to identity security, including phishing attacks, malware infections, social engineering, and data breaches. Understanding these threats is crucial for recognizing potential vulnerabilities and taking appropriate preventative measures.
Best Practices for Strengthening Identity Security
Now that we’ve highlighted the importance of identity security and identified common threats, let’s delve into practical tips to fortify your online presence:
1. Strong and Unique Passwords: Use complex passwords that combine letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using the same password across multiple platforms.
2. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA whenever possible to add an extra layer of security. This typically involves a secondary verification method, such as a code sent to your mobile device.
3. Regular Software Updates: Keep all your devices and applications current. Software updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities.
4. Beware of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of suspicious emails, messages, or calls asking for personal information. Verify the authenticity of requests before sharing sensitive data.
5. Secure Wi-Fi Networks: When connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and protect your data from potential eavesdroppers.
The Role of Privacy Settings
Privacy settings play a crucial role in controlling the visibility of your personal information. Platforms and applications often provide various options to customize privacy preferences. Take the time to review and adjust these settings according to your comfort level.
Monitoring and Detecting Suspicious Activity
Remaining vigilant is paramount in maintaining identity security. Regularly monitor your financial statements, credit reports, and online accounts for unusual activity. Promptly report any suspicious incidents to the relevant authorities.
Conclusion:
In an era where digital identities are constantly at risk, prioritizing identity security is non-negotiable. Implementing the best practices outlined in this blogpost can significantly enhance your online safety and protect your valuable personal information. Proactive measures and staying informed are vital to maintaining a secure digital identity.
- Fortinet’s new FortiOS 7.4 enhances SASE - April 5, 2023
- Comcast SD-WAN Expansion to SMBs - April 4, 2023
- Cisco CloudLock - April 4, 2023