Security Automation
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, ensuring the security of our online presence has become more critical than ever. With the ever-evolving threat landscape and increasing complexity of cyberattacks, manual security measures may no longer suffice. This is where security automation comes into play, revolutionizing the way we protect our digital assets. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of security automation and how it can effectively safeguard our digital world.
Security automation is the process of automating security tasks and processes to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of security operations. It involves leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation to streamline security processes, detect threats in real-time, and respond promptly to mitigate risks. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, security teams can focus on more strategic activities.
Enhanced Threat Detection and Response: With security automation, organizations can detect and respond to threats in real-time, significantly reducing the time it takes to identify and mitigate security incidents. Automated systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate alerts for potential threats, enabling security teams to respond swiftly and effectively.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity: By automating routine security tasks, organizations can free up valuable resources and allocate them to more critical security activities. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity within the security operations, allowing teams to better prioritize and manage security incidents.
Consistency and Accuracy: Manual security processes are prone to human error, which can have severe consequences in the realm of cybersecurity. Security automation ensures consistent execution of security measures, eliminating the possibility of human oversight or negligence. Automated systems follow predefined rules and guidelines, ensuring accuracy and reducing the risk of human-induced vulnerabilities.
Threat Intelligence and Analysis: Automated threat intelligence platforms can continuously monitor and analyze vast amounts of data from multiple sources, including threat feeds, vulnerability databases, and security event logs. By aggregating and correlating this information, organizations can gain valuable insights into emerging threats and proactively implement mitigation measures.
Incident Response and Remediation: Security automation facilitates rapid incident response by automating the process of gathering evidence, containing threats, and initiating remediation actions. Automated incident response workflows can be triggered based on predefined rules and playbooks, ensuring consistent and timely response to security incidents.
In an increasingly interconnected and digital world, security automation offers a powerful solution to safeguard our digital assets. By leveraging automation technologies, organizations can enhance threat detection and response capabilities, improve efficiency and accuracy, and proactively protect against emerging threats. Embracing security automation is not merely an option but a necessity in today's evolving threat landscape. Let us harness the power of automation to fortify our digital world and ensure a secure future.Matt Conran
Highlights: Security Automation
Automation Scenarios
We can apply our knowledge of automation to different scenarios and workloads that revolve around security. For example, when tedious and everyday tasks are automated, individuals doing those tasks can focus on solving the security problems they are dealing with. This enables a whole new way of looking at how we learn about security, how much we can store, process, and analyze log data (DFIR), and how we can keep applying security updates without interruptions (security operations).
At its core, security automation involves using advanced technologies and intelligent systems to automate various security processes. It enables organizations to streamline security operations, detect real-time threats, and respond swiftly and effectively. From threat intelligence gathering to incident response and recovery, automation is pivotal in strengthening an organization’s security posture.
Key Benefits of Security Automation:
a) Enhanced Threat Detection: By deploying intelligent monitoring systems, security automation can swiftly identify and respond to potential threats in real-time. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of breaches and allows security teams to stay one step ahead of malicious actors.
b) Accelerated Incident Response: Manual incident response can be time-consuming and prone to delays. However, with security automation, incidents can be detected, analyzed, and remediated swiftly and accurately. Automated incident response workflows can help contain and mitigate security breaches before they escalate, reducing the organization’s impact.
c) Efficient Vulnerability Management: Identifying and patching vulnerabilities is critical to maintaining a secure infrastructure. Security automation tools can continuously scan networks, applications, and systems, providing organizations with real-time vulnerability assessments. This enables security teams to prioritize and address vulnerabilities promptly, reducing the window of opportunity for potential attackers.
Integrated Automation Platform
If you are only using scripting in the security automation world, it will only get you so far. Eventually, you will need a fully integrated platform with your security and network infrastructure. For secure automation, there are different types of platforms you can use. This post will address two different types.
Example: Red Hat Tower can integrate and configure network and security devices—also, Splunk SOAR. The SOAR meaning is about abstracting complexity away with security-focused playbooks. This reduces repetitive work and the ability to respond to security events in a standardized way.
**Platform Examples**
Backing up configs and collecting logs is only a tiny part of automation. Red Hat Ansible Tower and Splunk SOAR have new ways to reach the most advanced use cases. For security automation, Splunk Security with Splunk SOAR has a security-focused application consisting of specially crafted playbooks for every security requirement.
**Red Hat Ansible Tower**
For example, you can check the domain and file reputation or create your own. On the other hand, Red Hat Tower Ansible Architecture allows you to securely reach and support the most edge use cases with increased portability using execution environments and automation mesh. In addition, you can securely bring automation to the edge with a certain overlay functionality.
**Splunk SOAR**
The difference between an attack being a routine annoyance and a catastrophic event comes down to a product’s robustness and the technologies you choose to adopt. Splunk has several products that can help you here, ranging from the Splunk SIEM to the Splunk SOAR. There are also several Observability products, all of which are well-integrated and can assist you with security automation.
Example: Splunk Enterprise & Cloud
Customers can solve their primary SIEM use cases using Splunk Enterprise and Cloud, core Splunk platforms that provide collection, indexing, search, and reporting capabilities. The Splunk SIEM collects or ingests machine data and can make this available to the Splunk SOAR.
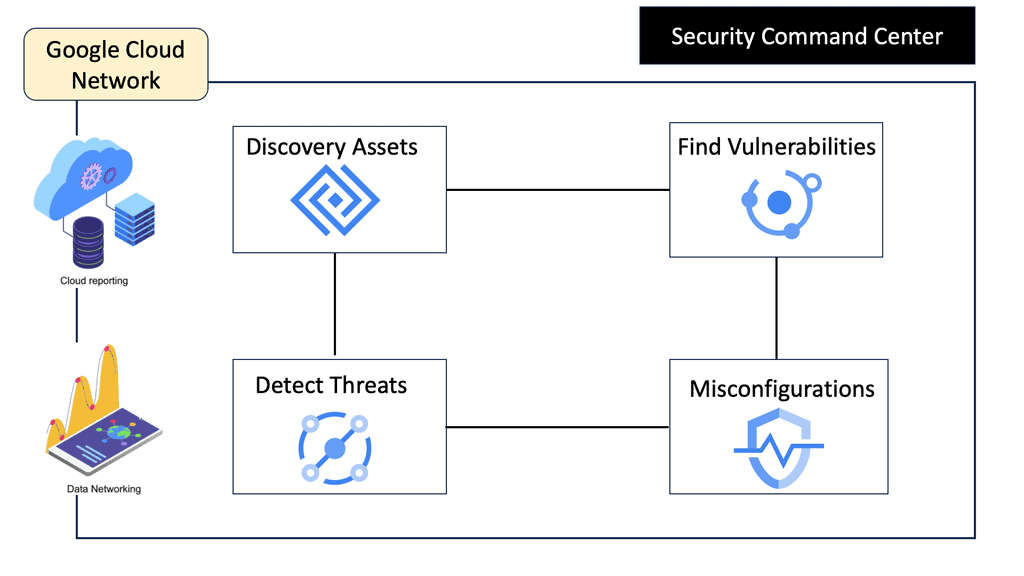
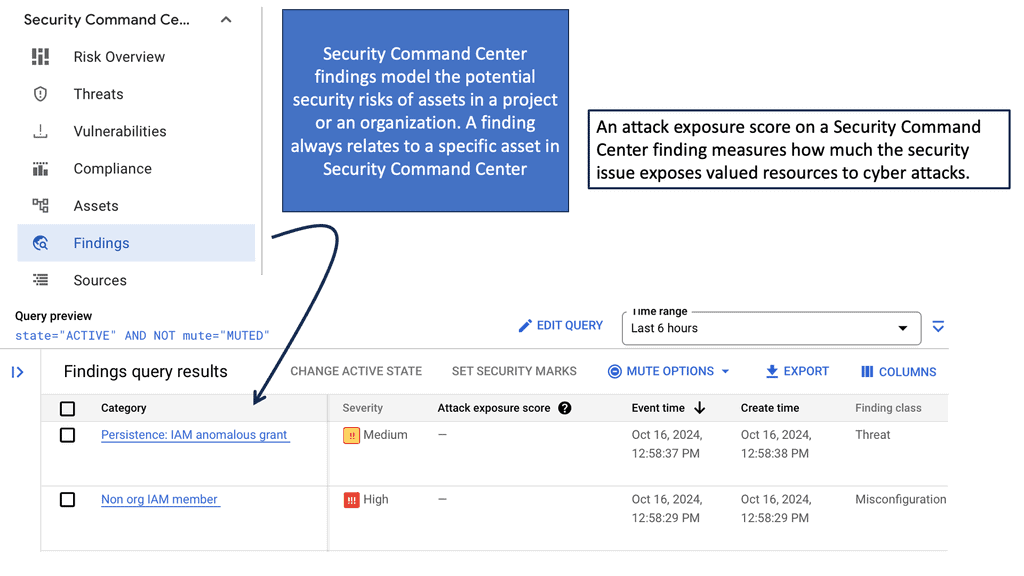
Automation with Security Command Center (SCC)
**Understanding the Core Features of Security Command Center**
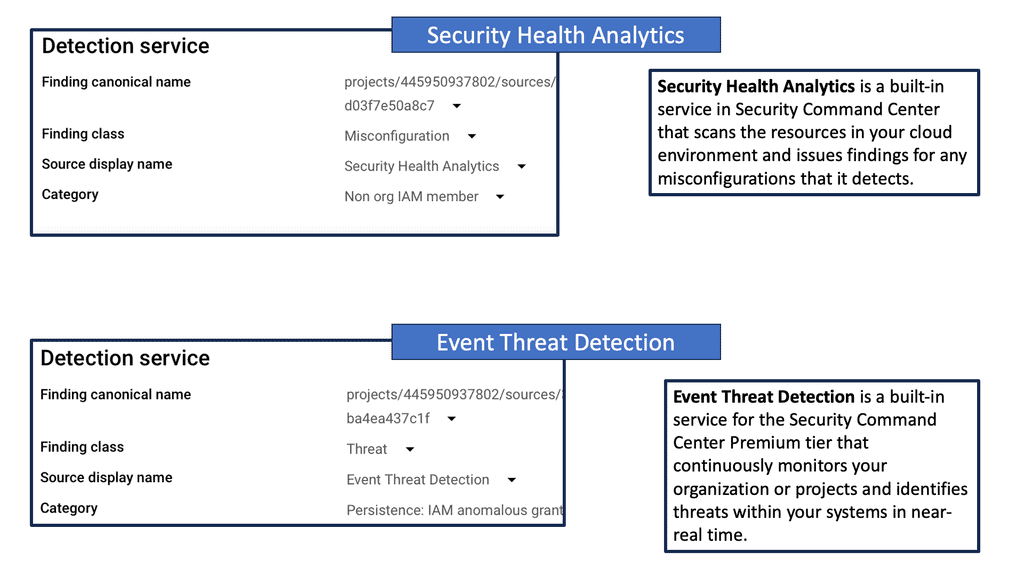
Security Command Center stands out with its robust set of features tailored for Google Cloud environments. At its core, SCC offers asset inventory management, enabling security teams to gain a clear view of their cloud assets and configurations. The integration with other Google Cloud security tools enhances its capabilities, providing automated threat detection that identifies vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and potential security threats across your cloud infrastructure. Moreover, the centralized dashboard of SCC allows for real-time monitoring and quick response to incidents, ensuring that your organization’s digital assets remain secure.
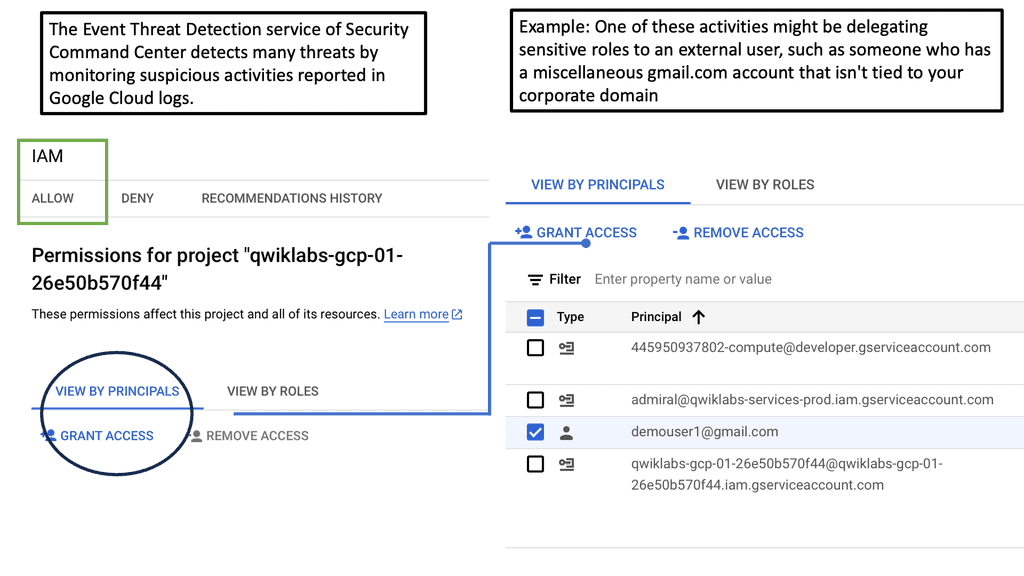
**Automating Threat Detection with Google Cloud Security**
One of the standout benefits of Security Command Center is its automation capabilities. By leveraging machine learning and advanced analytics, SCC automates the process of threat detection, significantly reducing the time and effort required by security teams. This automation not only minimizes the chances of human error but also ensures that threats are identified and addressed promptly. With built-in integration to Google Cloud’s security products like Cloud Armor and VPC Service Controls, SCC provides a seamless and holistic approach to safeguarding your cloud environment.
**Investigating Threats: A Step-by-Step Approach**
Once a threat is detected, the investigation phase is crucial to understanding and mitigating the risk. Security Command Center simplifies this process with its detailed logging and alerting system. Security teams can follow a structured approach to investigate threats, starting with analyzing alerts, examining the affected resources, and understanding the potential impact. SCC’s comprehensive logging capabilities provide valuable insights into the nature of threats, helping teams to develop effective response strategies and prevent future occurrences.
**Enhancing Your Security Posture with SCC**
Beyond threat detection and investigation, Security Command Center offers tools to enhance your organization’s overall security posture. By providing insights into security best practices and compliance requirements, SCC helps organizations align their security strategies with industry standards. The tool’s continuous monitoring capabilities ensure that your security measures are always up-to-date, adapting to the ever-changing threat landscape.
Security Automation: The World of Scripting
Challenge: Self-driving Scripts
In the traditional world of security automation, it was common to use custom in-house automation frequently. As a result, we have a variety of self-driving scripting methods that solve specific short-term security problems. For example, for secure automation, you may need to collect logs from several devices for security. However, this is far from a scalable and sustainable long-term approach to an enterprise’s automation strategy.
With more self-maintained scripting tools and working in siloed, you are creating more security blind spots. With more point tools, you have to make more silos and potential security blind spots, which may trigger the adoption of more narrowly focused tools. The more tools you have, the less control over your environment that could easily open up the spread of lateral movements.
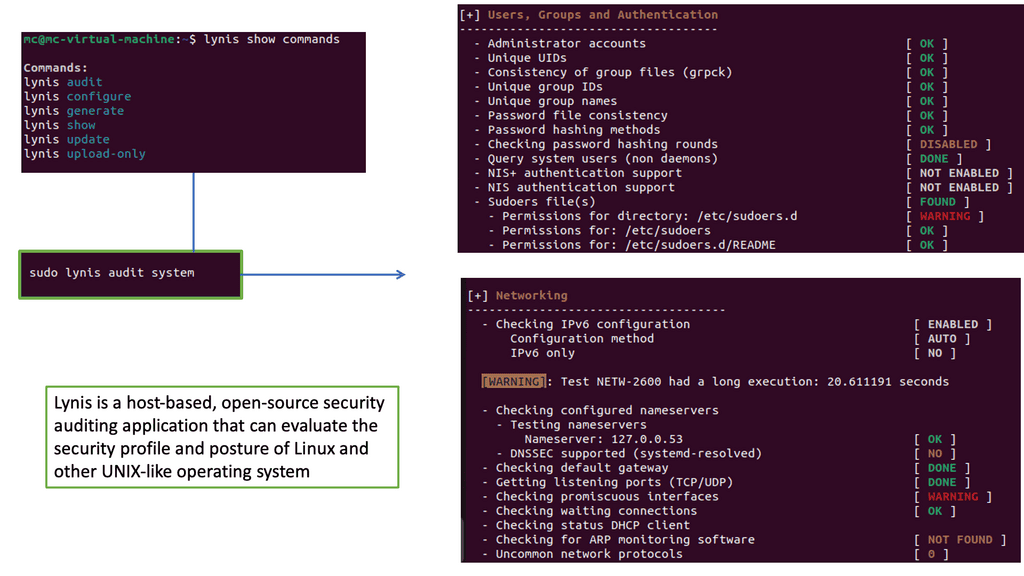
Example: Security Scan with Lynis
Lynis offers a wide range of features that contribute to its effectiveness as a security scanning tool. It utilizes a modular and extensible framework, allowing easy customization and integration with other security tools. With its powerful scripting abilities, Lynis can automate security audits and generate detailed reports. It also supports local and remote scanning, making it suitable for various environments.
Required: The need for a security platform
For example, look at lateral movements in an Active Directory (AD) network. Lateral movements are a real problem, and some advances in lateral movement techniques have been made using Metasploit, Impact, and PurpleSharp. However, detecting whether this is a bad actor or a sys admin carrying out daily activities can be challenging.
Once the bad actor stealthily navigates the network with lateral movements, they can compromise accounts, find valuable assets, and gradually exfiltrate data. All of this can be unnoticed with a below-the-radar style of attacks. A favored vector is to use DNS to exfiltrate data. Therefore, DNS often needs to be checked.
Related: For additional pre-information, you may find the following post helpful:
Security Automation
SOAR meaning: A quick point
In this case, you should integrate Splunk SOAR with User Behaviour Analytics (UBA) to detect deviations from the baseline. UBA works with unsupervised machine learning and builds profiles of entities on the network. Today’s attacks are distributed, and multiple entities are used to stage an attack.
An anomaly is sent once there is a significant deviation from normal entity behavior. Of course, an anomaly does not necessarily mean a threat. However, the anomaly can be combined with other network and infrastructure aspects to determine if a bad actor exists. So, for example, we would look at the time of day, frequency, or any other usual activity, such as privilege escalation techniques.
Lack of Speed
Without integrated security tools with security automation and a lack of automated and orchestration processes. The manual response slows MTTR and increases the possibility of a successful threat. Bad actors can breach and exfiltrate data when the mean time to detect (MTTD) is too long.
So, the manual approach to detecting, triaging, and responding to threats must be faster. For example, ransomware is quick; the game is over once the binaries are executed. It would help if you focused your efforts on the detection phase of the kill chain and caught any lateral movements, even when they pivot to valuable assets.
The Need for Security Automation
To address this challenge, you need a security solution that integrates its existing security products to reduce the response and remediation gap. In addition, these automation and orchestration events must be carried out across all its security vendors to consolidate response and remediation.
For secure automation, a unified and standard response to security can be made using pre-approved policies, consistently configuring resources according to pre-approved guidelines, and proactively maintaining them in a repeatable fashion.
Level of Automation Maturity
Security-focused content collection
This provides a faster, more efficient, and streamlined way to automate the identification, triage, and response processes to security events. In addition, we can use security-focused content. In the case of Red Hat Tower, this comes in the form of collections of roles and modules dedicated to security teams.
Splunk SOAR also has secure-focused applications and content ready to use in the Splunk database. The pre-approved policies and playbooks of Ansible Tower and Splunk SOAR will reduce the chances of misconfiguration and speed up all aspects of security investigation.
Secure Automation and Orchestration
When a few waves of Malware, Phishing, Ransomware, and under-the-radar attacks target you, automation and orchestration are the only ways to combat this. Security automation does most of the work, so you no longer have to weed through and manually address every alert as it comes in or process every security action or task.
For example, the level of automation you want to adopt depends on the maturity level of the automation you already have in our environments. If you are new to automation, you can have SOAR or Tower playbooks send an alert for further investigation. So, you can start with a semi-automated approach.
However, if you are further in your automation strategy, you can combine different playbooks to carry out coherent security detection and response. It’s easy to do this in SOAR with a playbook visualizer, and Ansible Tower has workflow templates that can be used with role-based access control.
**Red Hat Tower: How to Start**
In most organizations, we have IT operations and a security team. These teams have traditionally disjoint roles and responsibilities. The IT Operations are hardening systems, managing the infrastructure, and deploying and maintaining systems. The security operations team would track ongoing threats, perform intrusion detection/prevention, and perform firewall management activities.
A. Ansible has a common language.
With these two disjointed teams, we can use Ansible as the common automation language for everyone across your organization. Specifically, Red Hat Tower can be the common language between security tools and can be used for various security use cases that can bring the two teams together.
B. Red Hat Tower: Security Automation
Red Hat Tower can orchestrate security systems using a series of curated security collections of modules, roles, and playbooks to investigate and respond to threats using trusted content. This enables you to coordinate your enterprise security systems to perform several security duties, such as investigation enrichment, threat hunting, and incident response.
C. Pre-approved Playbooks
You can integrate Red Hat Tower with your security infrastructure here and have pre-approved playbooks ready to run upon threat detection. For example, a playbook can be automatically triggered by the results of a security scan. The following lists some of the use cases for Ansible Tower playbooks.
Security Automation Examples
1) Secure Automation: Security Patching
You could start with patching. Not patching your servers is one of the biggest causes of breaches. Automated patching boosts system security and stability, improving uptime. And this will be noticed straight away.
2) Secure Automation: System Hardening
Then, activities such as system hardening are something everyone can do for all systems. With automation, we can rapidly identify systems that require patches or reconfiguration. Then, applying patches or changing system settings consistently across many systems is easier according to defined baselines. For example, make changes to your SSH config.
Here, you can use automation to configure the SSH daemon and not allow authentication using an empty password. You can run these playbooks in check mode so those who don’t require full automation rights can run checks safely. Again, I would combine this with role-based access control.
3) Secure Automation: Network Configuration
For network management, you can configure an ACL or filter to restrict ACL or filter management access to the device from only the management network. You can also use automation to lock down who has managed to access specific subnets.
4) Secure Automation: Firewall Integration
If an increase in incident management tickets is due to incorrect firewall rules causing an increase in change requests, aim to reduce the number of tickets or change requests through automation. For our Firewall integration, the role of automation can speed up policy and log configuration changes.
For example, we can add an allowlist entry in the firewall configuration to allow traffic from a particular machine to another.
We can automate a playbook that adds the source and destination IPs as variables. Then, when a source and destination object are defined, the actual access rule between those is defined.
5) Secure Automation: Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Tower can simplify the rule and log management for your intrusion detection and prevention systems. Automation can be used to manage IDPS rules, and IDPS roles are offered. These roles can work with multiple IDPS providers, so the corresponding playbook needs to have a variable stating the actual IDPS provider.
Once the role is imported, and this is the first step, the new IDPS rule is handed over via defined variables:
6) Secure Automation: Privileged Access Management (PAM) Tools
Ansible Tower can streamline the rotation and management of privileged credentials to automate the prevention. So we can streamline credential management, which is hard to do manually.
7) Secure Automation: Endpoint Protection
Automation can simplify everyday endpoint management tasks, integrate into Endpoint Protection, and provide event-driven detection, quarantining, and remediation.
Advanced Red Hat Tower Features
Job Templates vs. Workflow Template
When creating a job template, we choose a job or workflow template. We choose the job template to develop simple employment out of it. However, creating more complex jobs composed of multiple job templates, with flow control features between one position and the next, is possible with a workflow template. This workflow template can also be integrated into your CI/CD pipelines and Jenkins.
Security Benefits
This makes it easier to have playbooks that are job templates from different teams. This is used in large environments, so multiple job templates are connected. Then, complex interactions between jobs can be defined in a workflow before the next job starts, depending on the previous position. Any inventory and any credentials can be used. So, it brings a lot of flexibility to automation.
In its multi-playbook workflows, the user can create pipelines of playbooks to be executed in sequence on any inventory using one or more users’ credentials. Security teams can configure a series of jobs that share inventory, playbooks, or permissions to fully automate investigations or remediations, bringing many consistency and security benefits.
Ansible Tower and Scheduling:
With Ansible Tower, we have Templates with the Launch feature; think of this as an ad hoc way to run Ansible for one of the tasks. However, if you are using Tower, you should use Schedules to control your automation better. For example, you may have a maintenance window when you apply changes. Here, we can set the times and frequency of playbook runs.
Scheduling this playbook in Tower will automatically refresh systems significantly out of spec. This includes calling back into Tower to apply our basic configuration once new instances are spun up with the provisioning callback feature. I find this useful for dynamic cloud environments.
GitHub for Playbooks
GitHub is all about version control, so multiple people can work on different types of code and review and merge changes. It’s also about managing change in your other environments. When Red Hat Tower runs the playbooks, it checks the URL specified in your playbooks, and here, we can have multiple options that can enhance your GitHub integrations, such as webhooks and personal access tokens.
Benefits: Removes Inconsistency of Playbooks
This is an important feature to enable as if you don’t have it checked; there is the possibility that someone notices a problem in a playbook and fixes it, then they run the playbook feeling sure that they are running the latest version.
Someone must remember to run the synchronization task before running the playbook, effectively running the older version.
Therefore, when using this option, we are removing the inconsistency of playbooks. So, increasing your security posture is very important. A lot of security breaches first start with a simple misconfiguration.
SOAR for Automation: SOAR Meaning
- Splunk SOAR Meaning
Splunk SOAR drives accuracy and consistency in the incident response process. With SOAR, workflows can be orchestrated via integrations with other technologies and automated to achieve desired outcomes. Utilizing automation with Splunk SOAR can dramatically reduce the time to investigate malware alerts, driving accuracy and consistency across its incident response processes.
- SOAR and Phantom
SOAR is the rebranding of Phantom but has multi-deployment options. Phantom was just on-premise, but now we have both on-premise and on-cloud delivery. Consider SOAR as a layer of connective tissue for all security operations.
Decision-making and action need to be automated. SOAR can turn proceeds into playbooks, allowing us to create complex security operation workflows.
We have an extensive collection of security-focused SOAR applications that interact with the API of existing security and network infrastructure, such as your Firewalls, to support activities such as containment and recovery. We’ll talk about these in a moment.
- Automation Broker
We have an Automation Broker, a modified version of Splunk SOAR with reduced features. It’s a reverse proxy for automation actions. The Automation Broker is a Docker container that uses an encrypted outbound connection from Splunk Cloud SOAR to the customer premises. As the communication is set outbound on the firewalls, it would help to open inbound ports to the perimeter firewall.
Security-Focused Playbooks
**SOAR Meaning: Security-Focused Playbooks**
Instead of manually going into other security tools and injecting data, enriching logs, and carrying out actions such as blocking or manual analysis intervention, SOAR playbooks can be used. You can have several security-focused playbooks that automatically carry out the tasks. The SOAR playbook can automate many repetitive duties. For example, you no longer have to respond manually to repetitive incidents. For example, you can have Splunk SOAR respond to malicious emails with playbooks.
**Actions based on the Playbooks**
Then, we could have a list of actions based on playbook results. This could include additional investigation tasks or notifying users. Finally, when you want to push the boundaries of automation, we could take several steps to isolate or quarantine hosts, depending on the results of the previous playbooks. These steps would be integrated with multi-factor authentication to ensure the action is appropriately authorized.
Splunkbase with Security-related Apps
Additionally, Splunkbase offers over 800 other security-related apps with pre-built searches, reports, and visualizations for specific third-party security vendors. These ready-to-use apps and add-ons help monitor security, a next-generation firewall, and advanced threat management capabilities. You can even build your custom application, from monitoring and Observability to improving safety.
**SOAR Meaning: SOAR Apps**
You are using many tools from many vendors, and when you respond, each one performs a different event and function. Splunk integrates with all devices with API, and SOAR can directly integrate all tools to act in a specific sequence.
So it can coordinate all security actions. With SOAR, you don’t get rid of your existing tools; instead, SOAR can sit between them and abstract a lot of complexity.
Think of Splunk as the conductor that supports over 350 apps. It has tools to build apps; you can create your own if it has an API. In addition, it can perform over 2000 actions. SOAR apps are Python modules that collect events from anything, such as SIEM, then normalize the information and make it available to playbooks.
**SOAR Meaning: Example: SOAR playbooks**
We have a network-based sandbox to detect malware that can enter via email. An Alert is received from SIEM, sent to SOAR, and triggers a playbook. SOAR communicates back to SIEM to query Active Directory to identify who is there and which department, and based on that, SOAR can query Carbon Black to see how the threat lives.
Finally, the SOAR can notify an analyst to manually intervene and double-check the results. This could take 30 mins by hand, but SOAR can do it in 30 seconds.
Let’s look at another SOAR playbook in action. A Splunk SOAR playbook is triggered when an email malware alert is received. Due to the lack of context in these alerts, Splunk SOAR’s first order within the playbook is to query the security information and event management (SIEM) solution for all recipients, then Active Directory to collect context from all affected users’ profiles, business groups, titles, and locations.
A key point: SOAR means with workbooks and phases
Another name for a playbook is the SOAR workbook. Each workbook can have several phases, each with tasks to carry out our security actions. In this scenario, one phase and several playbooks will be in a single step. Some playbooks can be triggered automatically, and some are invoked manually.
Then, some are being gathered manually but will have prompts for additional information. These tasks will be semi-automatic because they can automatically import data for you and enrich events. Furthermore, they can import this data and enhance events from several platforms.
Prevent Lateral Movements
A **Splunk and Lateral Movements**
You can have playbooks to hunt for lateral movements. There are many ways to move laterally in active directory networks. For example, Psexec is a sysadmin tool that allows admins to connect to other machines and perform admin tasks remotely. However, what if psexec is used to gain a remote shell or execute a PowerShell cradle on a remote device? When looking for lateral movement, we identify processes connecting remotely to a host.
B **Lateral Movement Activity**
To start a threat investigation, we could have a playbook to conduct an initial search for a known lateral movement activity. Windows security logs contain a wealth of information. The playbook can look for authentication events over the network from rare or unusual hosts or users.
C **Event Window Code**
For example, in a Windows event log, you would see a Windows event code for successful login, another log for a network connection, and another for privilege escalation events. Each event doesn’t mean much by itself but indicates a threat together. For example, here you can see that someone has used an admin account to connect over the network from a particular host and gained command-line access to a victim host.
D. Splunk SOAR’s visual playbook editor
Splunk SOAR comes with 100 pre-made playbooks, so you can start automating security tasks immediately and hunt for lateral movements. To simplify life, we have a Splunk SOAR visual playbook editor that makes creating, editing, implementing, and scaling automated playbooks easier to help your business eliminate security analyst grunt work.
Popular Playbook Examples
- Splunk Intelligence Management (TruSTAR) Indicator Enrichment
Then, we have a Splunk Intelligence Management (TruSTAR) Indicator Enrichment. This playbook uses Splunk Intelligence Management normalized indicator enrichment, which is captured within the notes of a container. An analyst can view details and specify subsequent actions directly within a single Splunk SOAR prompt for a manual response.
- Crowdstrike Malware Triage
There is a Cowdstrike Malware Triage. This playbook walks through the steps performed automatically by Splunk SOAR to triage file hashes ingested from Crowdstrike and quarantine potentially infected devices.
- Finding and Disabling Inactive Users on AWS Splunk SOAR’s
Then, there are playbooks specific to cloud environments. Finding and Disabling Inactive Users on AWS Splunk SOAR’s orchestration, automation, response, collaboration, and case management capabilities are available from your mobile device.
Summary: Security Automation
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, ensuring the security of our online presence has become paramount. With the ever-increasing number of cyber threats, organizations and individuals alike are seeking efficient and effective ways to protect their sensitive information. This is where security automation steps in, revolutionizing the way we defend ourselves from potential breaches and attacks. In this blog post, we explored the concept of security automation, its benefits, and how it can fortify your digital world.
Understanding Security Automation
Security automation refers to the process of automating security-related tasks and operations, reducing the need for manual intervention. It involves utilizing advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to streamline security processes, detect vulnerabilities, and respond to potential threats in real-time.
Benefits of Security Automation
Enhanced Threat Detection and Response:
By leveraging automation, security systems can continuously monitor networks, applications, and user behavior, instantly detecting any suspicious activities. Automated threat response mechanisms allow for swift actions, minimizing the potential damage caused by cyber attacks.
Time and Cost Efficiency:
Automation eliminates the need for manual security tasks, freeing up valuable time for security teams to focus on more critical issues. Additionally, by reducing human intervention, organizations can achieve significant cost savings in terms of personnel and resources.
Strengthening Security Measures
Proactive Vulnerability Management:
Security automation enables organizations to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors. Automated vulnerability scanning, patch management, and configuration checks help maintain a robust security posture.
Continuous Compliance Monitoring:
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is crucial for organizations. Security automation can ensure continuous compliance by automating the monitoring and reporting of security controls, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Integration and Scalability
Seamless Integration with Existing Systems:
Modern security automation solutions are designed to seamlessly integrate with a variety of existing security tools and systems. This allows organizations to build a comprehensive security ecosystem that works harmoniously to protect their digital assets.
Scalability for Growing Demands:
As organizations expand their digital footprint, the security landscape becomes more complex. Security automation provides the scalability required to handle growing demands efficiently, ensuring that security measures keep pace with rapid business growth.
Conclusion:
Security automation is a game-changer in the world of cybersecurity. By harnessing the power of automation, organizations can bolster their defenses, detect threats in real-time, and respond swiftly to potential breaches. The benefits of security automation extend beyond cost and time savings, providing a proactive and scalable approach to safeguarding our digital world.
- Fortinet’s new FortiOS 7.4 enhances SASE - April 5, 2023
- Comcast SD-WAN Expansion to SMBs - April 4, 2023
- Cisco CloudLock - April 4, 2023