SSL Security
In today's digital age, ensuring online security has become paramount. One crucial aspect of protecting sensitive information is SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encryption. In this blog post, we will explore what SSL is, how it works, and its significance in safeguarding online transactions and data.
SSL, or Secure Sockets Layer, is a standard security protocol that establishes encrypted links between a web server and a browser. It ensures that all data transmitted between these two points remains private and integral. By employing a combination of encryption algorithms and digital certificates, SSL provides a secure channel for information exchange.
SSL plays a vital role in maintaining online security in several ways. Firstly, it encrypts sensitive data, such as credit card details, login credentials, and personal information. This encryption makes it extremely difficult for hackers to intercept and decipher the transmitted data. Secondly, SSL verifies the identity of websites, ensuring users can trust the authenticity of the platform they are interacting with. Lastly, SSL protects against data tampering during transmission, guaranteeing the integrity and reliability of the information.
Implementing SSL on your website offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it instills trust in your visitors, as they see the padlock icon or the HTTPS prefix in their browser's address bar, indicating a secure connection. This trust can lead to increased user engagement, longer browsing sessions, and higher conversion rates. Additionally, SSL is crucial for e-commerce websites, as it enables secure online transactions, protecting both the customer's financial information and the business's reputation.
There are different types of SSL certificates available, each catering to specific needs. These include Domain Validated (DV) certificates, Organization Validated (OV) certificates, and Extended Validation (EV) certificates. DV certificates are suitable for personal websites and blogs, while OV certificates are recommended for small to medium-sized businesses. EV certificates offer the highest level of validation and are commonly used by large corporations and financial institutions.
SSL security is an indispensable aspect of the online world. It not only protects sensitive data but also builds trust among users and enhances the overall security of websites. By implementing SSL encryption and obtaining the appropriate SSL certificate, businesses and individuals can ensure a safer online experience for their users and themselves.
Matt Conran
Highlights: SSL Security
Understanding SSL Security
**What is SSL Security?**
SSL, or Secure Socket Layer, is a standard security protocol that establishes encrypted links between a web server and a browser. This ensures that all data passed between them remains private and integral. SSL is the backbone of secure internet transactions, providing privacy, authentication, and data integrity. When you see a padlock icon in your browser’s address bar, it signifies that the website is SSL-secured, giving users peace of mind that their data is protected from prying eyes.
**The Importance of SSL Certificates**
An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a website’s identity and enables an encrypted connection. Businesses and website owners must prioritize obtaining an SSL certificate to protect their users’ data and build trust. Not only does it prevent hackers from intercepting sensitive information such as credit card details and login credentials, but it also enhances your website’s reputation. In fact, search engines like Google give preference to SSL-secured sites, potentially boosting your site’s ranking in search results.
1: – ) SSL, which stands for Secure Sockets Layer, is a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication over the Internet. It establishes an encrypted link between a web server and a user’s browser, ensuring that all data transmitted remains private and confidential.
2: – ) SSL certificates, websites can protect sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card details, and personal data from falling into the wrong hands.
3: – ) SSL certificates play a pivotal role in the implementation of SSL security. These certificates are issued by trusted third-party certificate authorities (CAs) and are digital website passports.
4: – ) When a user visits an SSL-enabled website, their browser checks the validity and authenticity of the SSL certificate, establishing a secure connection if everything checks out.
How SSL Encryption Works
– SSL encryption involves a complex process that ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. When users access an SSL-enabled website, their browser initiates a handshake process with the web server.
– This handshake involves the exchange of encryption keys, establishing a secure connection. Once the connection is established, all data transmitted between the user’s browser and the web server is encrypted and can only be decrypted by the intended recipient.
– The implementation of SSL security offers numerous benefits for website owners and users alike. Firstly, it provides a secure environment for online transactions, protecting sensitive customer information and instilling trust.
– Additionally, SSL-enabled websites often experience improved rankings as search engines prioritize secure websites. Furthermore, SSL security helps prevent unauthorized access and data tampering, ensuring the integrity of data transmission.
**Benefits of SSL Security**
1. Data Protection: SSL encryption ensures the privacy and confidentiality of sensitive information transmitted over the internet, making it extremely difficult for hackers to decrypt and misuse the data.
2. Authentication: SSL certificates authenticate websites’ identities, assuring users that they interact with legitimate and trustworthy entities. This helps prevent phishing attacks and protects users from submitting personal information to malicious websites.
3. Search Engine Ranking: Search engines like Google consider SSL security as a ranking factor to promote secure web browsing. Websites with an SSL certificate enjoy a higher search engine ranking, thus driving more organic traffic and increasing credibility.
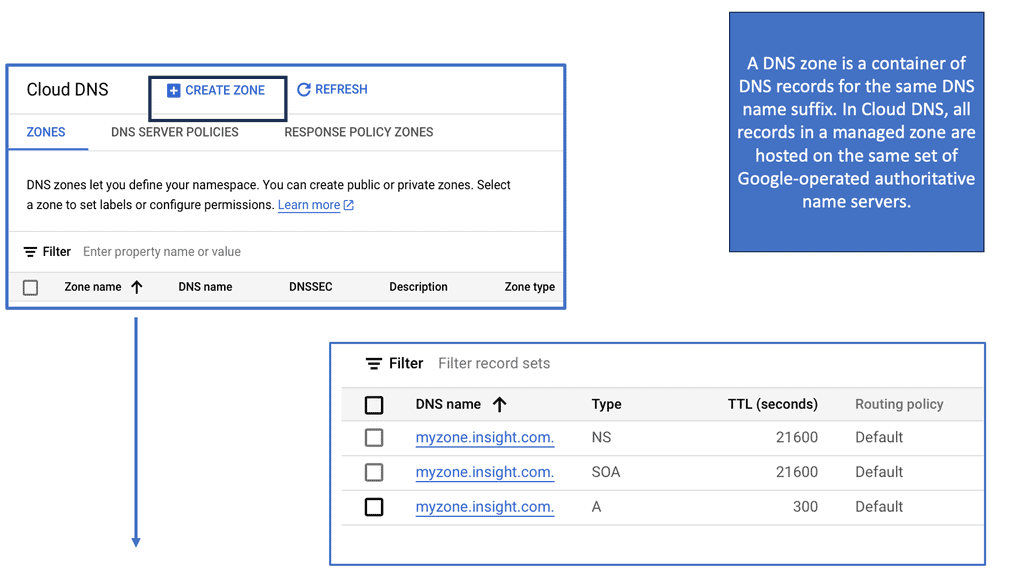
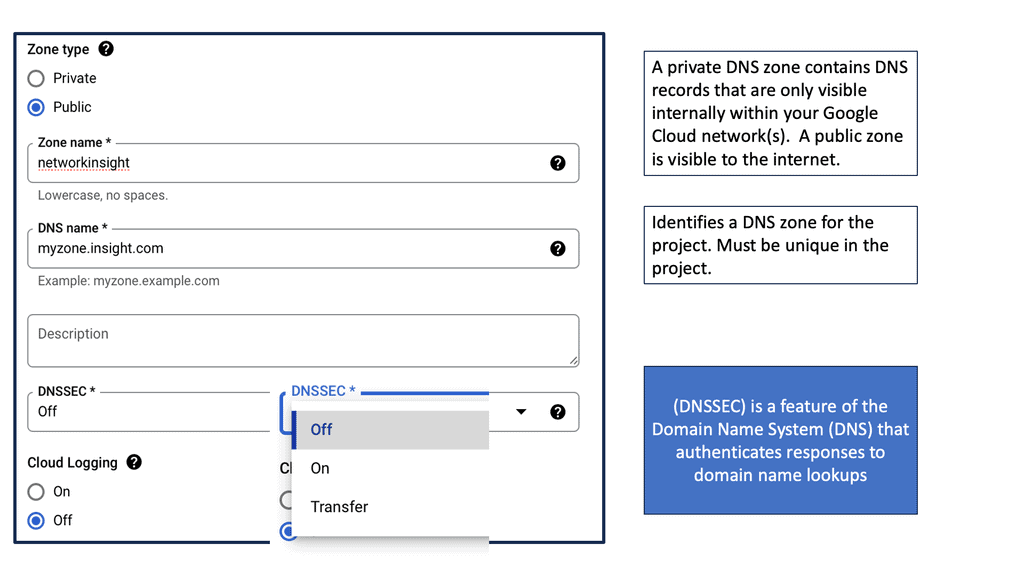
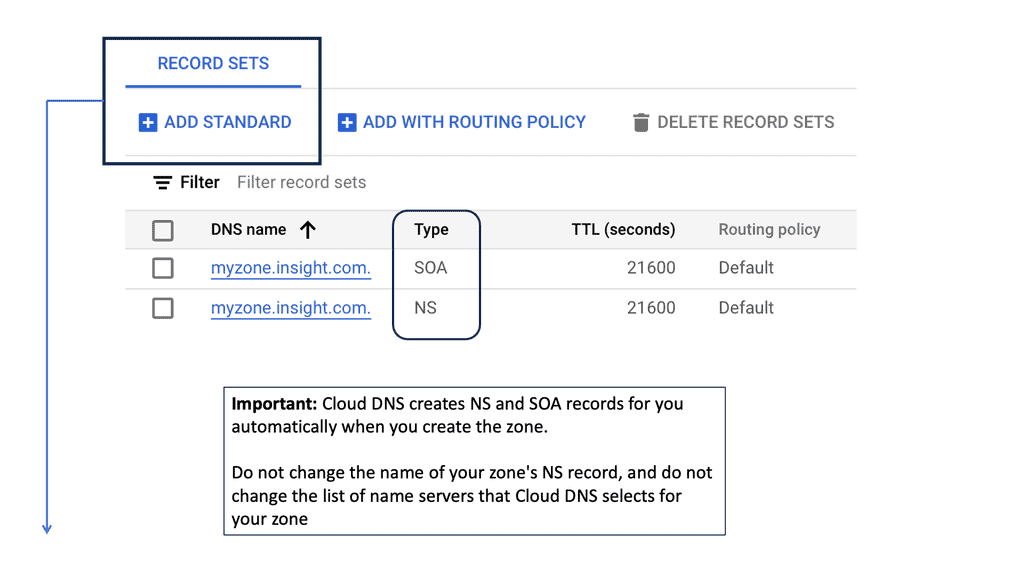
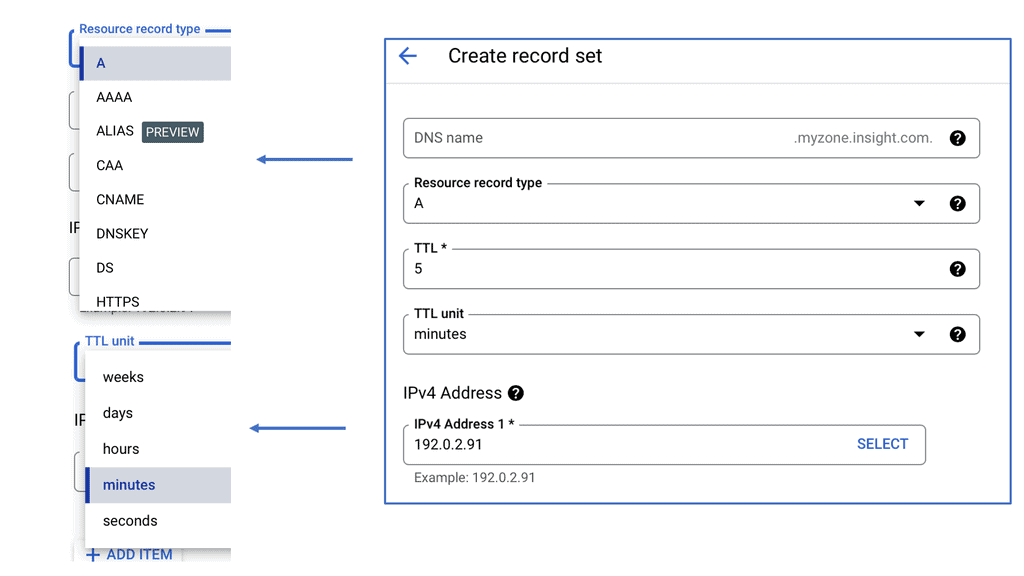
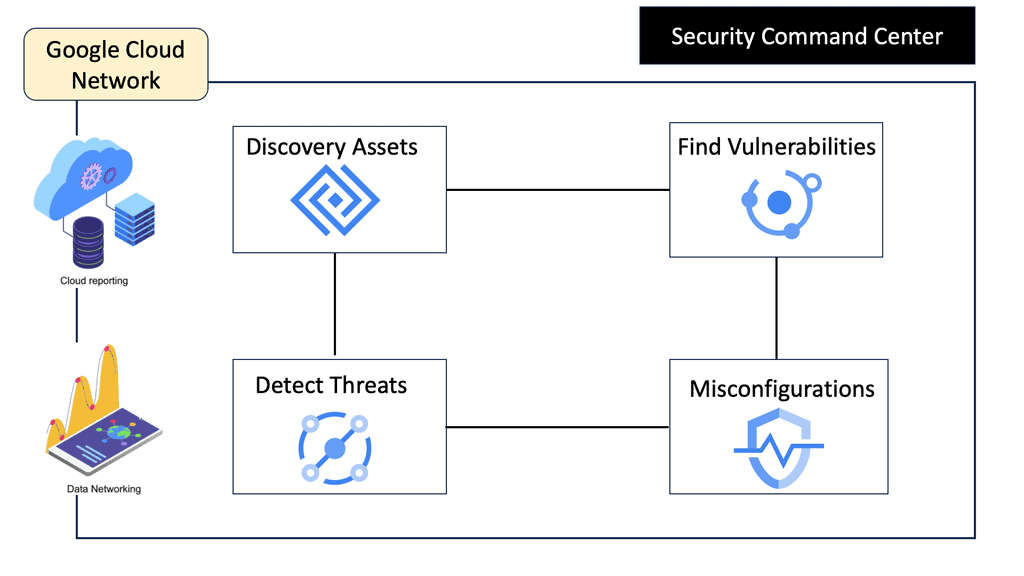
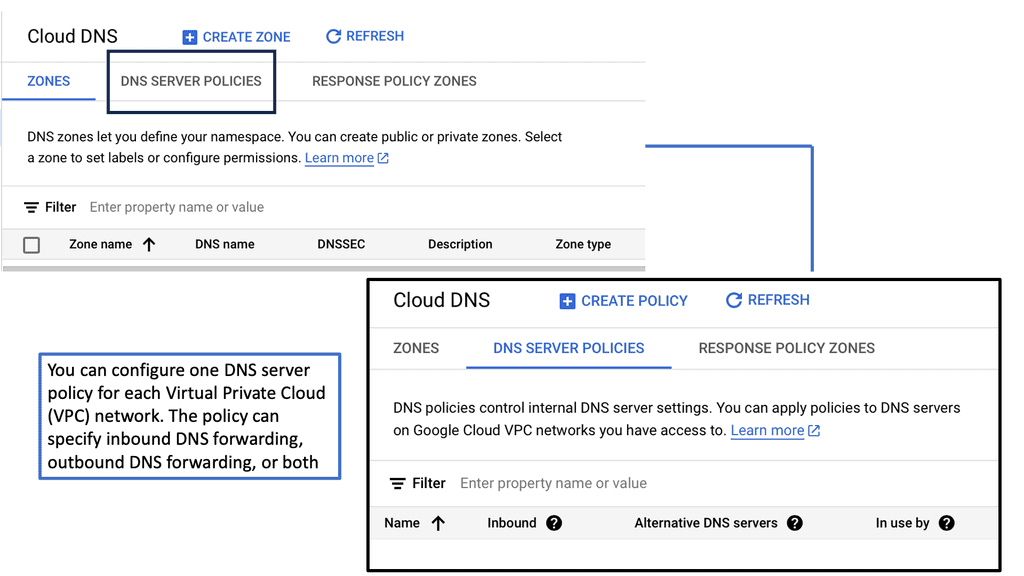
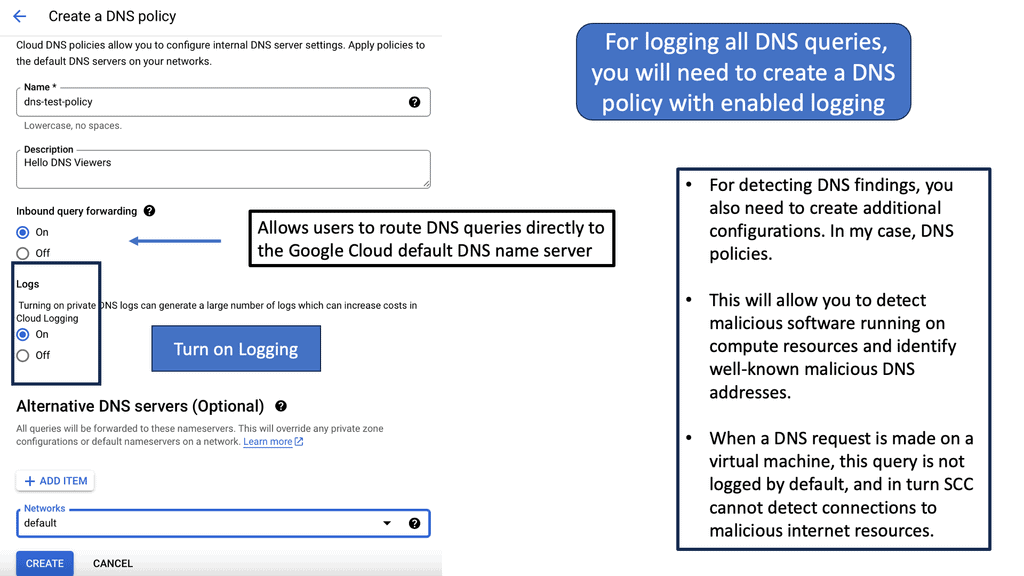
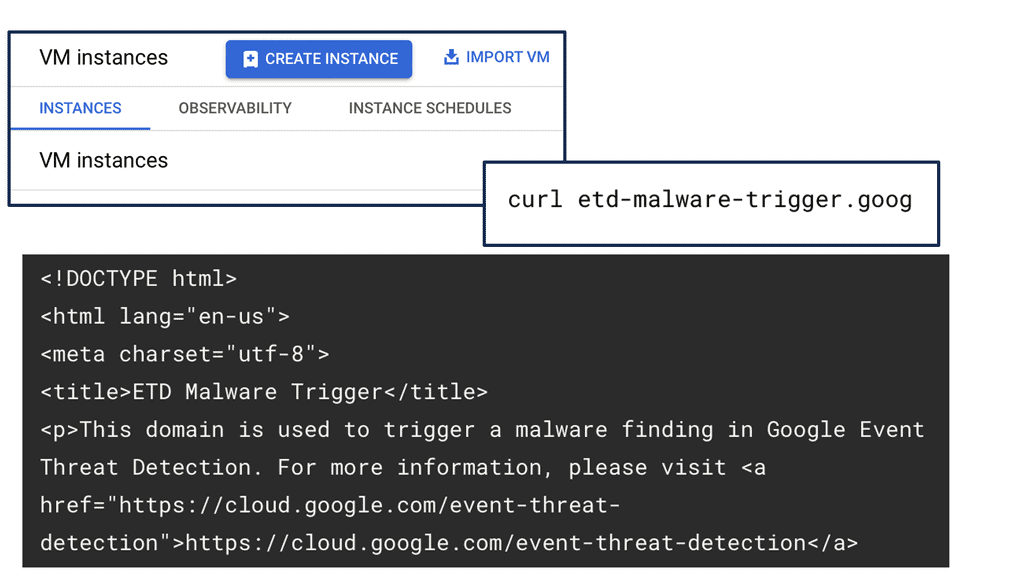
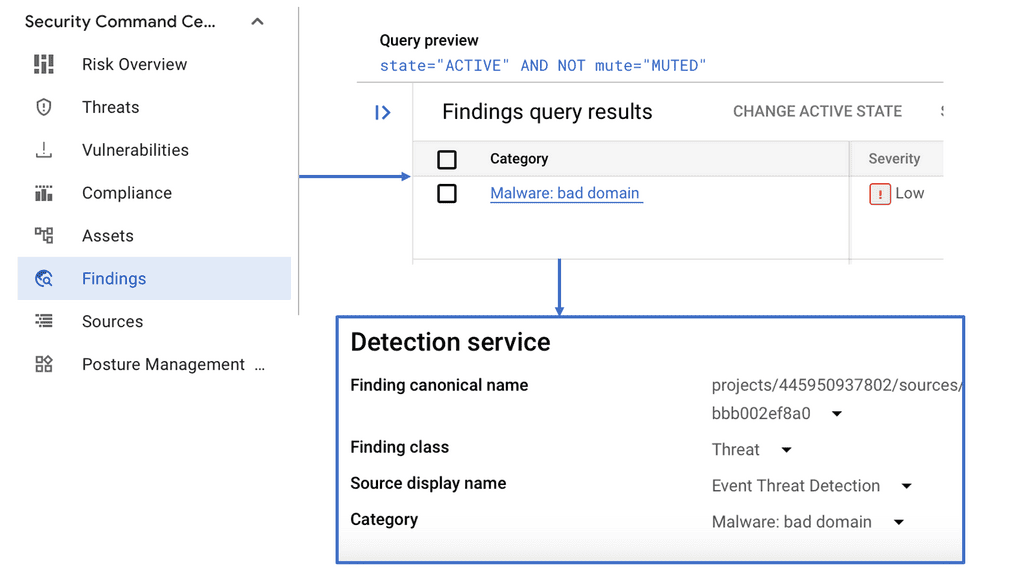
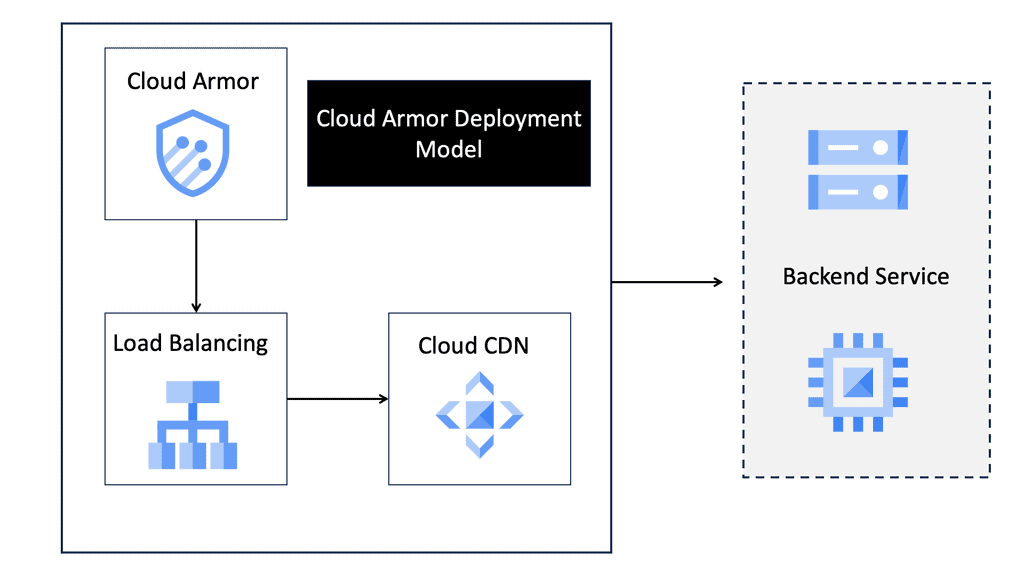
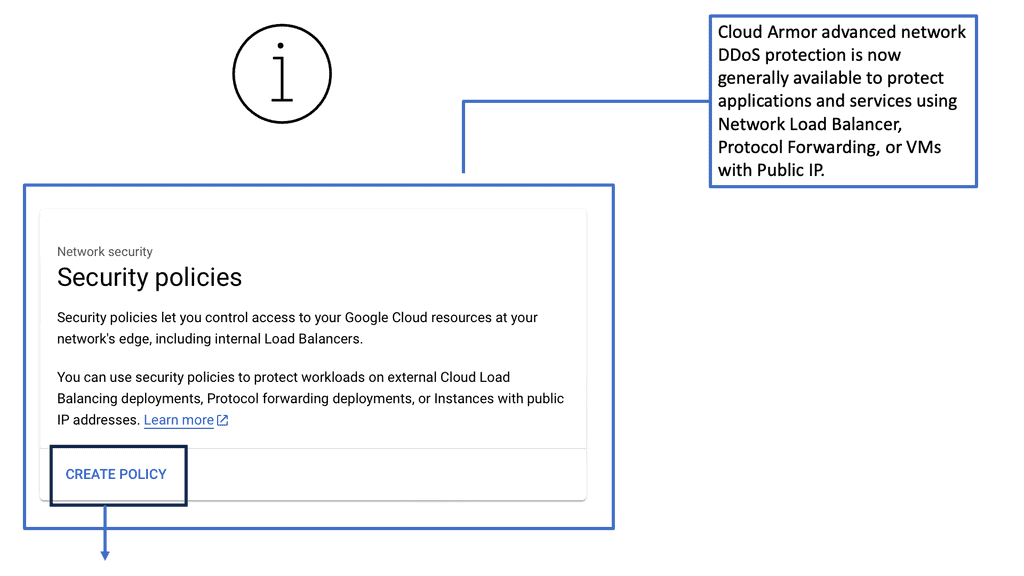
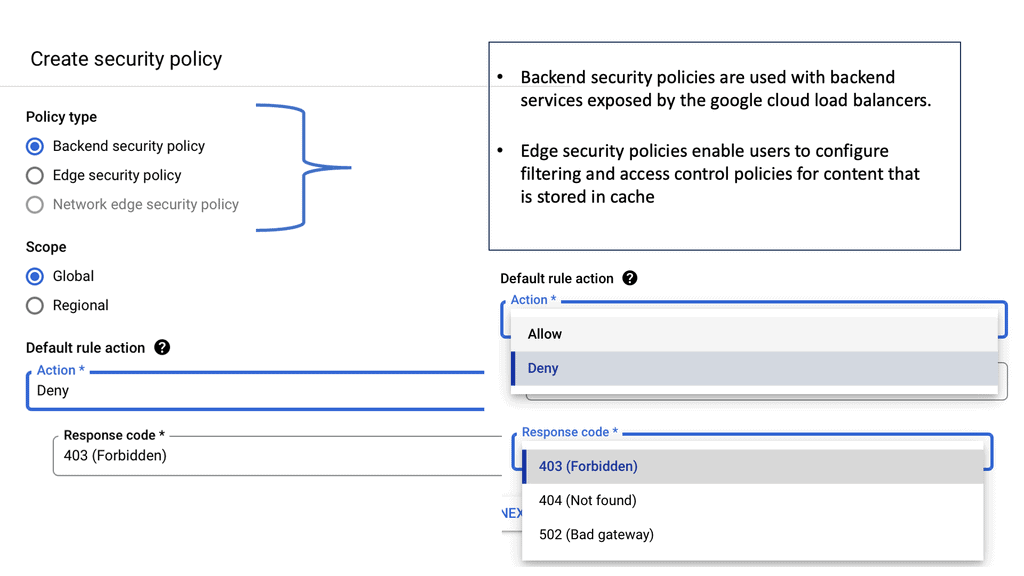
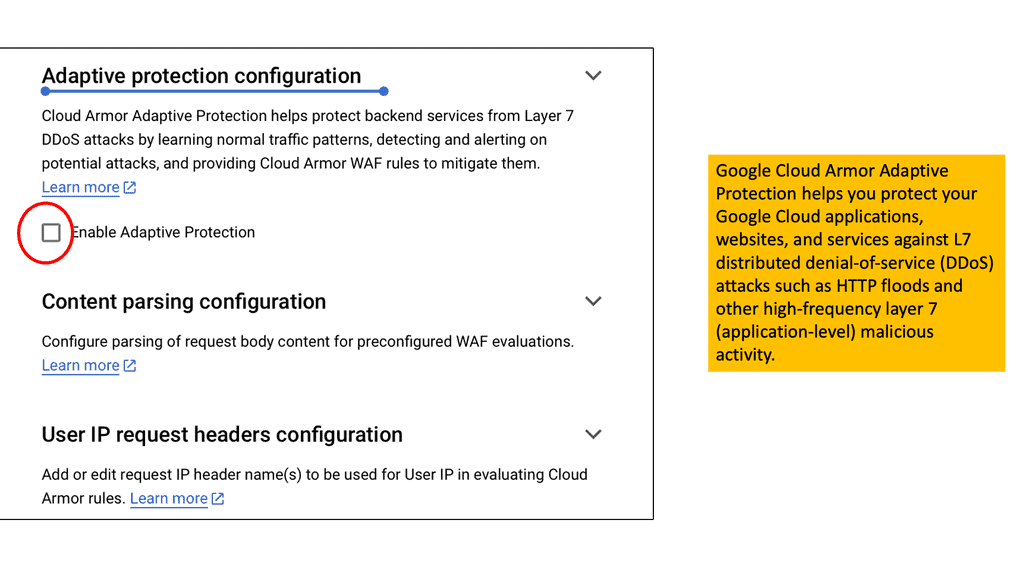
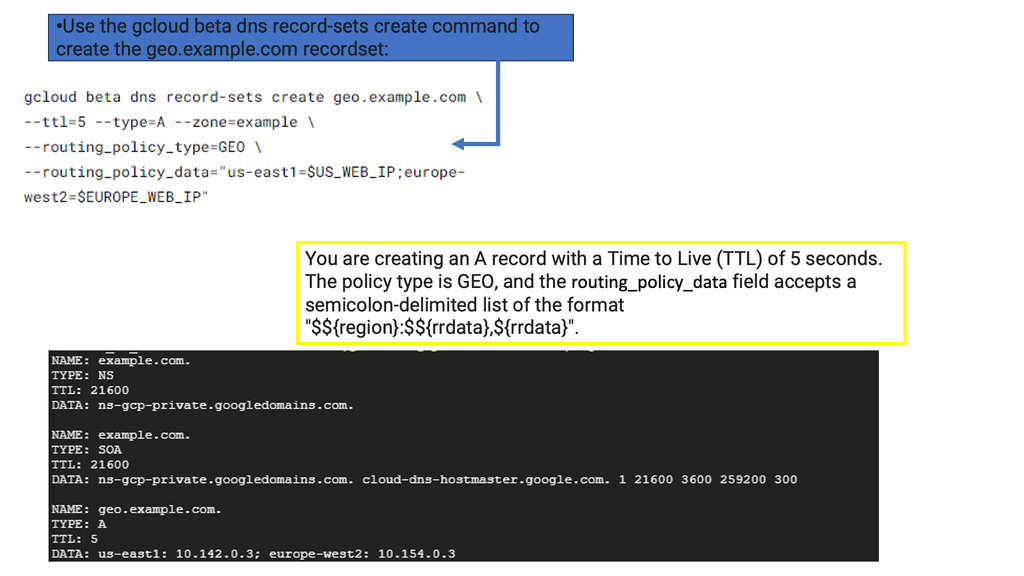
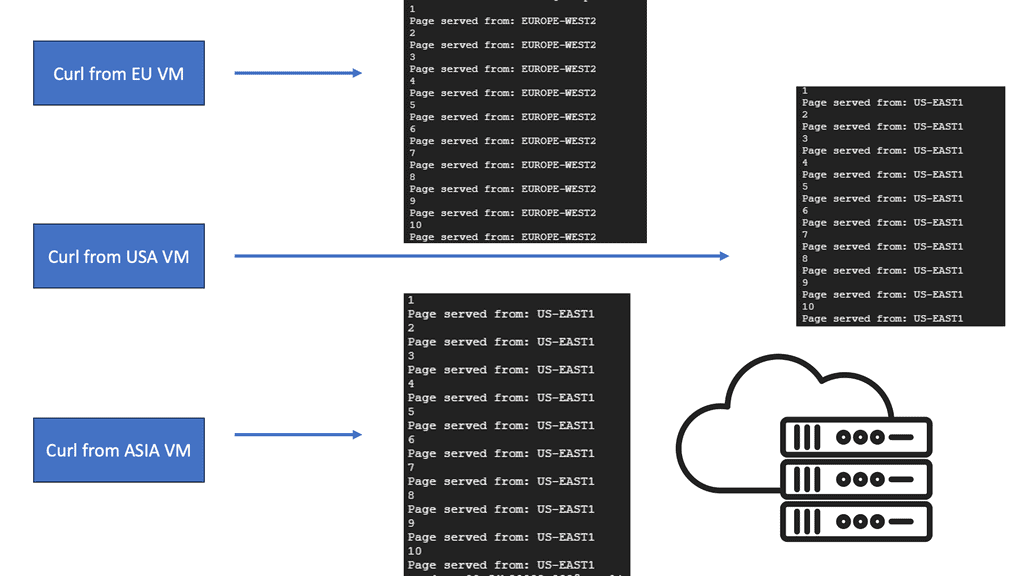
Example SSL Technology: SSL Policies
### Implementing SSL Policies on Google Cloud
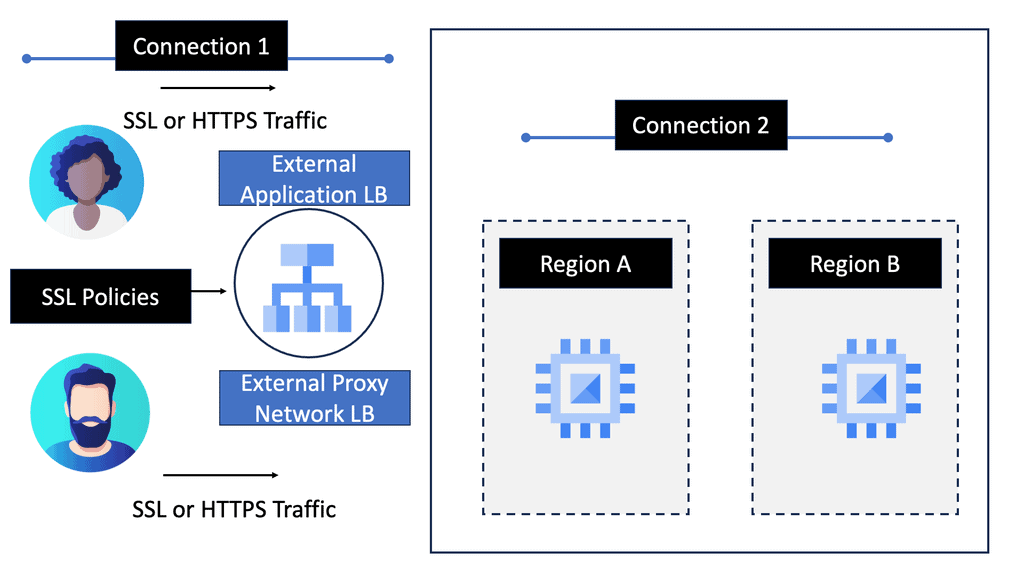
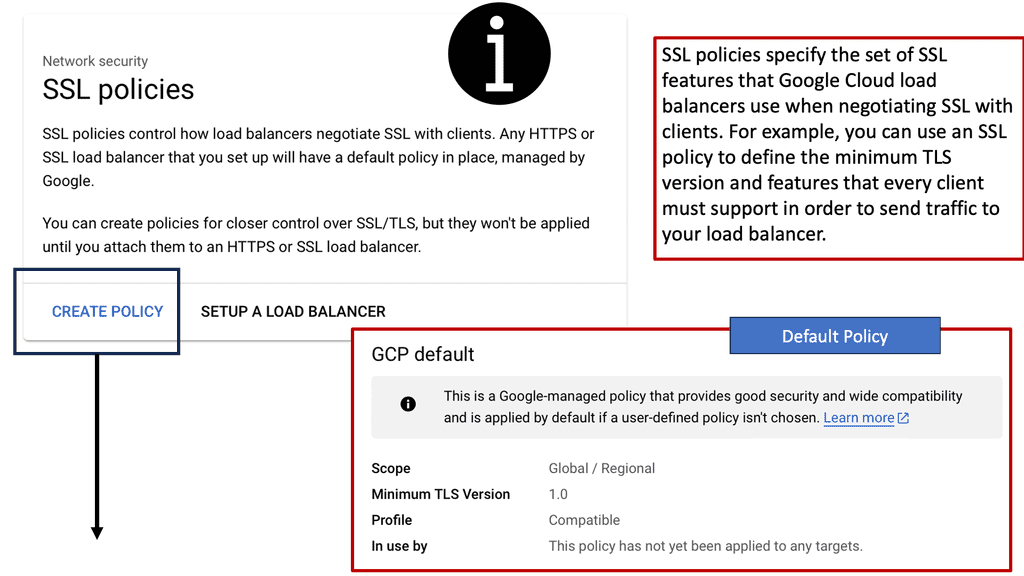
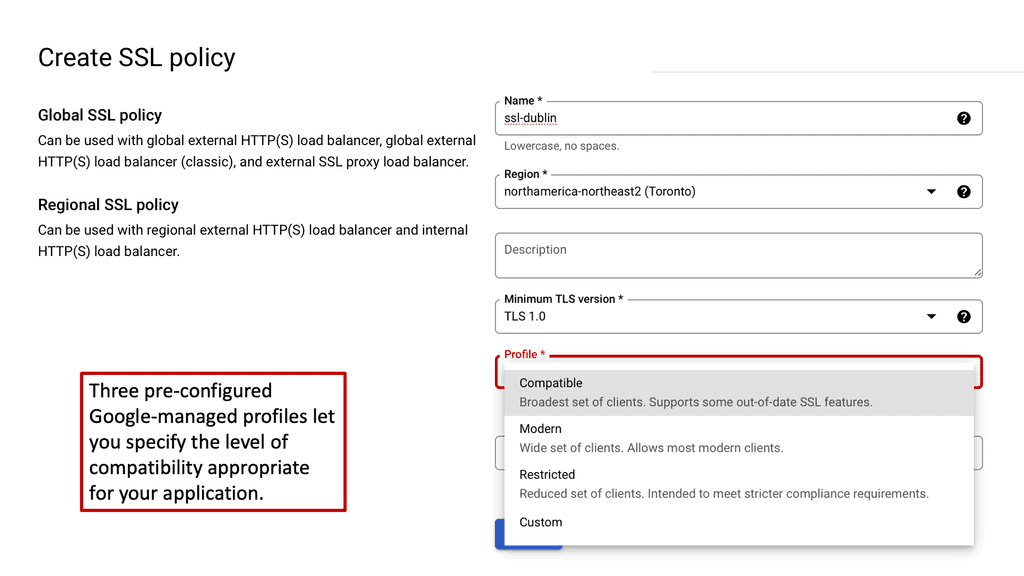
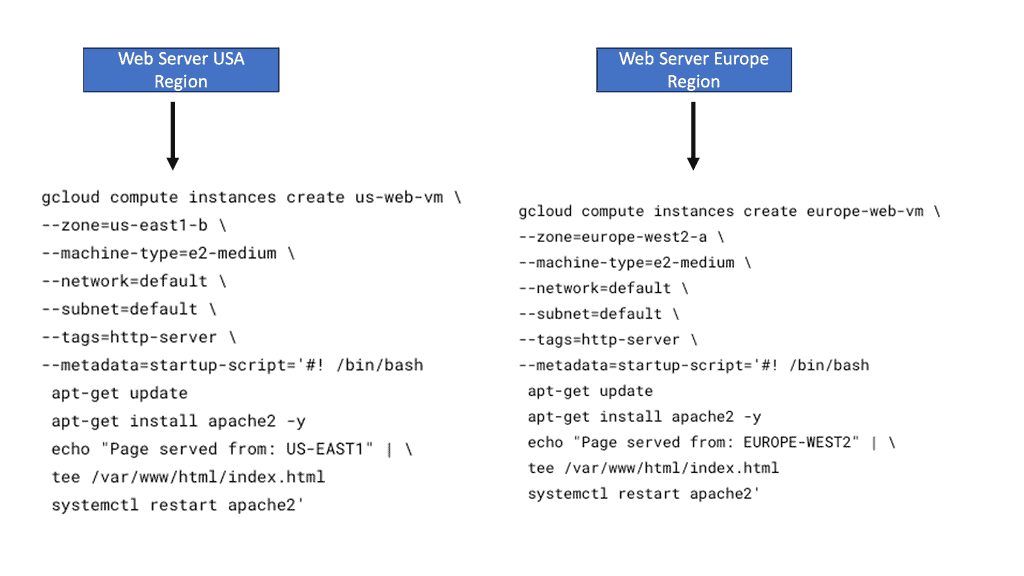
Google Cloud offers robust tools and services to implement SSL policies, ensuring secure data transmission. One of the primary tools is the Cloud Load Balancing service, which provides SSL offloading. This service allows you to manage SSL certificates, ensuring encrypted connections without burdening your servers. Additionally, Google Cloud offers the Certificate Manager, a user-friendly tool to obtain, manage, and deploy SSL certificates across your cloud infrastructure seamlessly.
### Best Practices for SSL Policies on Google Cloud
To maximize the efficacy of SSL policies on Google Cloud, consider the following best practices:
1. **Regularly Update Certificates**: Ensure that SSL certificates are up to date to maintain secure connections and avoid potential security vulnerabilities.
2. **Use Strong Encryption Algorithms**: Opt for robust encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, to safeguard data effectively.
3. **Implement Automated Certificate Management**: Utilize Google Cloud’s automated tools to manage SSL certificates, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring timely renewals.
4. **Monitor and Audit SSL Traffic**: Regularly monitor SSL traffic to detect and mitigate any unusual activities or potential threats.
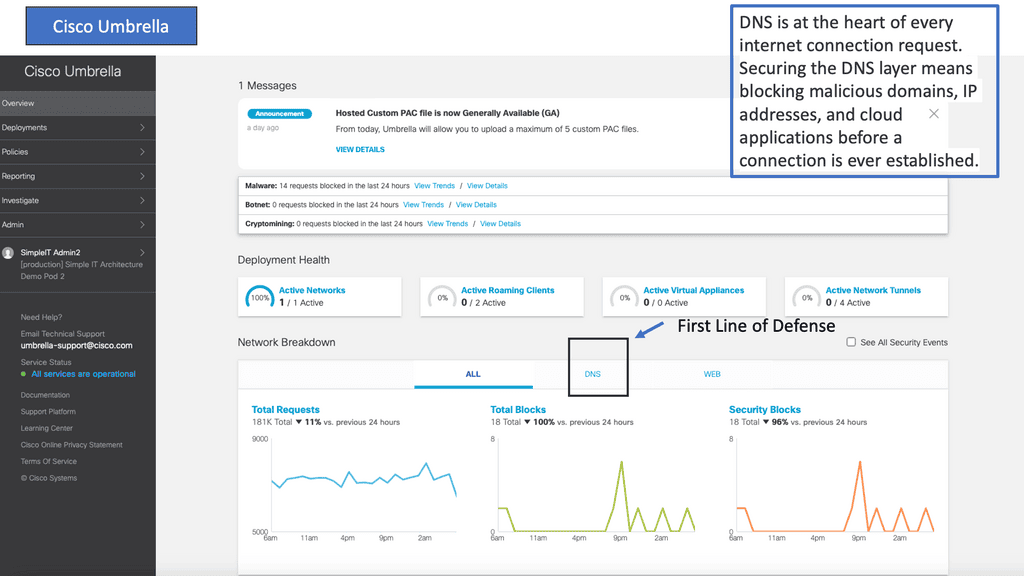
Example Product: Cisco Umbrella
#### What is Cisco Umbrella?
Cisco Umbrella is a cloud-delivered security service that provides enterprises with a first line of defense against internet threats. It uses the power of DNS (Domain Name System) to block malicious domains, IP addresses, and cloud applications before a connection is ever established. By leveraging Cisco Umbrella, businesses can ensure that their network is safeguarded against a wide range of cyber threats, including malware, phishing, and ransomware.
#### The Importance of SSL Security
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a server and a client. This technology ensures that all data passed between the web server and browsers remain private and integral. SSL security is crucial because it protects sensitive information such as credit card numbers, usernames, passwords, and other personal data. Without SSL security, data can be intercepted and accessed by malicious actors, leading to significant breaches and financial loss.
#### How Cisco Umbrella Enhances SSL Security
Cisco Umbrella plays a pivotal role in bolstering SSL security by providing several key benefits:
1. **Automated Threat Detection**: Cisco Umbrella continuously monitors web traffic, identifying and blocking suspicious activities before they can cause harm. This proactive approach ensures that threats are neutralized at the DNS layer, providing an additional layer of security.
2. **Encrypted Traffic Analysis**: With the rise of encrypted traffic, traditional security measures often fall short. Cisco Umbrella’s advanced analytics can inspect encrypted traffic, ensuring that SSL/TLS connections are secure and free from malicious content.
3. **Global Threat Intelligence**: Cisco Umbrella leverages global threat intelligence from Cisco Talos, one of the largest commercial threat intelligence teams in the world. This wealth of data ensures that Cisco Umbrella can quickly identify and respond to emerging threats, keeping SSL connections secure.
4. **User and Application Visibility**: Cisco Umbrella provides comprehensive visibility into user and application activities. This insight helps in identifying risky behaviors and potential vulnerabilities, allowing IT teams to take corrective actions promptly.
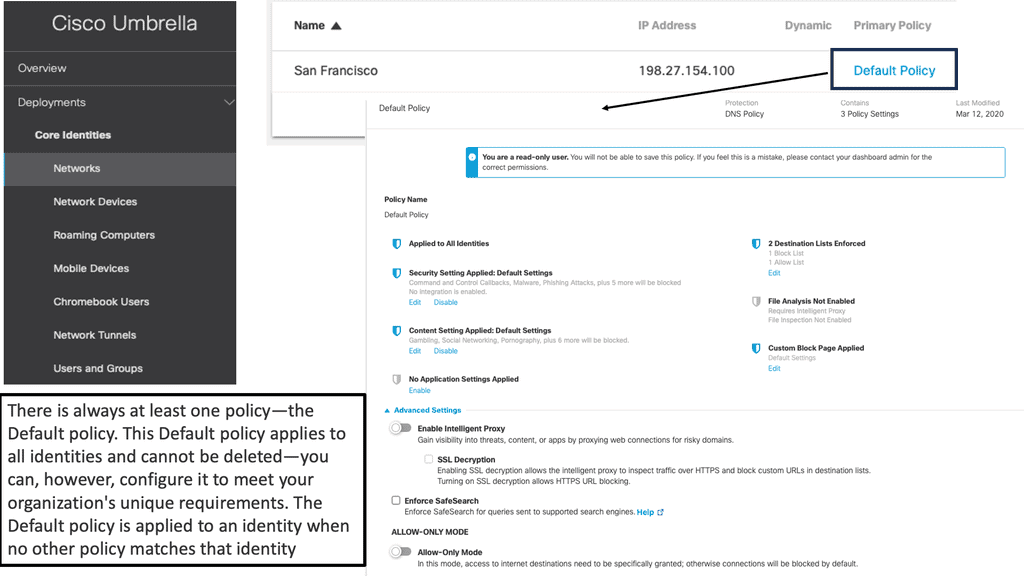
#### Implementation of Cisco Umbrella
Implementing Cisco Umbrella is straightforward and can be integrated with existing security frameworks. It involves a simple change in the DNS settings, pointing them to Cisco Umbrella’s servers. Once configured, Cisco Umbrella starts offering protection immediately, with minimal impact on network performance. Businesses can also customize policies to align with their specific security needs, ensuring a tailored security posture.
Motivation for SSL
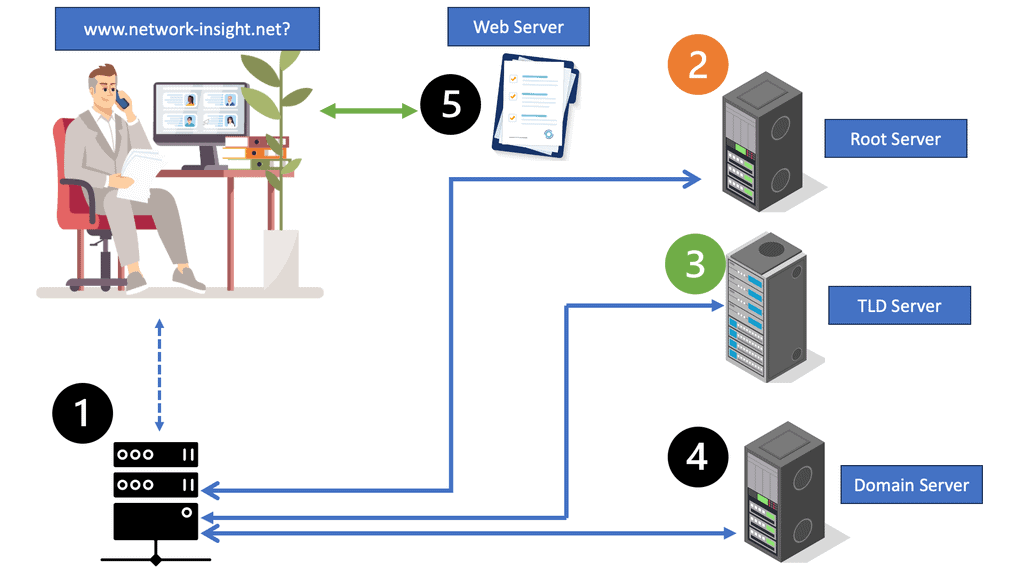
SSL was also primarily motivated by HTTP. It was initially designed as an add-on to HTTP, called HTTPS, but it is not a standalone protocol. Additionally, HTTP has improved from a security perspective. With HTTP, data traveling over the network is encrypted using SSL and TLS protocols. As a result, man-in-the-middle attacks are complicated to execute.
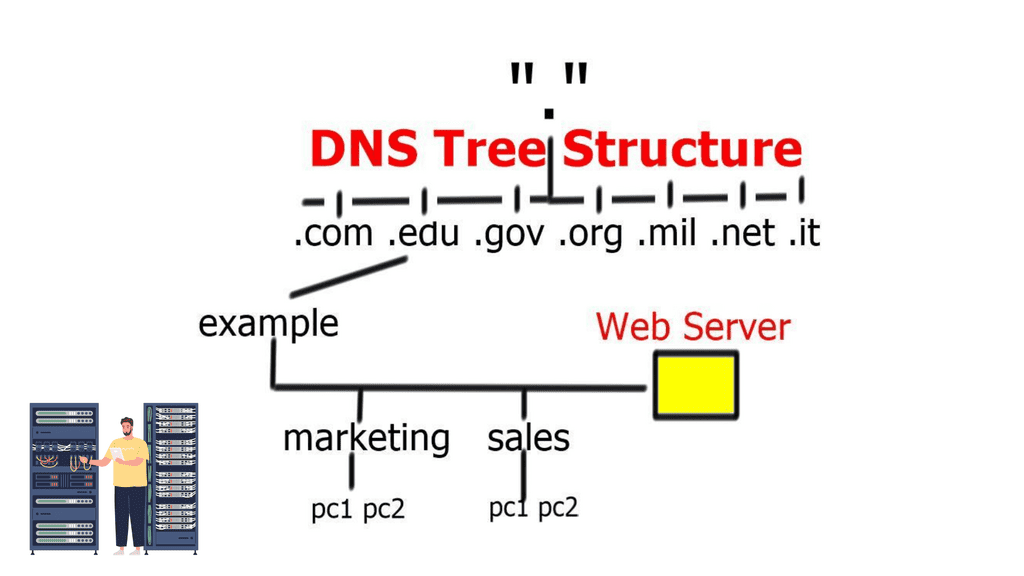
The Role of HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application-based protocol used for communications over the Internet. It is the foundation for Internet communication. Of course, as time has passed, there are new ways to communicate over the Internet. Due to its connectionless and stateless features, HTTP has numerous security limitations at the application layer and exposure to various TCP control plane attacks.
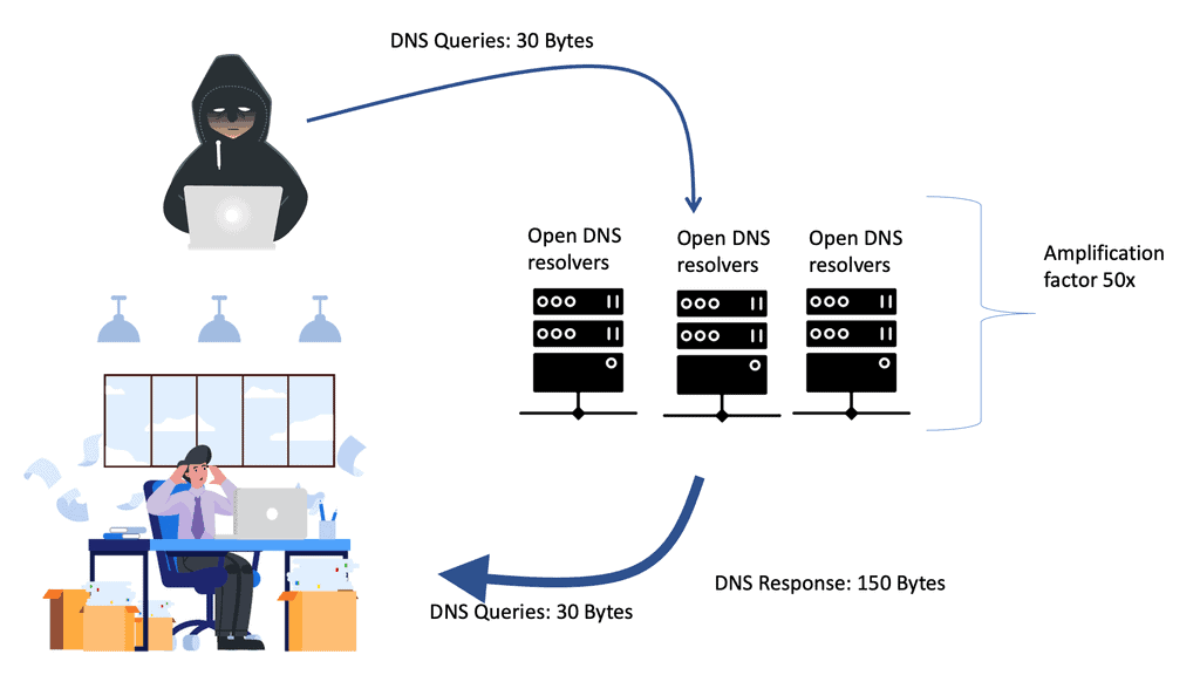
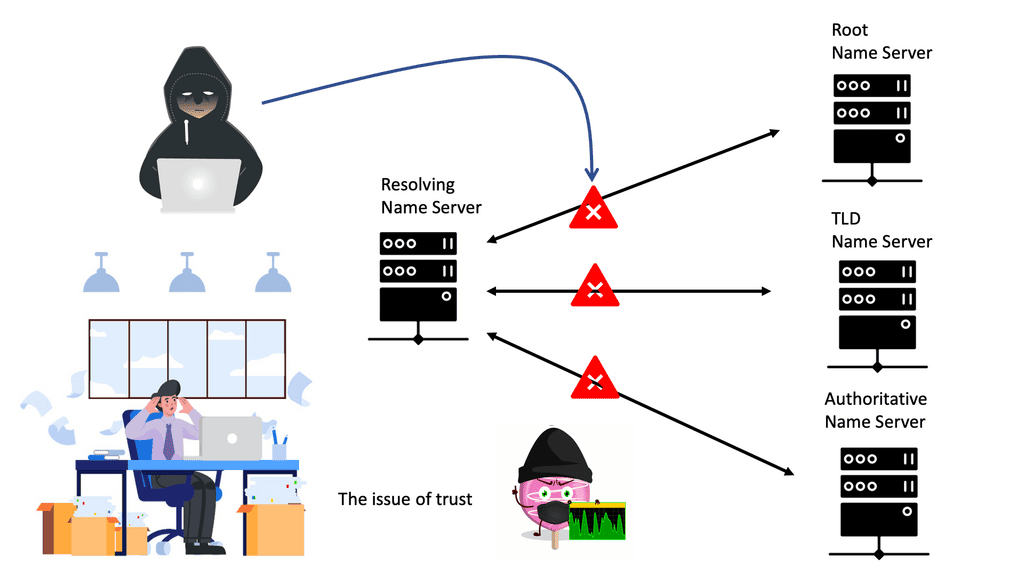
Challenges: Attack Variations
It is vulnerable to many attacks, including file and name-based attacks, DNS Spoofing, location headers and spoofing, SSL decryption attacks, and HTTP proxy man-in-the-middle attacks. In addition, it carries crucial personal information, such as usernames/passwords, email addresses, and potentially encryption keys, making it inherently open to personal information leakage. All of which are driving you to SSL security.
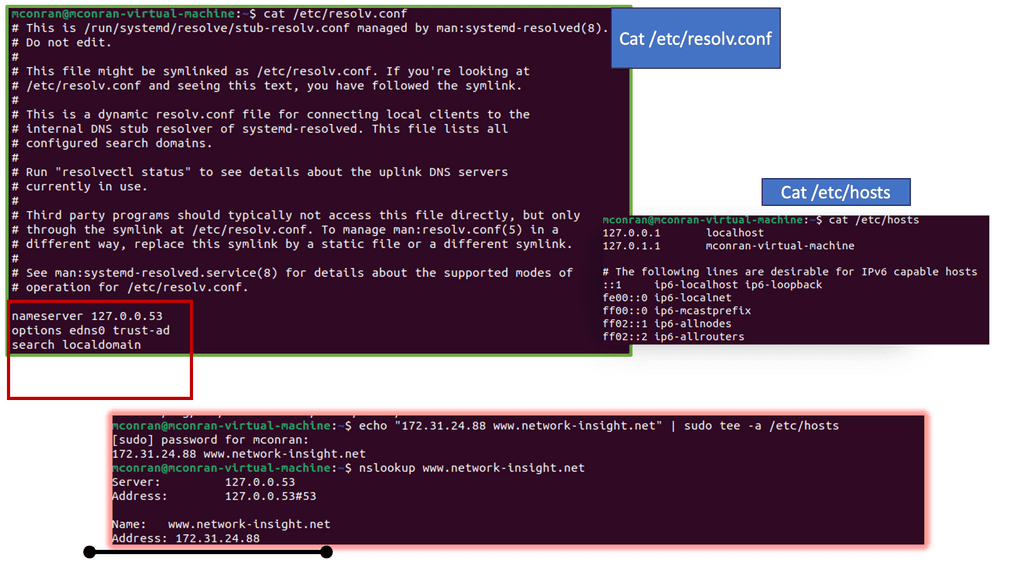
For additional pre-information, you may find the following helpful information:
SSL Security
The Importance of SSL Security
– All our applications require security, and cryptography is one of the primary tools used to provide that security. The primary goals of cryptography, data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation (accountability) can be used to prevent multiple types of network-based attacks. These attacks may include eavesdropping, IP spoofing, connection hijacking, and tampering.
– We have an open-source version of SSL, a cryptographic library known as OpenSSL. It implements the industry’s best-regarded algorithms, including encryption algorithms such as 3DES (“Triple DES”), AES, and RSA, as well as message digest algorithms and message authentication codes.
– SSL security is essential for maintaining trust and confidence in online transactions and communications. With increasing cyber threats, SSL encryption helps protect sensitive information such as credit card details, login credentials, and personal data from falling into the wrong hands. By encrypting data, SSL security ensures that the information remains unreadable and unusable to unauthorized individuals even if intercepted.
How SSL Security Works:
When users access a website secured with SSL, their browser initiates a secure connection with the web server. The server sends its SSL certificate, containing its public key, to the browser. The browser then verifies the authenticity of the SSL certificate and uses the server’s public key to encrypt data before sending it back to the server. Only the server, possessing the corresponding private key, can decrypt the encrypted data and process it securely.
SSL Operations
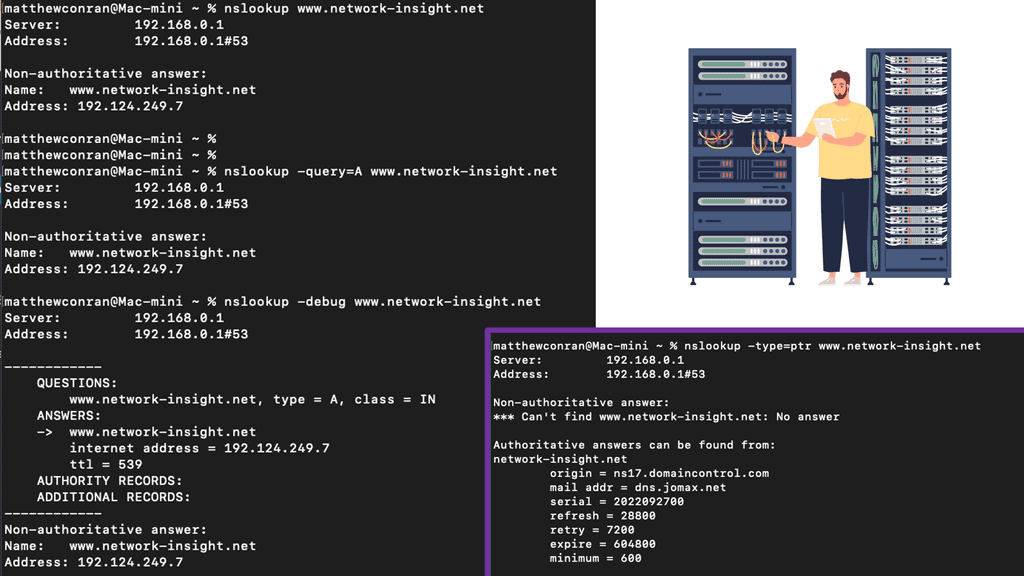
A: – SSL was introduced to provide security for client-to-server communications by a) encrypting the data transfer and b) ensuring the authenticity of the connection. Encryption means that a 3rd party cannot read the data.
B: – They are essential, hiding what is sent from one computer to another by changing the content. Codes encrypt traffic, and SSL puts a barrier around the data. Authenticity means that you can trust the other end of the connection.
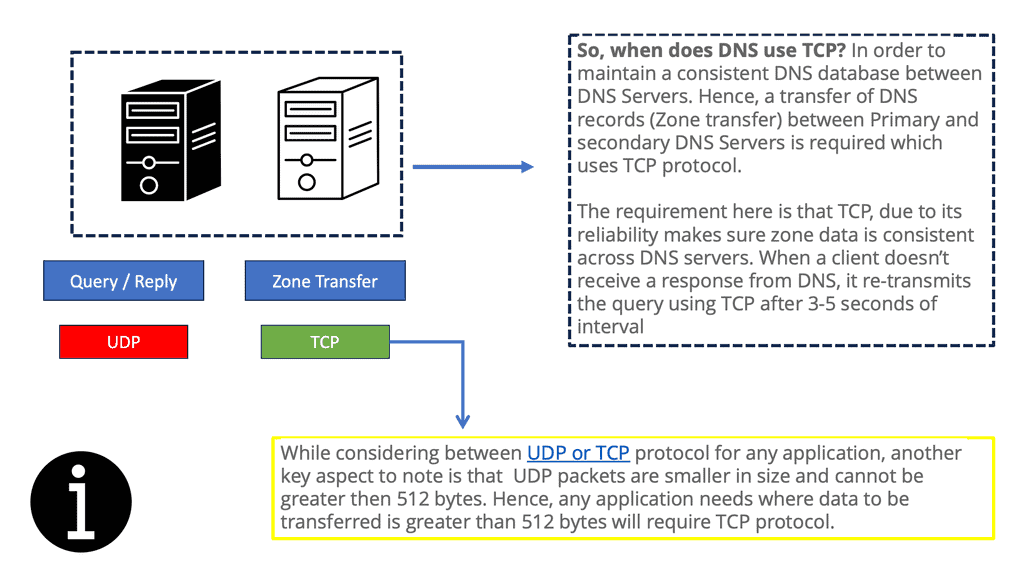
SSL uses TCP for transport:
SSL uses TCP as the transport protocol, enabling security services for other application-based protocols that ride on TCP, including FTP and SMTP. Some well-known TCP ports for SSL are 443 HTTPS, 636 LDAP, 989 FTPS-DATA, 990 FTPS, 992 TELNET, 993 IMAPS, 994 IRCS, 995 POP3, and 5061 SIPS. It relies on cryptography; shared keys encrypt and decrypt the data. SSL certificates, assigned by certificate authorities (CA), issue public keys, creating trusted 3rd parties on the Internet.
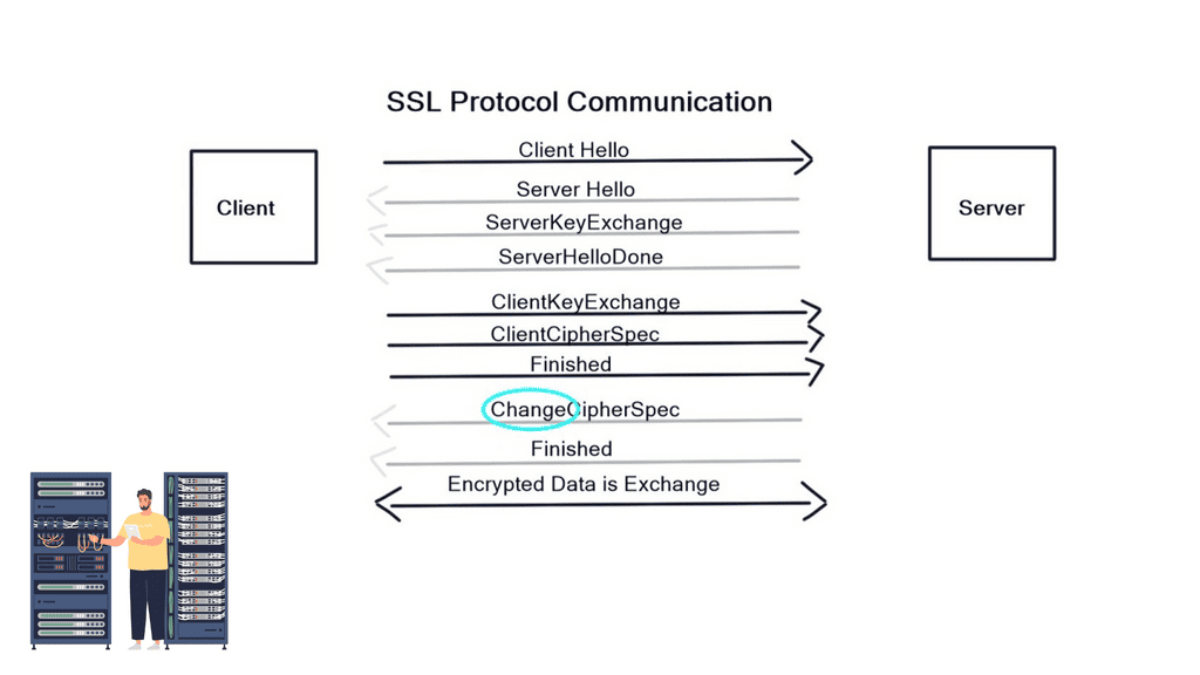
Firstly, the client and server agree on “how” to encrypt data by sending HELLO messages containing Key Exchange Message, Cipher, version of SSL, and the Hash. The server replies with a HELLO message with the chosen parameters (The client offers what it can do, and the server replies with what it will do). In the next stage, the server sends a certificate to the client containing its public key.
Next, a client key exchange message is used, and once this message is sent, both computers calculate a master secret code, which is used to encrypt communications. The computer then changes to the Cipher Spec agreed in the previous HELLO messages. Encryption then starts.
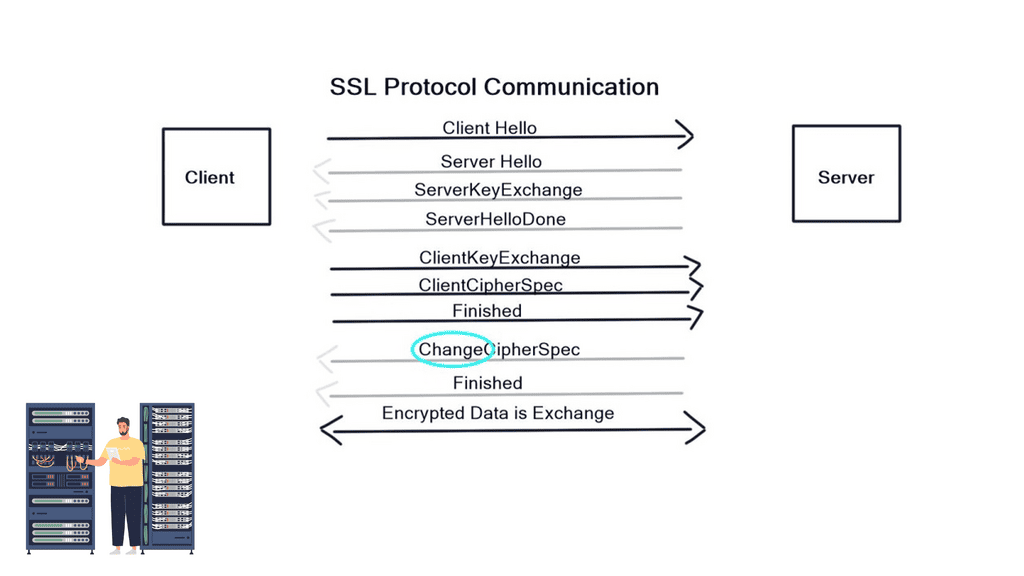
Certificates are used for identification and are signed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Firstly, you need to apply for a certificate via a CA (Similar to the analogy of a passport application). Then, the CA creates the certificate and signs it. The signature is created by condensing all the company details into a number through a Hash function. The CA encrypts with the private keys, so anyone holding the public key can encrypt. For example, the certificate is installed on a web server at the customer’s site and used in the handshake process.
1: SSL security and forward secrecy
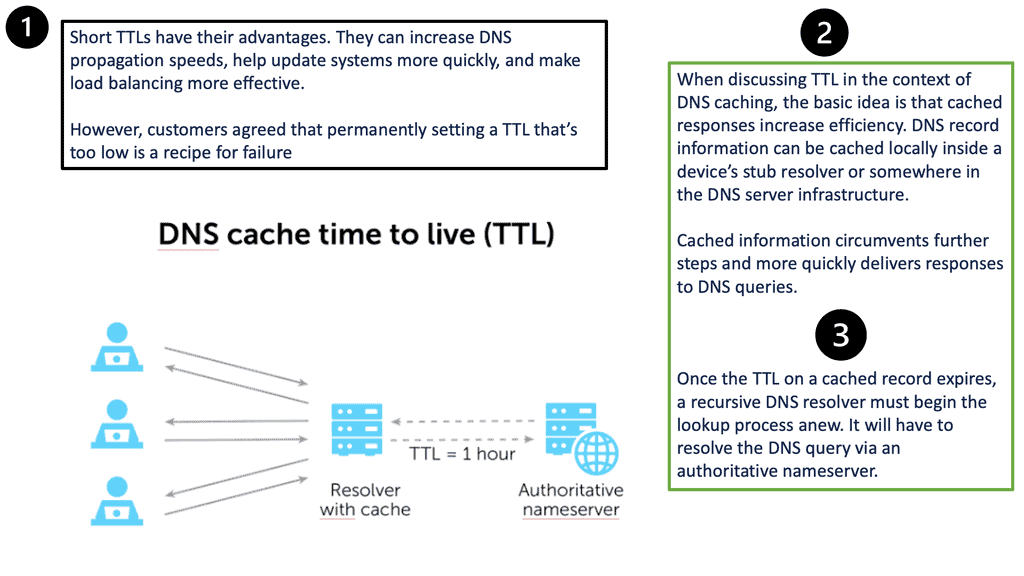
Most sites supporting HTTPS operate in a non-forward secret mode, exposing themselves to retrospective decryption. Forward secrecy is a feature that prevents the compromise of a long-term secret key. It allows today’s information to be kept secret even if the private key gets compromised in the future. For example, if someone tries to sniff client-to-server communications but can’t, as the server uses a 128-bit key, they can record the entire transmission for the next five years.
When the server is decommissioned, they attempt to get the key and decrypt the traffic. Forward secrecy solves this problem by double-encrypting every connection. So even if someone gets the key in the future, they can’t decrypt the traffic. Google supports forward secrecy on many of its HTTPS websites, such as Gmail, Google Docs, and Google+. Around the world? The Internet uses forward secrecy.
2: Strict transport security (HSTS)
In 2009, a computer security researcher named Moxie Marlinspike introduced the concept of SSL stripping. He released a tool called “sslstrip,” which could prevent a browser from upgrading to SSL in a way that would go unnoticed by the end user. Strict Transport Security is a security feature that lets a website inform browsers it should be communicating with HTTPS and not HTTP to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. Although the deployment of HSTS has been slow, around 1% of the Internet uses it.
3: POODLE Attack – Flaw in SSLv3
In October 2014, Google’s security team uncovered the POODLE attack (Padding Oracle On Downgraded Legacy Encryption) and released a paper called “POODLE bites.” They revealed a flaw in SSLv3 that allowed an attacker to decrypt HTTP cookies and hijack your browser session—essentially another man-in-the-middle attack.
Many browsers will revert to SSL 3.0 when a TLS connection is unavailable, and an attacker may force a server to default to SSL v3.0 to exploit the vulnerability. One way to overcome this is to permanently disable SSL ver 3.0 on the client and server. However, there are variants of POODLE for TLSv1 and TLS v2. Before the poodle attack, a large proportion of the Internet supported SSL Ver 3.0, but this has considerably dropped in response to the attack.
4: SSL Decryption Attack
Assaults on trust through SSL-encrypted traffic are common and growing in frequency and sophistication. The low-risk, high-reward nature of SSL/TLS vulnerability ensures that these trends will continue, leading to various SSL decryption attacks.
An SSL decryption attack is a DoS attack that targets the SSL handshake protocol either by sending worthless data to the SSL server, which will result in connection issues for legitimate users, or by abusing the SSL handshake protocol itself.
5: 2048-bit keys SSL certificate
Strong recommendations exist for using 2048-bit certificates. The NIST and other companies feel the encryption of 1048-bit keys is insufficient. Computers are getting faster, and 1048-bit keys will not protect you for the lifetime of the secret. On the other hand, 2048-bit certificates will give you about 30 years of security.
The impact of a larger key length is a reduction in performance. 2048-bit keys will reduce transactions per second (TPS) by five times. There are options to configure a “Session Reuse” feature that lets you reuse the session ID negotiated asymmetrically. Session Reuse is a mechanism that allows you to do fewer asymmetric key exchanges.
SSL to the server can cripple the application. Generic hardware is not optimized for this type of handling, and 2048-bit keys don’t work well on generic software and processors. Consolidating the SSL with an appliance that handles the SSL load is better for TPS and performance. Additionally, the driver for SSL offload on optimized hardware is more compelling with 2048-bit keys.
SSL Security – Closing Points
SSL works by using encryption algorithms to scramble data in transit, preventing hackers from reading it as it is sent over the connection. When a browser attempts to connect to a secured website, the server and browser engage in an “SSL handshake.” During this process, they establish a secure connection by generating unique session keys. This ensures that the information exchanged remains confidential and is only accessible to the intended parties.
Having an SSL certificate is crucial for any website, especially if it involves handling sensitive information like credit card details or personal data. SSL certificates serve multiple purposes: they authenticate the identity of the website, ensure data integrity, and provide encryption. Websites with SSL certificates are marked with a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, which builds trust and credibility with users. Moreover, search engines like Google favor SSL-secured websites, giving them a higher ranking in search results.
There are several types of SSL certificates, each catering to different levels of security needs. The most common types include:
1. **Domain Validated (DV) SSL Certificates**: These provide a basic level of encryption and are usually the quickest to obtain.
2. **Organization Validated (OV) SSL Certificates**: These offer a higher level of security, requiring verification of the organization’s identity.
3. **Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates**: These provide the highest level of security and trust, involving a thorough vetting process. Websites with EV SSL certificates display a green address bar in the browser.
Choosing the right type of SSL certificate depends on the specific security requirements of your website.
Despite its widespread use, there are several misconceptions about SSL security. Some believe that SSL is only necessary for e-commerce websites, but it is essential for any site that collects user data. Others assume that SSL encryption slows down website performance, but modern technologies have optimized SSL to ensure minimal impact on speed.
Summary: SSL Security
In today’s digital age, where online security is paramount, understanding SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) security is crucial. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of SSL, exploring its significance, how it works, and why it is essential for safeguarding sensitive information online.
What is SSL?
SSL, or Secure Sockets Layer, is a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication over the internet. It establishes an encrypted link between a web server and a user’s web browser, ensuring that all data transmitted between them remains private and secure.
The Importance of SSL Security
With cyber threats constantly evolving, SSL security plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information. It prevents unauthorized access, data breaches, and man-in-the-middle attacks. By encrypting data, SSL ensures that it cannot be intercepted or tampered with during transmission, providing users with peace of mind while sharing personal or financial details online.
How Does SSL Work?
SSL works through a process known as the SSL handshake. When a user attempts to establish a secure connection with a website, the web server presents its SSL certificate, which contains a public key. The user’s browser then verifies the certificate’s authenticity and generates a session key. This session key encrypts and decrypts data during the communication between the browser and server.
Types of SSL Certificates
Various types of SSL certificates are available, each catering to different needs and requirements. These include Domain-Validated (DV) certificates, Organization-Validated (OV) certificates, and Extended Validation (EV) certificates. Each type offers different validation and trust indicators, allowing users to make informed decisions when interacting with websites.
SSL and SEO
In addition to security benefits, SSL has implications for search engine optimization (SEO). In recent years, major search engines have prioritized secure websites, giving them a slight ranking boost. By implementing SSL security, website owners can enhance their security and improve their visibility and credibility in search engine results.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, SSL security is a fundamental component of a safe and trustworthy online experience. It protects sensitive data, prevents unauthorized access, and instills confidence in users. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, understanding SSL and its importance is crucial for both website owners and internet users alike.