What is BGP Protocol in Networking
In the vast interconnected network of the internet, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and reliable routing. As the primary protocol for exchanging routing information between internet service providers (ISPs) and networks, BGP serves as the backbone of the internet. In this blog post, we will delve into BGP's functionalities, benefits, and challenges, shedding light on its significance in today's digital landscape.
Border Gateway Protocol, commonly known as BGP, is an exterior gateway protocol that facilitates the exchange of routing information between different autonomous systems (AS). An autonomous system represents a collection of networks under a single administrative domain. BGP is responsible for determining the best path for data packets to traverse between ASes, allowing efficient communication across the internet.
BGP serves as the backbone of the Internet, enabling the interconnection of various networks and facilitating efficient routing decisions. Its primary purpose is to determine the best path for data transmission between networks, considering factors such as network policies, path attributes, and performance metrics.
BGP operates on a peer-to-peer basis, where routers establish connections with other routers to exchange routing information. These connections, known as BGP sessions, allow routers to exchange information about network reachability and determine the optimal path for data transmission.
BGP utilizes a range of attributes to evaluate and select the best path for routing. These attributes include the autonomous system path, next hop, origin, local preference, and community values. By analyzing these attributes, BGP routers make informed decisions about the most suitable path for data transmission.
BGP is of utmost importance to Internet Service Providers (ISPs) as it enables them to connect their networks to the rest of the Internet. ISPs rely on BGP to exchange routing information with other networks, ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission for their customers.
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) plays a vital role in the world of networking, serving as the backbone of the Internet. Its ability to facilitate routing decisions between autonomous systems and exchange routing information makes it a fundamental protocol for efficient data transmission. Understanding the basics of BGP and its operation is essential for anyone involved in the field of networking.
Matt Conran
Highlights: What is BGP Protocol in Networking
Understanding BGP Basics
– Border Gateway Protocol is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information between autonomous systems (AS) on the internet. Unlike interior gateway protocols that operate within a single domain, BGP is used for routing between different domains. By advertising the best paths for data packets, BGP ensures that internet traffic flows efficiently and reliably. It’s a protocol that not only chooses the shortest path but also considers policies and rules set by network administrators.
– At the core of BGP’s functionality are BGP routers, which communicate with each other to exchange routing information. These routers use a “path vector” approach to inform others of the paths available and the network policies associated with those paths. When a BGP router receives multiple routes to the same destination, it evaluates them based on a variety of factors, including path length, policy preferences, and network reliability. Once the best path is determined, it is advertised to other routers, creating a dynamic and adaptive routing system.
BGP Key Considerations:
A: – BGP, the routing protocol of the internet, plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient data transmission between autonomous systems (AS). It operates on the principle of path vector routing, taking into account multiple factors such as network policies, path attributes, and path selection.
B: – BGP serves as the backbone of internet routing, facilitating the exchange of routing information between different AS. It enables autonomous systems to establish connections, exchange reachability information, and make informed decisions about the best path to route traffic.
C: – Configuring BGP requires a comprehensive understanding of its parameters, policies, and attributes. Peering, the process of establishing connections between BGP routers, is crucial for information exchange and maintaining a stable routing environment. This section explores the intricacies of BGP configuration and peering relationships.
D: – As a critical component of internet infrastructure, BGP is vulnerable to security threats such as route hijacking and prefix hijacking. This section delves into the various security mechanisms and best practices that network administrators can employ to mitigate these risks and ensure the integrity of BGP routing.
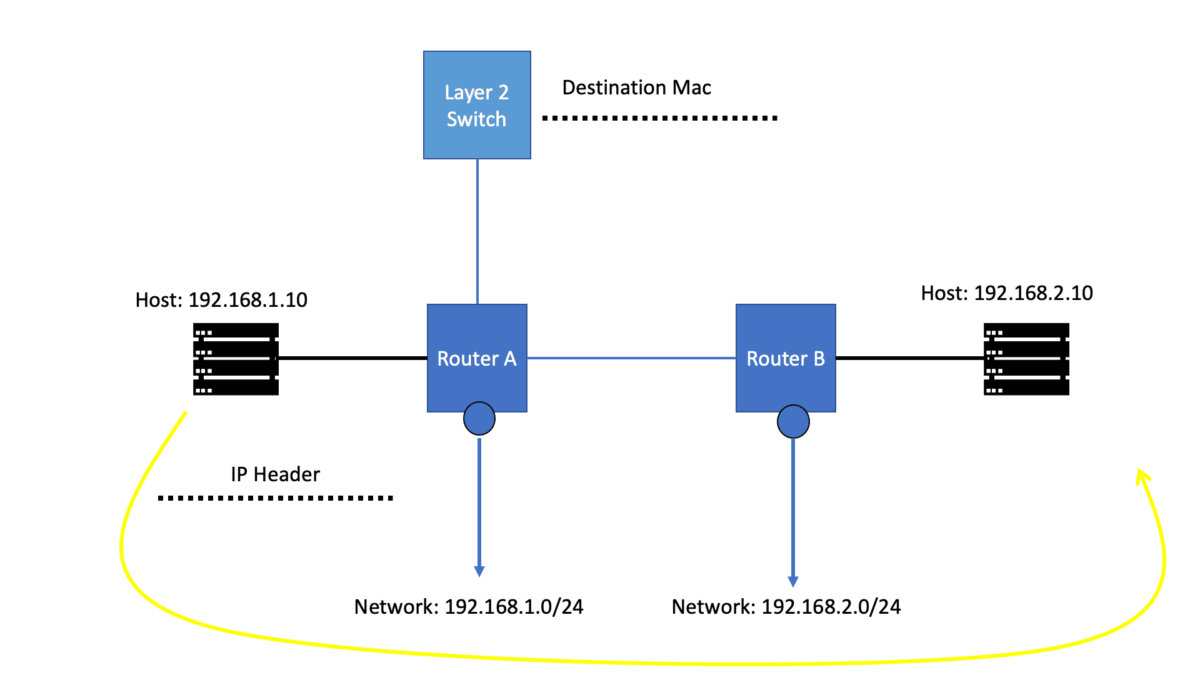
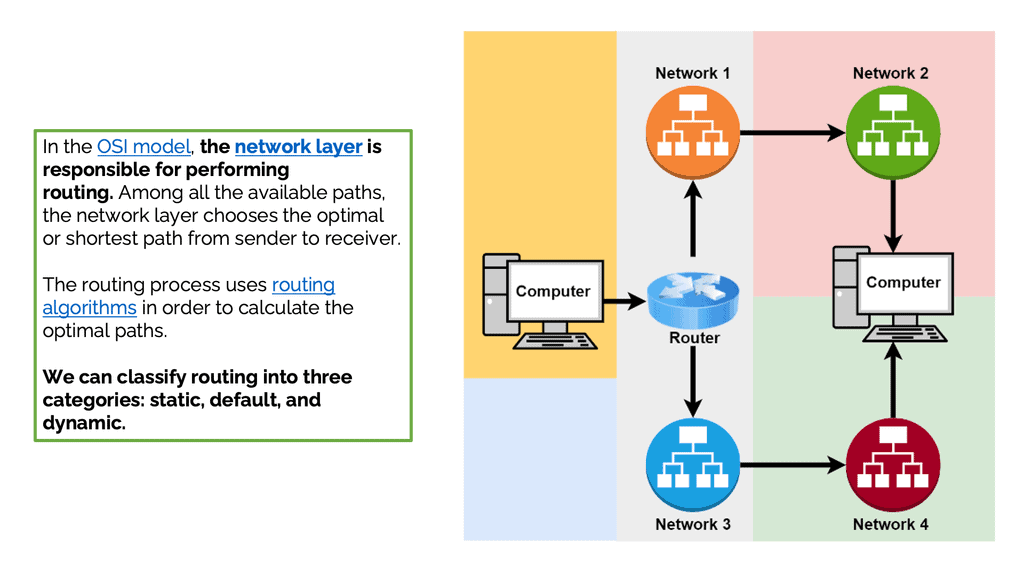
**Moving packets between networks**
A router is primarily responsible for moving packets between networks. Dynamic routing protocols distribute network topology information between routers so they can learn about unattached networks. Routers try to select the fastest loop-free path in a network based on the destination network. Link flaps, router crashes, and other unexpected events could impact the most efficient path, so the routers must exchange information with each other so that the network topology updates during these events.
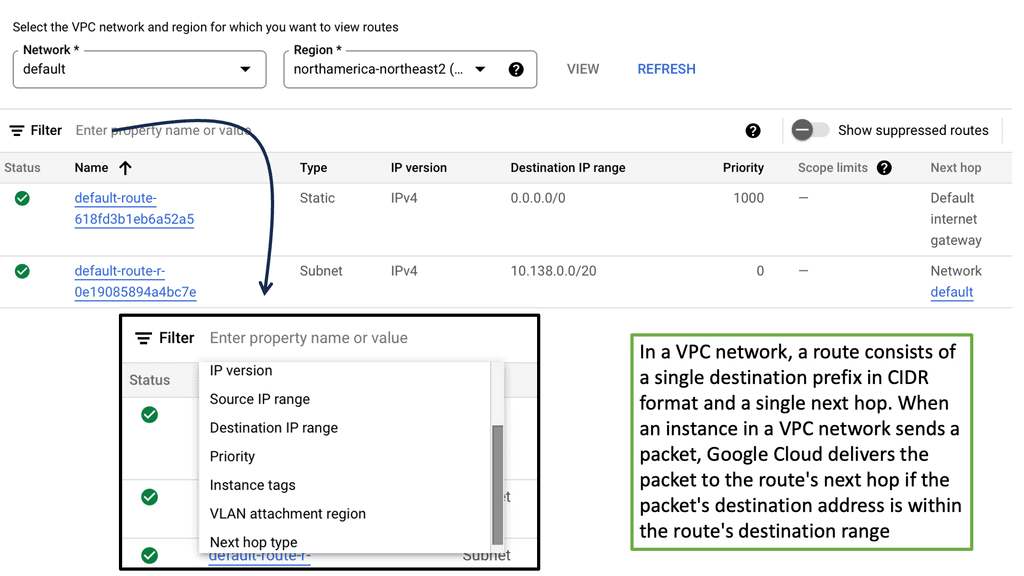
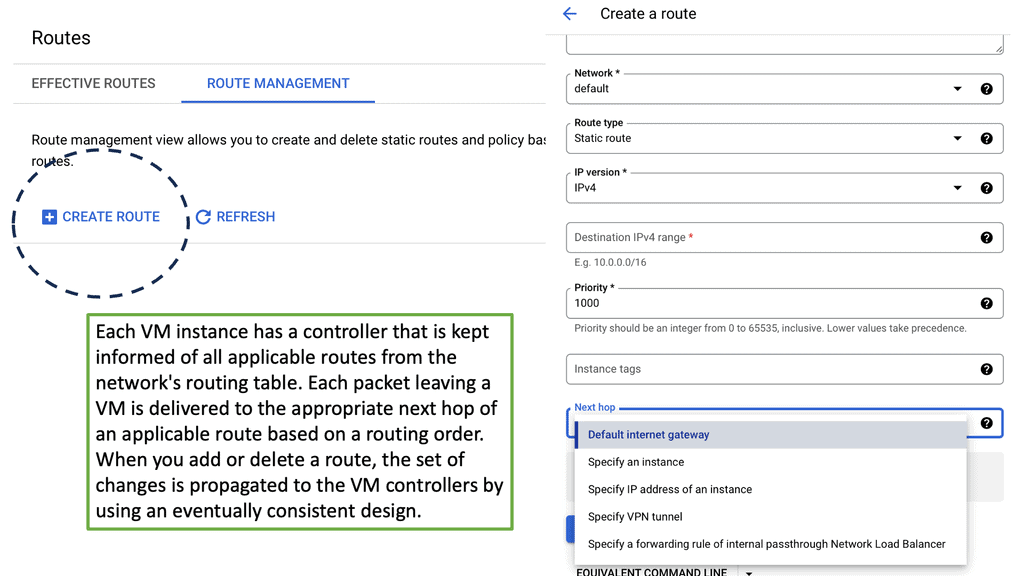
Discussing Routing Protocols
Routing protocols are rules and algorithms that determine the best path for data travel within a network. They facilitate the exchange of routing information between routers, allowing them to update and maintain routing tables dynamically. Routing protocols rely on various algorithms and mechanisms to determine the best path for data transmission. They consider network topology, link costs, and routing metrics to make informed decisions.
Routing tables store information about known networks, associated costs, and the next hop to reach them. Routing protocols update these tables dynamically to adapt to network changes. Routing updates are messages exchanged between routers to share information about network changes. These updates help routers to adjust their routing tables and maintain accurate routing information.
**Choosing a IGP or EGP**
Depending on whether the protocol is designed to exchange routes within or between organizations, routing protocols are classified as Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) or Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGP). All routers in the routing domain use the same logic to find the shortest path to a destination in IGP protocols. A unique routing policy may be required for each external organization with which EGP protocols exchange routes.
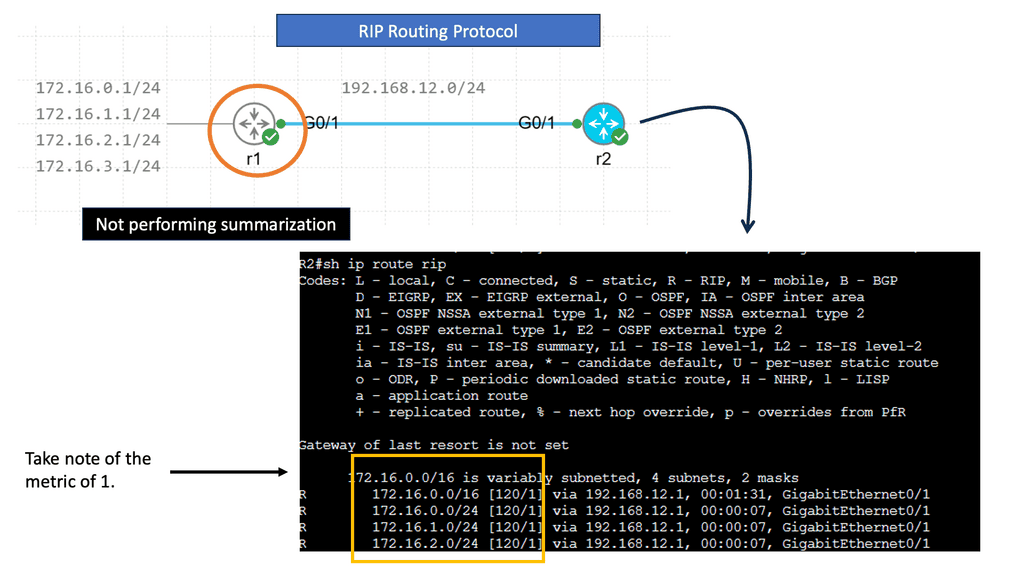
Example: Functionality of RIP
RIP operates by exchanging routing information between neighboring routers at regular intervals. It uses a routing table to store network information and associated hop counts. RIP routers share their routing tables with neighboring routers, allowing them to update their tables and determine the best path for forwarding packets.
RIP is known for its simplicity and ease of implementation. Its basic configuration and operation make it ideal for small to medium-sized networks. RIP’s distance-vector approach makes it less resource-intensive than other routing protocols. Its widespread use also means a wide range of networking devices supports it.
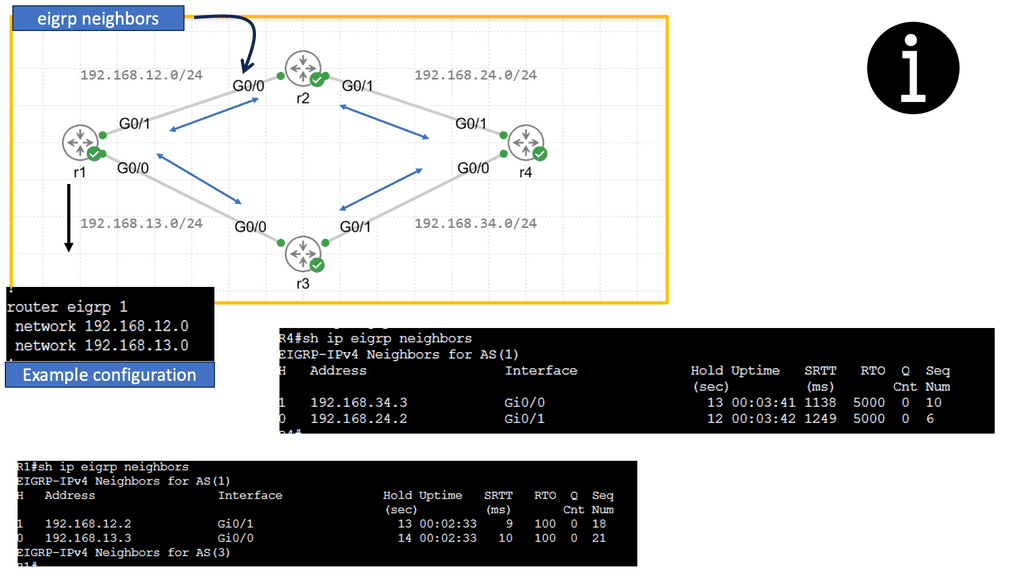
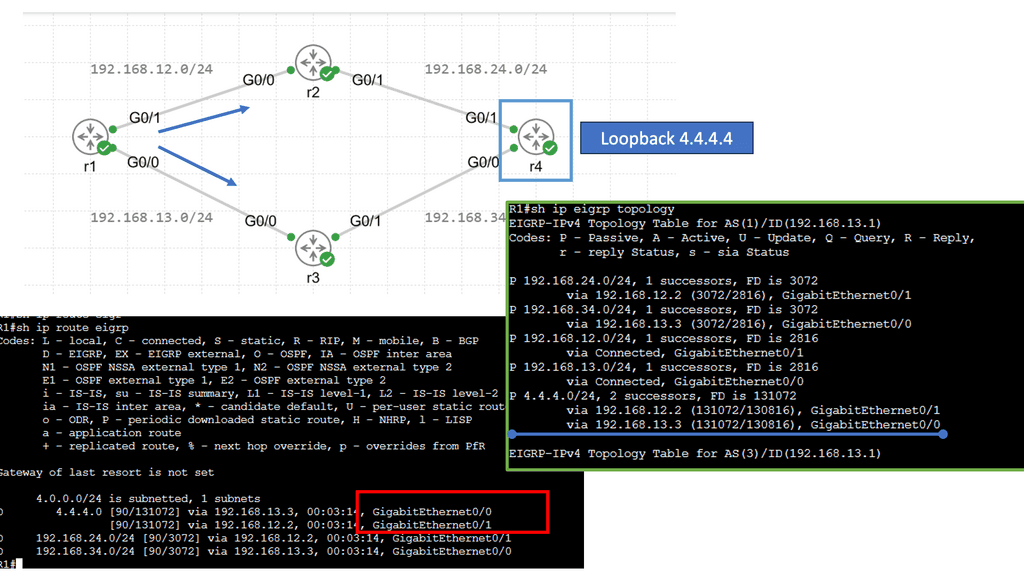
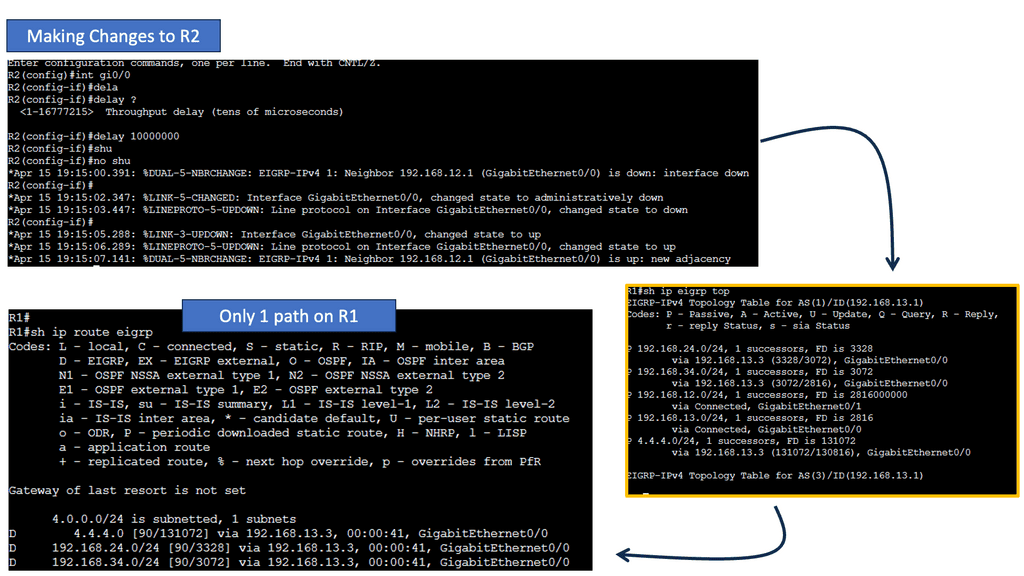
Example Functionality: EIGRP
EIGRP is an advanced routing protocol developed by Cisco Systems. It operates at the OSI model’s Network Layer (Layer 3) and utilizes the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to calculate the best path for routing packets. With its support for IPv4 and IPv6, EIGRP offers a versatile solution for network administrators.
EIGRP boasts several key features that make it a robust routing protocol. One of its notable strengths is its ability to support unequal-cost load balancing, allowing for optimized traffic distribution across multiple paths. Additionally, EIGRP utilizes a bandwidth-aware metric, considering network congestion and link quality to make intelligent routing decisions.
Border Gateway Protocol
Path-Vector Protocol
– Before diving into the complexities, let’s start with the basics. BGP is a path-vector protocol that determines the optimal path for routing packets across different ASs. Unlike interior gateway protocols (IGPs), BGP focuses on exchanging routing information between ASs, considering factors like policy, path length, and network performance.
– BGP establishes connections between neighboring routers in different ASs. These connections, known as BGP peers, exchange routing information and update each other about network reachability. The neighbor establishment process involves a series of message exchanges, including OPEN, KEEPALIVE, and UPDATE messages.
– BGP employs a sophisticated decision-making process to select the best route among various available options. AS path length, origin type, and next hop significantly determine the optimal path. Additionally, network administrators can implement policies to influence BGP’s route selection behavior based on their specific requirements.
EGP standardized BGP
EGP standardized Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) provides scalability, flexibility, and network stability via path-vector routing. In designing BGP, the primary focus was on IPv4 inter-organization connectivity on public networks, such as the Internet and private networks. There are more than 600,000 IPv4 routes on the Internet, and BGP is the only protocol that exchanges them.
OSPF and ISIS advertise incremental updates and refresh network advertisements, but BGP does not. Due to the possibility that thousands of routes could be calculated if there is a link flap in the network, BGP prefers stability within the network.
BGP defines an autonomous system (AS) as a collection of routers controlled by a single organization, using one or more IGPs and standard metrics. An AS must appear consistent with external ASs in routing policy if it uses multiple IGPs or metrics. ASs need not use an IGP and can also use BGP as their only routing protocol.
Decrease Complexity
When considering BGP protocol in networking, we must first highlight a common misconception that Border Gateway Protocol ( BGP ) is used solely for network scalability, replacing Interior Gateway Protocol ( IGP ) once a specific prefix or router count has been reached. Although BGP does form the base for large networks, an adequately designed IGP can scale tens of thousands of routers.BGP is not just used for scalability; it is used to decrease the complexity of networking rather than size.
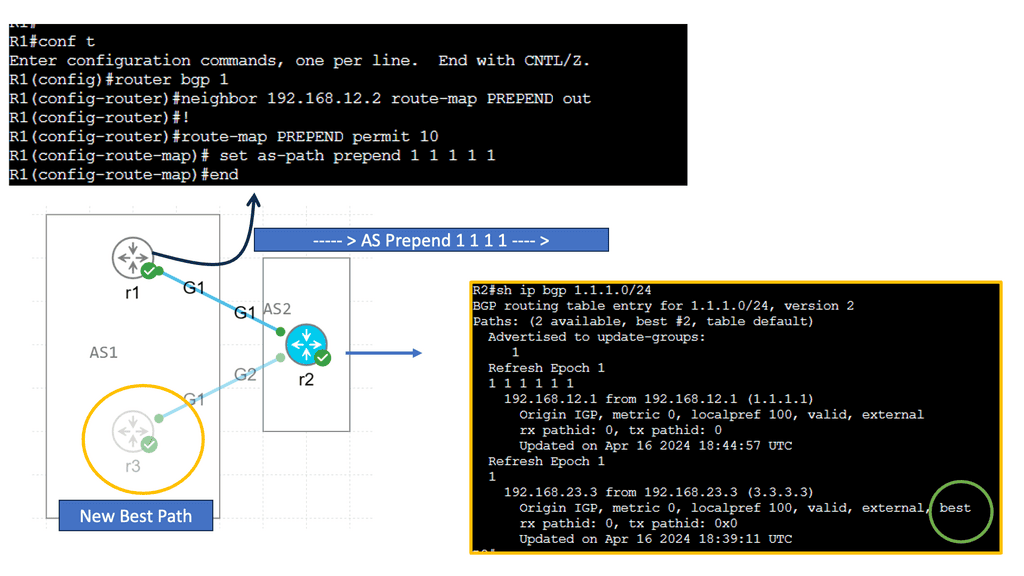
Example Feature: BGP and AS Prepending
AS prepending is a technique for influencing routing path selection by adding repetitive AS numbers to the AS_PATH attribute of BGP advertisements. By artificially lengthening the AS_PATH, network administrators can influence inbound traffic and steer it towards desired paths. AS prepending offers several benefits for network optimization.
Firstly, it provides greater control over inbound traffic, allowing organizations to distribute the load across multiple links evenly.
Secondly, it assists in implementing traffic engineering strategies, ensuring efficient utilization of available network resources. Lastly, AS prepending enables organizations to establish peering relationships with specific providers, optimizes connectivity, and reduces latency.
Split into smaller pieces.
The key to efficient routing protocol design is to start with business design principles and break failure domains into small pieces. Keeping things simple with BGP is critical to stabilizing large networks. What usually begins as a single network quickly becomes multiple networks as the business grows. It is easier to split networks into small pieces and to “aggregate” the information as much as possible. Aggregating routing information hides parts of the network and speeds up link/node failure convergence.
**BGP and TCP**
BGP is reliably transported through the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Since TCP handles update fragmentation, retransmission, acknowledgment, and sequencing, BGP no longer needs to implement these functions. BGP can also use any TCP authentication scheme. BGP maintains session integrity by using regular keepalives after establishing a session. Hold timers are reset by update messages, typically three times the keepalive timer. Three consecutive keepalives are required to close a BGP session without an Update message.
Accurate routing information is essential for reliable forwarding. BGP uses several measures to increase accuracy. A BGP attribute called AS_PATH (which lists the autonomous systems the route has traversed) is checked when updates are received to detect loops. AS updates originating from or passing through the current AS are denied. Using inbound filters, you can ensure that all updates adhere to local policies. The next hop must be reachable for a valid BGP route.
Route information must be kept accurate by promptly removing unreachable routes. As unreachable routes become unavailable, BGP promptly removes them from their peers.
BGP Advanced Topic
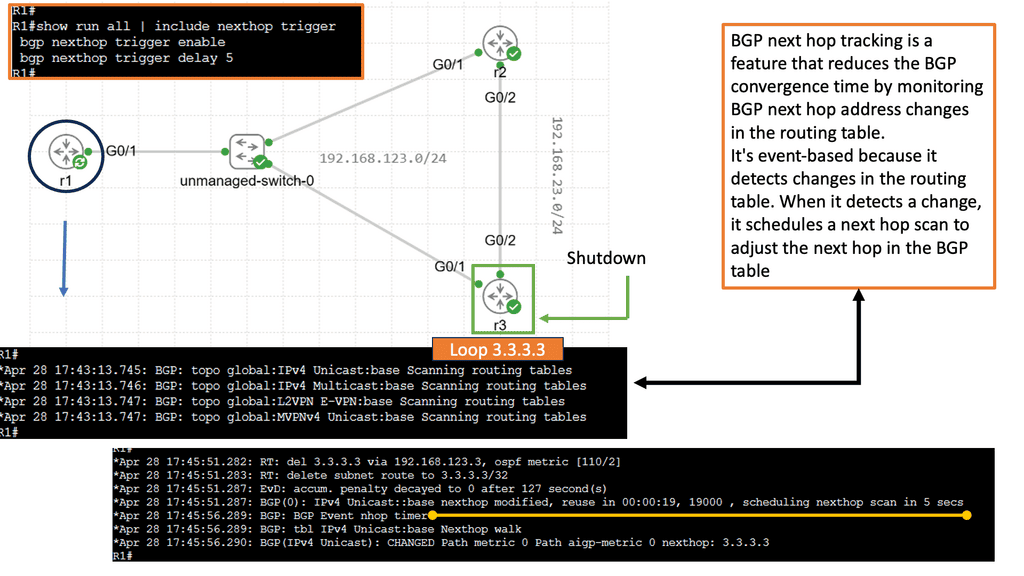
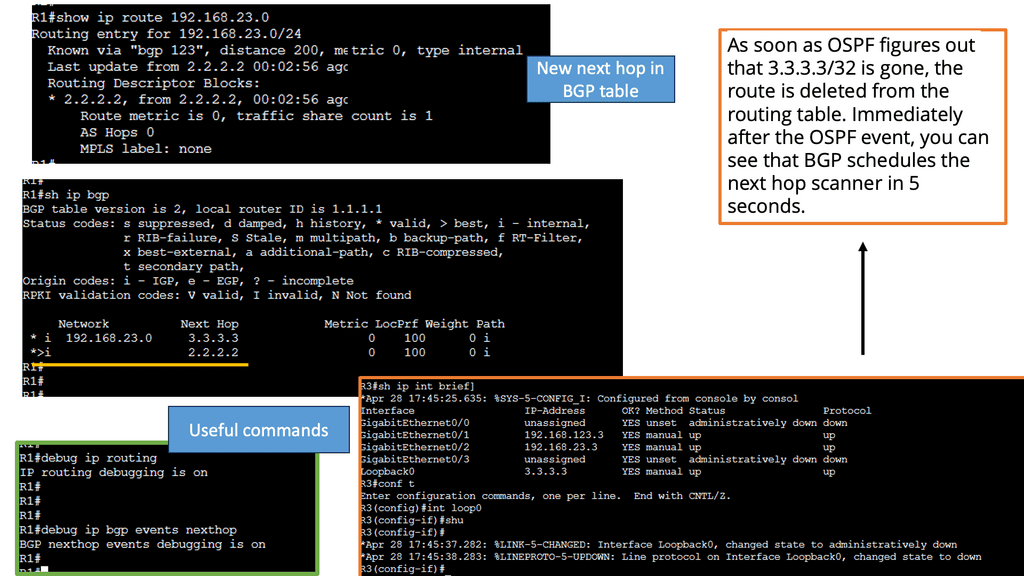
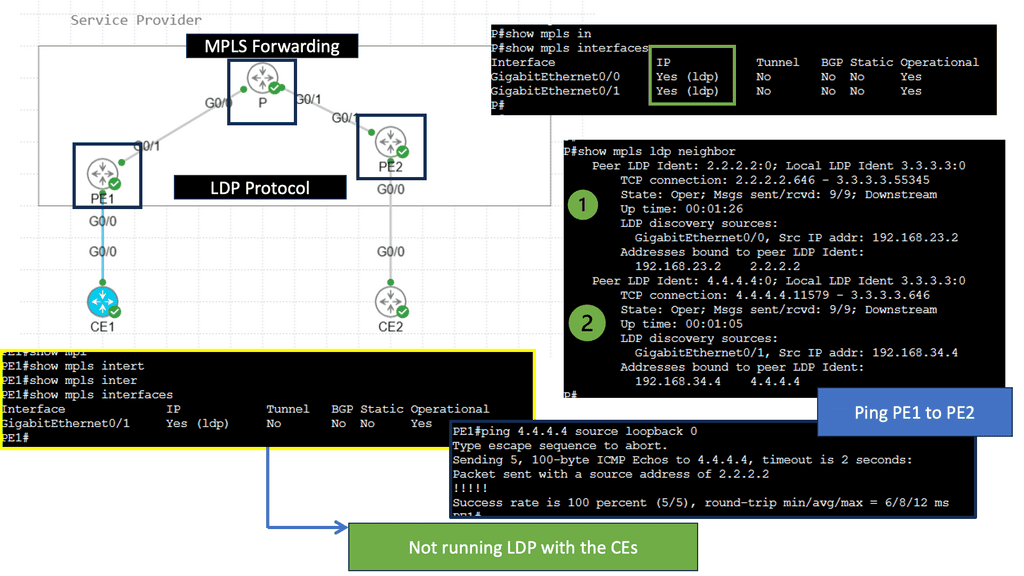
BGP Next Hop Tracking:
The first step in comprehending BGP next-hop tracking is to grasp the concept of the next hop itself. In BGP, the next hop represents the IP address to which packets should be forwarded to reach the destination network. It serves as the gateway or exit point towards the desired destination.
Next-hop tracking is essential for ensuring efficient routing decisions in BGP. By monitoring and verifying the availability of next-hop IP addresses, network administrators can make informed choices about the best paths for traffic to traverse. This tracking mechanism enables the network to adapt dynamically to changes in the network topology and avoid potential routing loops.
Understanding BGP Route Reflection
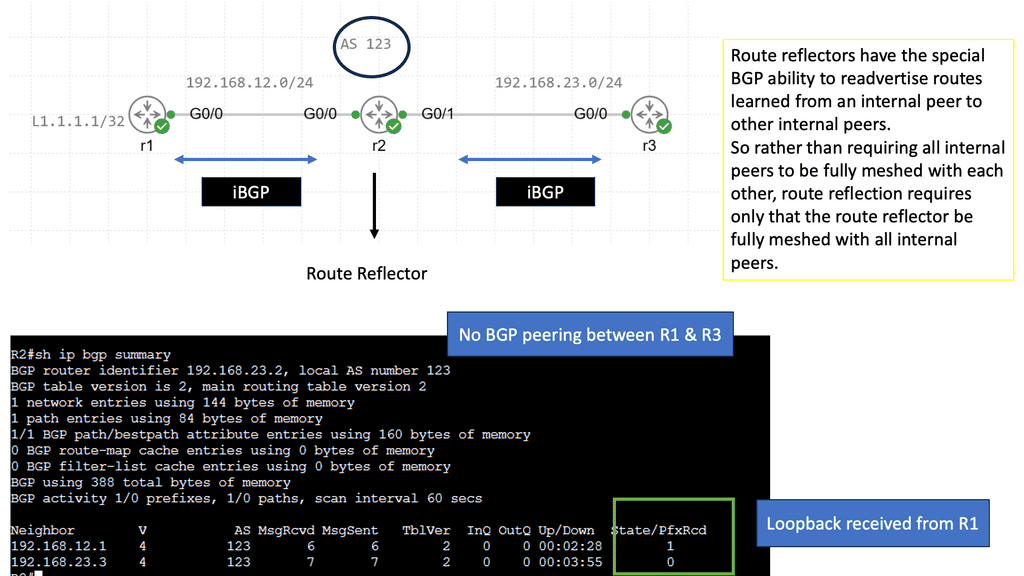
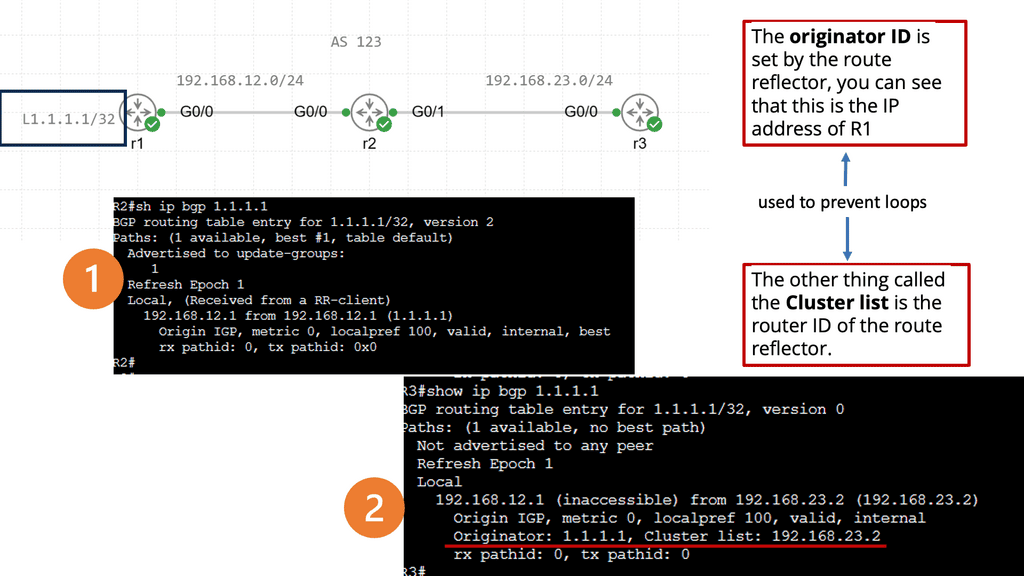
BGP route reflection is a technique used to address the scalability issues in large BGP networks. It allows for efficiently distributing routing information without creating unnecessary traffic and overhead. In a traditional BGP setup, all routers within an autonomous system (AS) need to maintain a full mesh of BGP peerings, leading to increased complexity and resource utilization. Route reflection simplifies this by introducing a hierarchical structure that reduces the number of peering relationships required.
Route reflectors serve as the focal point in a BGP route reflection setup. They are responsible for reflecting BGP routes to other routers within the AS. Route reflectors receive BGP updates from their clients and reflect them to other clients, ensuring that routing information is efficiently propagated throughout the network. By eliminating the need for full-mesh connectivity, route reflectors reduce the number of required BGP sessions and improve scalability.
A Key Note: When considering what is BGP protocol in networking
BGP-Based Networks:
1 🙂 Networks grow and should be allowed to grow organically. Each business unit may require several different topologies and design patterns. Trying to design all these additional requirements would increase network complexity. In the context of a single IGP, it may add too many layers of complexity. BGP provides a manageable approach to policy abstraction by controlling specific network traffic patterns within and between Autonomous Systems.
2 🙂 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth functioning of the internet by facilitating efficient routing between autonomous systems. Its scalability, flexibility in path selection, and ability to adapt to network changes contribute to the overall resilience and reliability of the internet.
3 🙂 However, challenges such as BGP hijacking and route flapping require ongoing attention and mitigation efforts to maintain the security and stability of BGP-based networks. By understanding the intricacies of BGP, network administrators can effectively manage their networks and contribute to a robust and interconnected internet ecosystem.
You may find the following posts helpful for pre-information:
What is BGP Protocol in Networking
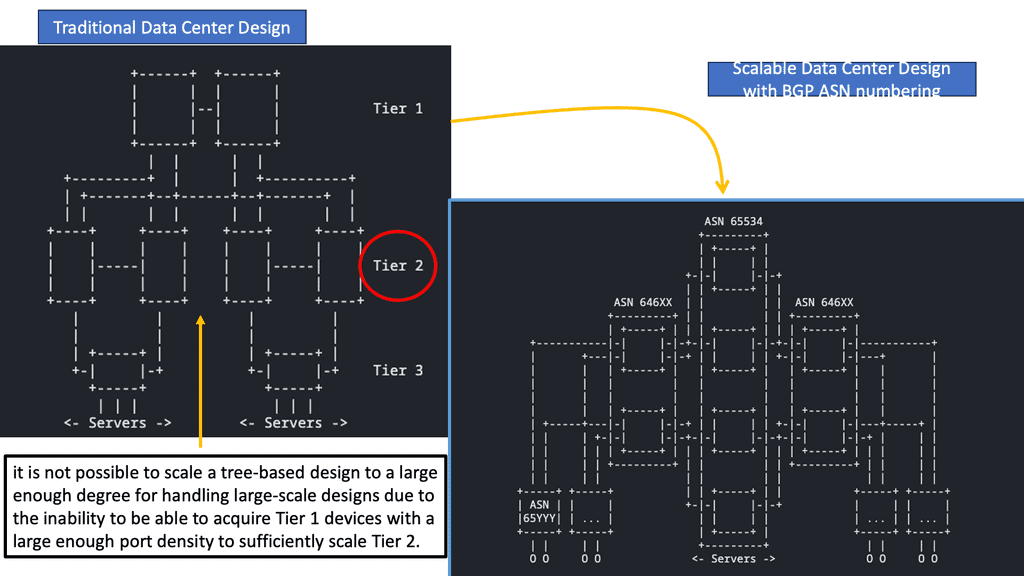
BGP is mature and powers the internet. Many mature implementations of BGP exist, including in the open-source networking world. A considerable benefit to BGP is that it is less chatty than its link state and supports multiple protocols (i.e., it supports advertising IPv4, IPv6, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), and VPNs natively). Remember that BGP has been understood for decades for helping internet-connected systems find one another. However, it is helpful within a single data center, as well. In addition, BGP is standards-based and supported by many free and open-source software packages.
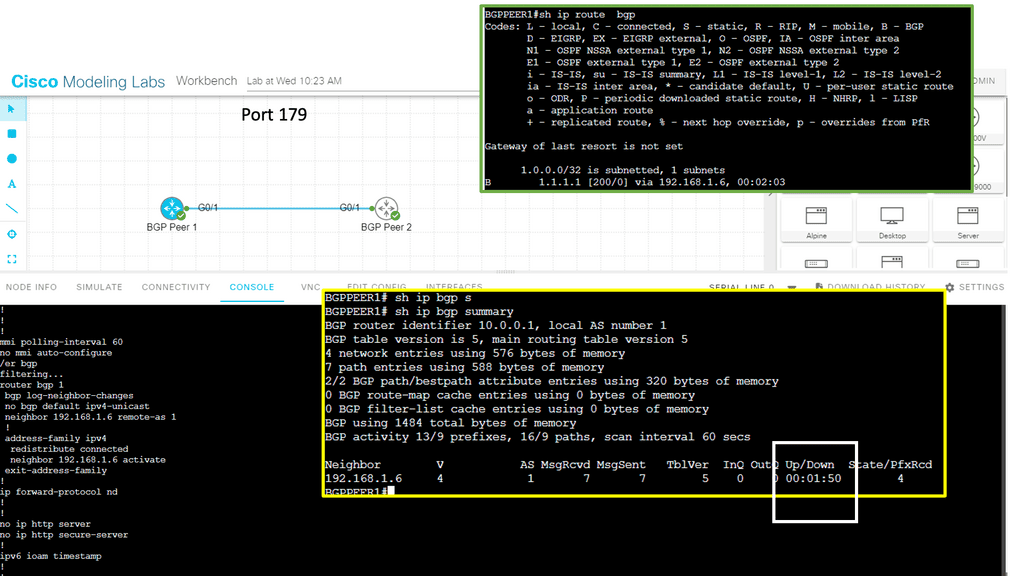
How does BGP work?
BGP operates on a distributed architecture, where routers exchange routing information using rules and policies. It uses a path-vector algorithm to select the best path based on various attributes, such as the number of AS hops and the quality of the network links. BGP relies on the concept of peering, where routers establish connections with each other to exchange routing updates.
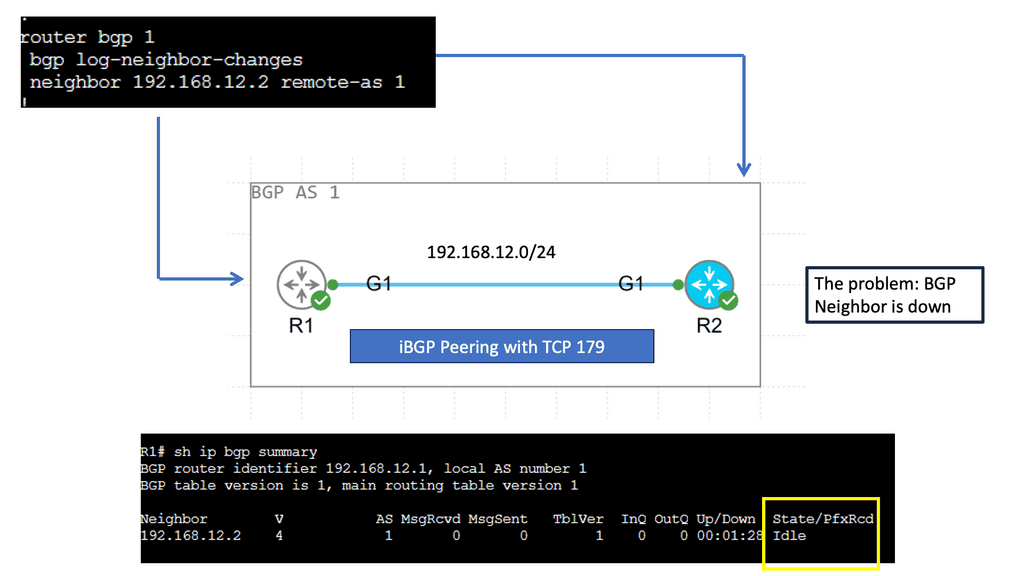
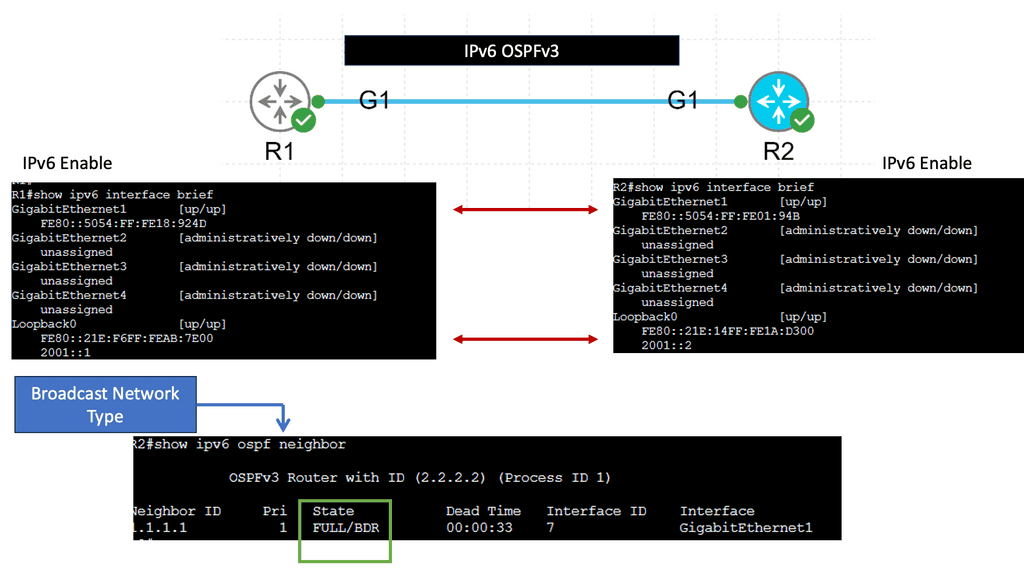
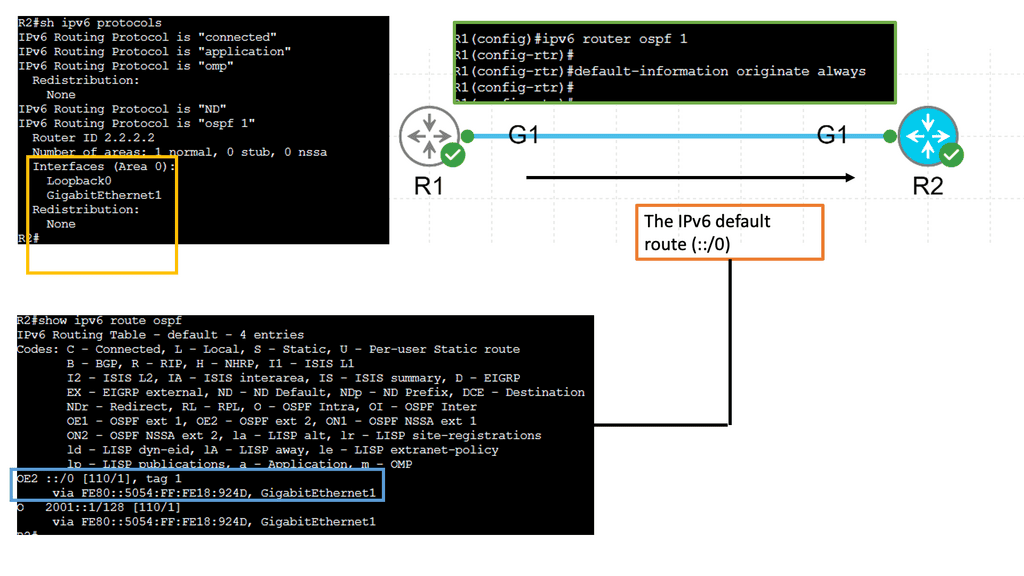
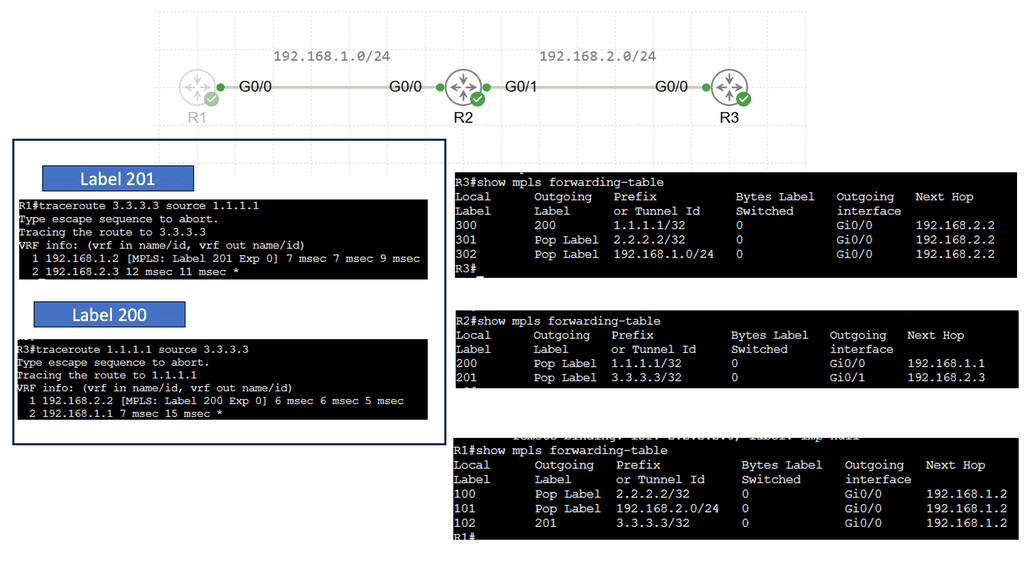
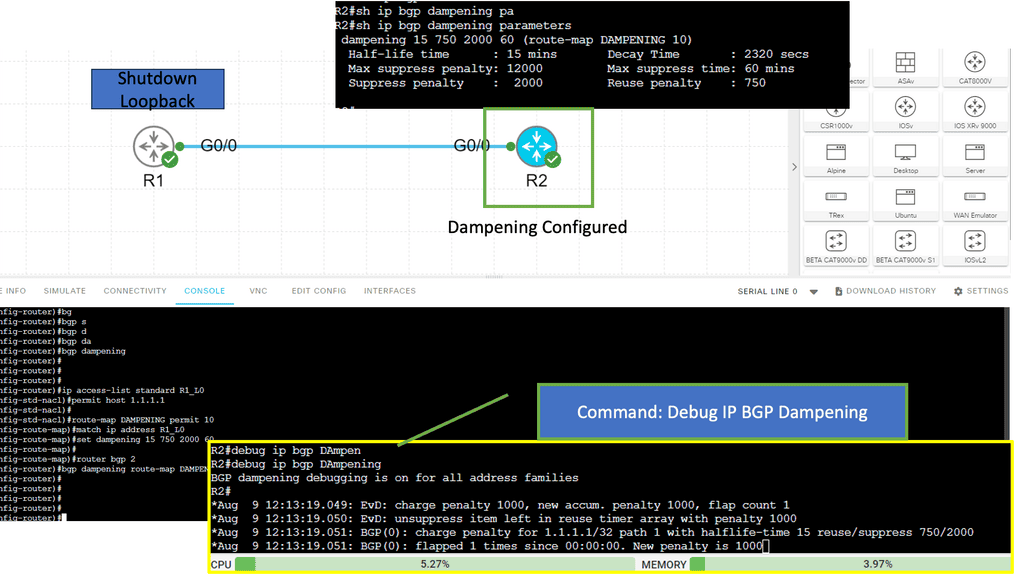
Guide on BGP Dampening
In the following sample, we have two routers with BGP configured. Each BGP peer is in its own AS, and BGP dampening is configured on R2 only. Notice the output of the debug ip bgp dampening on R2 once the loopback on R1 is shut down.
The concept behind BGP dampening is relatively simple. When a router detects a route flapping, it assigns a penalty to that route. The penalty is based on the number of consecutive flaps and the configured dampening parameters. As the penalty accumulates, the route’s desirability decreases, making it less likely to be advertised to other routers.
The purpose of BGP dampening is to discourage the propagation of unstable routes and prevent them from spreading throughout the network. By penalizing flapping routes, BGP dampening helps to stabilize the network by reducing the number of updates sent and minimizing the impact of routing instability.
**The Significance of BGP**
Scalability: BGP’s hierarchical structure enables it to handle the massive scale of the global internet. By dividing the internet into smaller autonomous systems, BGP efficiently manages routing information, reducing the burden on individual routers and improving scalability.
Path Selection: BGP allows network administrators to define policies for path selection, giving them control over traffic flow. This flexibility enables organizations to optimize network performance, direct traffic through preferred paths, and ensure efficient resource utilization.
Internet Resilience: BGP’s ability to dynamically adapt to changes in network topology is crucial for ensuring internet resilience. If a network or path becomes unavailable, BGP can quickly reroute traffic through alternative paths, minimizing disruptions and maintaining connectivity.
**Challenges and Security Concerns**
BGP Hijacking: BGP’s reliance on trust-based peering relationships makes it susceptible to hijacking. Malicious actors can attempt to divert traffic by announcing false routing information, potentially leading to traffic interception or disruption. Initiatives like Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) aim to mitigate these risks by introducing cryptographic validation mechanisms.
Route Flapping: Unstable network connections or misconfigurations can cause routes to appear and disappear frequently, causing route flapping. This can lead to increased network congestion, suboptimal routing, and unnecessary router strain. Network administrators need to monitor and address route flapping issues carefully.
A policy-oriented control plane reduces network complexity.
BGP is a policy-oriented control plane-routing protocol used to create islands of networks that match business requirements to administrative domains. When multiple business units present unique needs, designing all those special requirements using a single set of routing policies is hard. BGP can decrease policy complexity and divide the complexity into a manageable aggregation of policies.
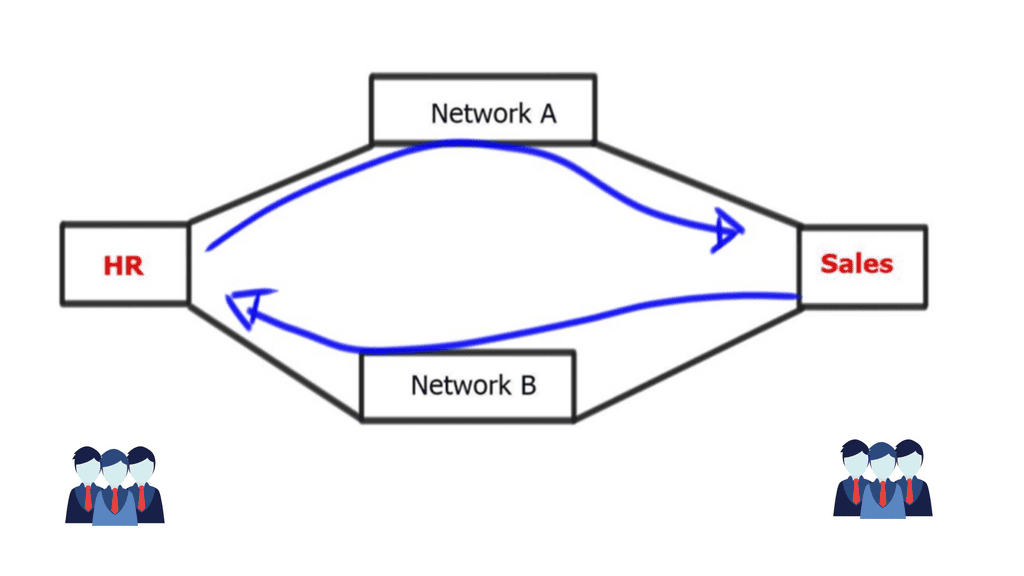
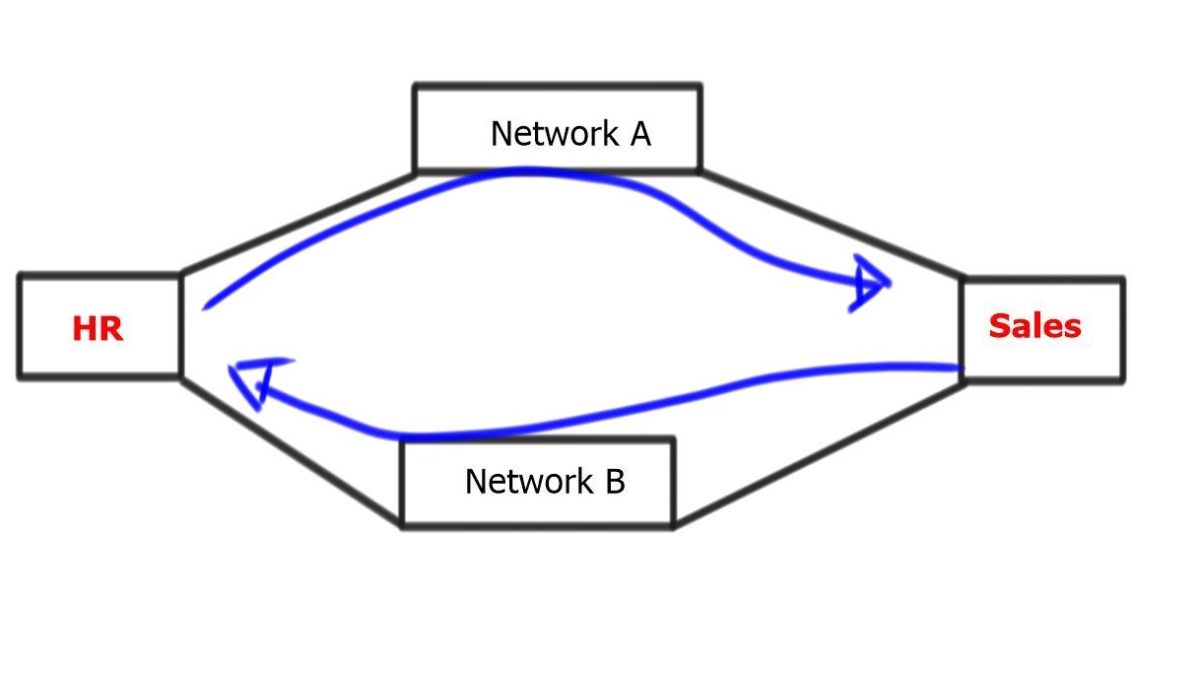
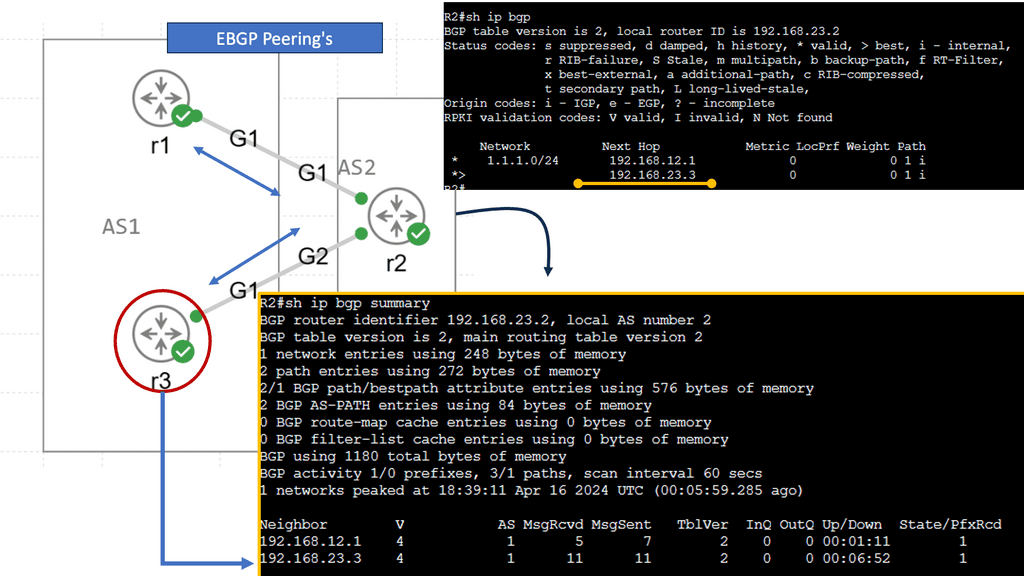
**Example: BGP Considerations**
Two business units, for example, HR, represented by a router on the left, and the Sales department, represented by a router on the right. The middle networks form a private WAN, used simply as transit. However, the business has decided that these networks should be treated differently and have different traffic paths.
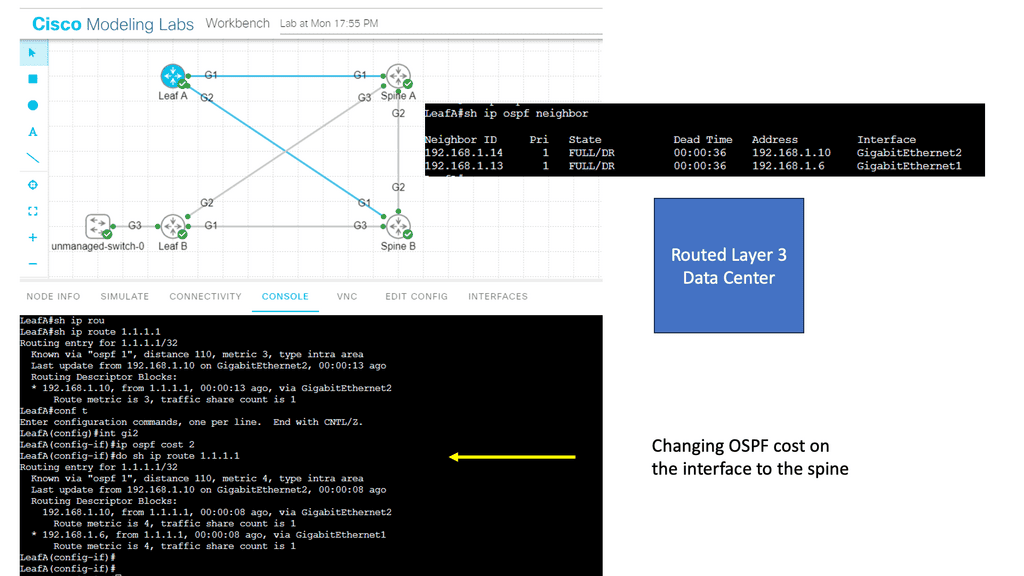
For example, HR must pass through the top section of routers, and Sales must pass through the bottom half of routers. With an Interior Gateway Protocol ( IGP ), such as OSPF, traffic engineering can be accomplished by manipulating the cost of the links to influence the traffic path.
Per-destination basis:
However, the metrics on the links must be managed on a per-destination basis. If you have to configure individual links per destination, it will become almost impossible to do with a link-state IGP. If BGP is used, this logic can be encoded using Local Preference or Multiple Exit Discriminator. Local preference is used for a single AS design, and MED is used for multiple AS. Local preference is local and does not traverse various AS.
BGP Protocol: Closing Points
At its core, BGP is a path vector protocol. This means it uses paths, or routes, to determine the best path for data to travel. BGP routers exchange routing information and select the optimal path based on various factors, such as path length, policies, and rules set by network administrators. This flexibility allows BGP to adapt to changing network conditions and maintain reliable communication across vast distances.
BGP plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and reliability of the internet. By managing the flow of data between different networks, BGP ensures that disruptions are minimized and that data can be rerouted efficiently in the event of a network failure. This resilience is essential in a world where millions of users rely on uninterrupted access to online services and information.
Despite its strengths, BGP is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns with BGP is its vulnerability to certain types of cyberattacks, such as BGP hijacking and route leaks. These attacks can disrupt network traffic and lead to data breaches, making security enhancements a top priority for network engineers. Efforts to improve BGP security include deploying technologies like RPKI (Resource Public Key Infrastructure) to verify the authenticity of routing announcements.
Summary: What is BGP Protocol in Networking
In today’s interconnected world, where the internet plays a pivotal role, understanding how data is routed is crucial. One of the fundamental protocols responsible for routing data across the internet is the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). In this blog post, we delved into the inner workings of BGP, exploring its essential components and shedding light on how it facilitates the efficient flow of information.
What is BGP?
BGP, short for Border Gateway Protocol, is an exterior gateway protocol that enables the exchange of routing information between different autonomous systems (ASes). It acts as the backbone of the internet, ensuring that data packets are efficiently forwarded across diverse networks.
Autonomous Systems (ASes)
An Autonomous System (AS) is a collection of interconnected networks operated by a single administrative entity. ASes can range from Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to large organizations managing their networks. BGP operates at the AS level, enabling ASes to exchange routing information and make informed decisions about the best paths for data transmission.
BGP Route Selection
When multiple paths exist for data to travel from one AS to another, BGP employs a sophisticated route selection process to determine the optimal path. Factors such as the path length, AS path attributes, and policies defined by AS administrators all play a role in this decision-making process.
BGP Peering and Neighbors
BGP establishes connections between routers in different ASes, forming peering relationships. These peering relationships define the rules and agreements for exchanging routing information. BGP peers, also known as neighbors, communicate updates about network reachability and ensure that routing tables are synchronized.
BGP Updates and Routing Tables
BGP updates provide crucial information about network reachability changes and modifications in routing paths. When a BGP router receives an update, it processes the data and updates its routing table accordingly. These updates are crucial for maintaining an accurate and up-to-date view of the internet’s routing topology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) plays a vital role in the functioning of the Internet. Through its intricate mechanisms, BGP enables the efficient exchange of routing information between autonomous systems (ASes), ensuring that data packets reach their destinations in a timely and reliable manner. Understanding the fundamentals of BGP empowers us to appreciate the complexity behind internet routing and the robustness of the global network we rely on every day.