Cisco Umbrella CASB
In today's digital landscape, businesses face numerous security challenges. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulations are top priorities. This is where Cisco Umbrella CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker) comes into play. In this blog post, we will explore the key features and benefits of Cisco Umbrella CASB, and how it empowers organizations to secure their cloud environments effectively.
CASB, short for Cloud Access Security Broker, is a critical component of modern cybersecurity strategies. It provides organizations with visibility and control over cloud services, ensuring data protection and compliance. Cisco Umbrella CASB takes this to the next level, offering a comprehensive solution that covers all aspects of cloud security.
Cisco Umbrella CASB boasts a wide range of features that make it a powerful tool for securing cloud environments. From advanced threat protection to data loss prevention, here are some key features that set it apart:
Cloud Application Visibility: Cisco Umbrella CASB provides detailed visibility into all cloud applications in use within an organization. This allows administrators to identify potential risks and enforce policies to mitigate them effectively.
Threat Detection and Response: With its advanced threat detection capabilities, Cisco Umbrella CASB helps organizations identify and respond to potential security breaches promptly. It leverages machine learning algorithms and behavioral analytics to detect anomalous activities and prevent data exfiltration.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Protecting sensitive data is a top priority for organizations. Cisco Umbrella CASB enables granular data loss prevention policies, ensuring that confidential information remains protected throughout its lifecycle in the cloud.
One of the significant advantages of Cisco Umbrella CASB is its seamless integration with existing security infrastructure. It can easily integrate with other Cisco security solutions, such as Cisco Secure Email Gateway and Cisco Advanced Malware Protection, providing a unified approach to cloud security.
Compliance with industry regulations is crucial for organizations across various sectors. Cisco Umbrella CASB offers robust compliance and governance features that help organizations meet regulatory requirements. It provides visibility into user activities, enforces policies, and generates detailed compliance reports.
Cisco Umbrella CASB is a game-changer in the realm of cloud security. Its comprehensive features, seamless integration capabilities, and enhanced compliance and governance make it a go-to solution for organizations seeking to secure their cloud environments effectively. By leveraging the power of Cisco Umbrella CASB, businesses can confidently embrace the cloud while safeguarding their valuable data.Matt Conran
Highlights: Cisco Umbrella CASB
Understanding Cisco Umbrella CASB
**Understanding the Basics of Cisco Umbrella CASB**
Cisco Umbrella CASB is designed to provide comprehensive security for cloud applications. It acts as an intermediary between cloud service users and providers, ensuring that data and applications are used securely. By offering visibility and control over user activities, it helps organizations mitigate risks associated with unmanaged devices and shadow IT. Its seamless integration into existing security frameworks makes it a preferred choice for IT administrators looking to enhance their cloud security posture.
**Key Features and Capabilities**
One of the standout features of Cisco Umbrella CASB is its ability to provide detailed insight into cloud service usage. It offers real-time monitoring and analytics, allowing organizations to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities quickly. Additionally, the platform supports advanced threat protection, data loss prevention, and compliance management, ensuring that all cloud activities adhere to regulatory standards. These capabilities make Cisco Umbrella CASB a comprehensive solution for businesses looking to secure their cloud environments.
**Implementing Cisco Umbrella CASB in Your Organization**
Deploying Cisco Umbrella CASB is a straightforward process that can significantly enhance your organization’s cloud security. By integrating with existing security tools and systems, it provides a unified approach to managing cloud access and protecting sensitive data. Organizations can customize policies to meet specific security needs, ensuring a tailored approach to risk management and compliance. This flexibility makes Cisco Umbrella CASB an invaluable asset in the quest for secure cloud operations.
Deployment: CASB Solution
– CASBs operate using two approaches: Inline CASB solutions reside in the users and service connection path. They may do this through a hardware appliance or an endpoint agent that routes requests through the CASB.
– This approach requires the configuration of the network and endpoint devices. However, it provides the advantage of seeing requests before they are sent to the cloud service, allowing the CASB to block submissions that violate policy.
– API-based CASB solutions do not interact directly with the user but rather with the cloud provider through the provider’s API. This approach provides direct access to the cloud service and does not require any user device configuration. However, it also does not allow the CASB to block requests that violate policy. As a result, API-based CASBs are limited to monitoring user activity and reporting on or correcting policy violations after the fact.
Key Features and Benefits:
a) Cloud Application Visibility: Cisco Umbrella CASB offers real-time visibility into cloud applications being used within your organization. This enables you to identify shadow IT, assess the risk associated with different applications, and enforce appropriate security policies.
b) Data Loss Prevention: With advanced data loss prevention capabilities, Cisco Umbrella CASB helps prevent unauthorized access, sharing, or leakage of sensitive data. It allows you to define granular policies, monitor data movement, and take proactive measures to mitigate data breaches.
c) Threat Detection and Response: Powered by machine learning and artificial intelligence, Cisco Umbrella CASB proactively detects and blocks threats in real-time. It analyzes user behavior, identifies anomalies, and provides actionable insights to secure your cloud environment against malware, phishing attacks, and other cyber threats.
d) A Platform Approach
We must opt for a platform approach to visibility and control. More specifically, a platform that works in a 3rd party environment. So, for cloud security, this is where secure access service edge (SASE) can assist. In particular, the Cisco version is SASE, or Cisco Umbrella CASB, which comes with various versions depending on your needs. The SASE Cisco umbrella CASB solution has a variety of CASB security functions and CASB tools, Data Loss Prevention (DLP), and Umbrella Remote Browser Isolation (RBI), which can help you better understand and control your environment.
e) Automatic Discovery and Risk Profiling
The manual process involves investigating and mapping traffic patterns, data movement, and usage. For this, we need automatic discovery and risk profiling. It would help if you had visibility into applications, files, and data you may know and those you do not know about. You will be amazed by the number of malicious files and data already in sanctioned applications.
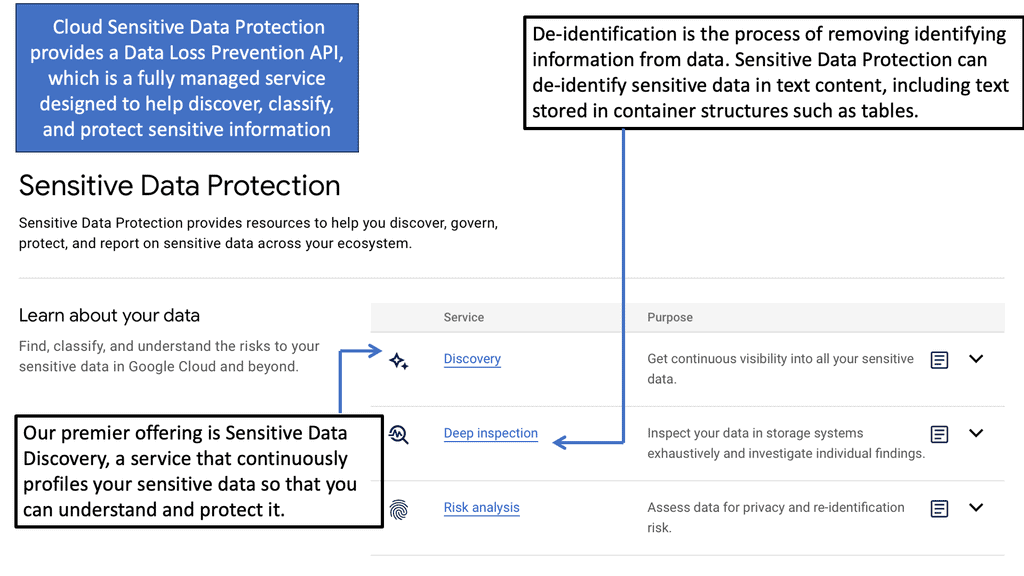
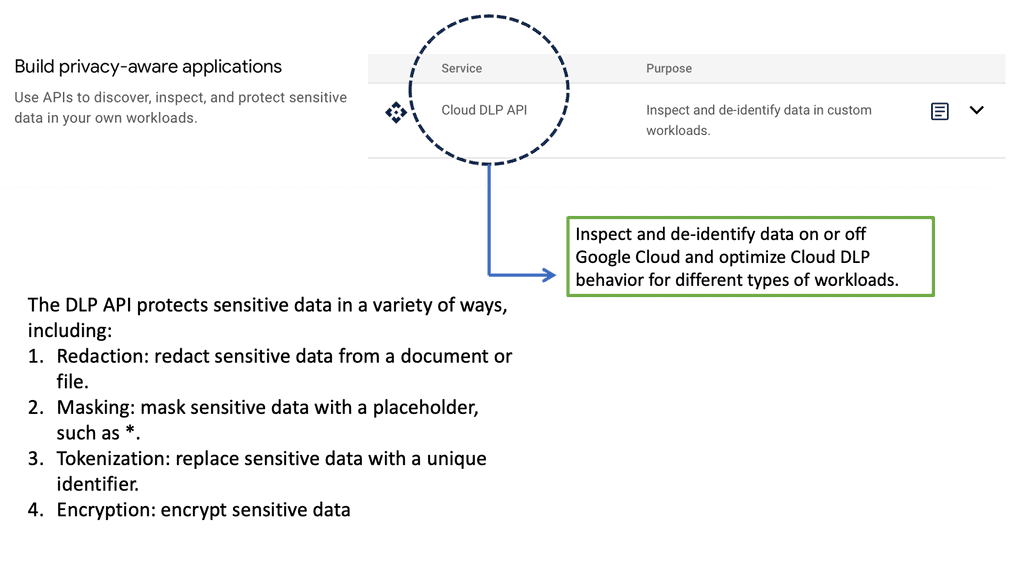
Example Technology: Sensitive Data Protection
Cloud Security Threats
- Cloud Challenges:
Today’s shared challenge is that organizations need to know what applications they have in their environment. They also need to figure out what to do with specific types of data or how to find users and assign policies to them. These requirements must be met on someone else’s infrastructure, the cloud.
Working in cloud environments, which differ significantly from on-premises, involves significant risks. Could you consider storage? For example, unprotected storage environments pose a much greater security risk in the public cloud than in a private data center.
- On-premise Data Centers
Within an on-premise private data center, the firewall controls generally restrict direct access to storage, limiting the exposure of an unprotected file to users who already have access to data center systems. On the other hand, an improperly managed storage bucket in the public cloud may be entirely unfiltered for the entire Internet, with only a few clicks by a single person or automated playbooks without role-based access control (RBAC).
Related: For pre-information, you may find the following helpful:
Cisco Umbrella & SASE
The Role of SASE
The Cisco Umbrella SASE solution offers other security functionality, such as a cloud-delivered Layer 7 Firewall, Secured Web Gateways (SWG), DNS-layer security, SD-WAN, and Thousand Eyes integration for Monitoring and Observability conditions. So, we have the traditional security stack you are familiar with and added enhancements to make it more cloud-friendly. These functionalities are part of a single SASE solution, and you can benefit from a Cisco Umbrella dashboard with API integrations.
The Cisco Umbrella CASB fulfills a variety of CASB security use cases. The use case for the CASB solution depends on where you are in your SASE and cloud security voyage. For example, if you are interested in blocking Malware and content, then Umbrella DNS filtering would be fine.
Umbrella Security Features:
However, you may be looking for additional security requirements. For example, you will need Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB), and Umbrella Remote Browser Isolation (RBI). In that case, we need to move toward Umbrella SIG, which includes Layer 7 Firewalls. Cisco Umbrella offers several packages ranging from DNS Security Essentials to SIG Advantage. More information can be found here: Cisco Umbrella Packages.
1.**Continuous File Monitoring**
Along with these security features, Cisco Umbrella also has continuous file monitoring. You scan data at rest for any sanctioned application and files within those approved applications that could be malicious. These tools will improve your security posture and protect organizations against cloud-specific risks.
The Cisco Umbrella CASB components take you from the initial Discovery to understanding the Risk to maintaining activity by controlling access to specific applications for certain users and actions.
These security activities are carried out by the Cisco Umbrella’s Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB), and Remote Browser Isolation engines.
2.**Umbrella Remote Browser Isolation**
What is Remote Browser Isolation? Browsing the Internet is a dangerous activity. Unfortunately, there are an abundance of threats. These include malicious Javascript, malvertising, exploit kits, and drive-by downloads. All of these target users who interact with web content via their browsers.
Typically, when a user’s browser is compromised, the attacker achieves access to the machine the browser runs on. However, the bad actors’ target assets are rarely on the first machine they compromise. For this, they will commonly proceed to move throughout the network laterally.
Challenge: Lateral Movements
**Remote Browser Isolation**
Unfortunately, the tool they use to move laterally is often a good sys admin tool, so it can be hard to detect as a security best practice; it’s much better to eliminate the availability of any lateral movements.
However, with Umbrella Remote Browser Isolation (RBI), the remote browser runs in an isolated container in the cloud, thus mitigating the attack surface to an absolute minimum and removing the potential to move laterally.
Therefore, the most sensible thing to do is to isolate the browsing function. With browser isolation technologies, Malware is kept off the end user’s system, reducing the surface area for attack by shifting the risk of attack to the server sessions, which can be reset to a known good state on every new browsing session, tab opened, or URL accessed.
**Redirect Browsings**
Umbrella Remote Browser Isolation protects users from Malware and threats by redirecting browsing to a cloud-based host, which for some is based on a containerized technology. Isolation is achieved by serving web content to users via a remotely spun-up surrogate browser in the cloud.
The Umbrella Remote Browser Isolation allows users to access whatever content they want, such as a web location or document. The user is sent via an isolation engine, which strips away anything that can be malicious, such as Macros or Malware, and then gives them a fully rendered version of the content.
**Rendered Clean Version**
For example, this could be a web app or a website. With remote browser isolation, you scrub away anything that could be malicious and give it a rendered clean version.
So, to the user, it is fully transparent, and they have no idea that they are looking at a rendered version. However, it provides clean and safe content that will not introduce malware into the environment without a performance hit.
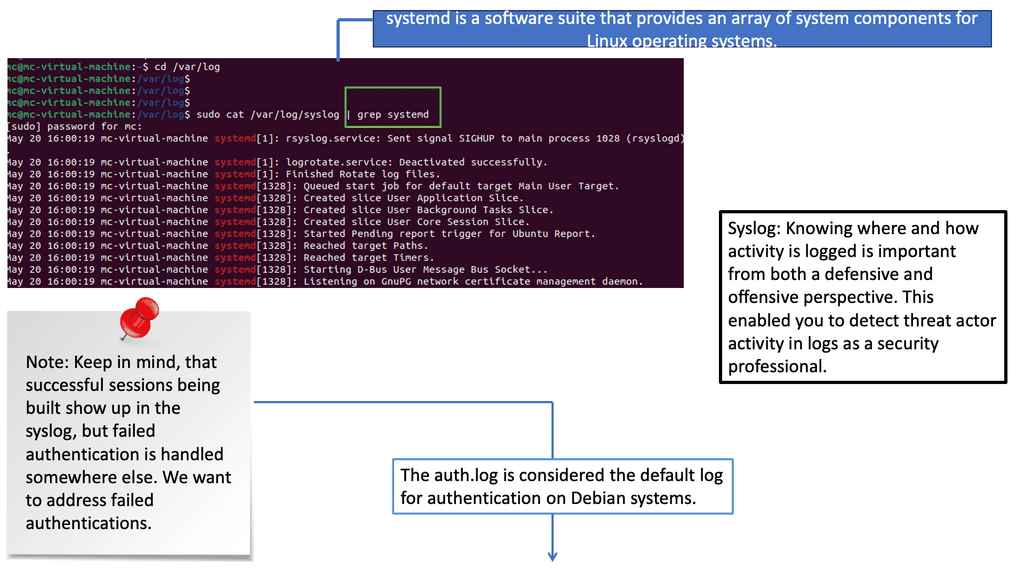
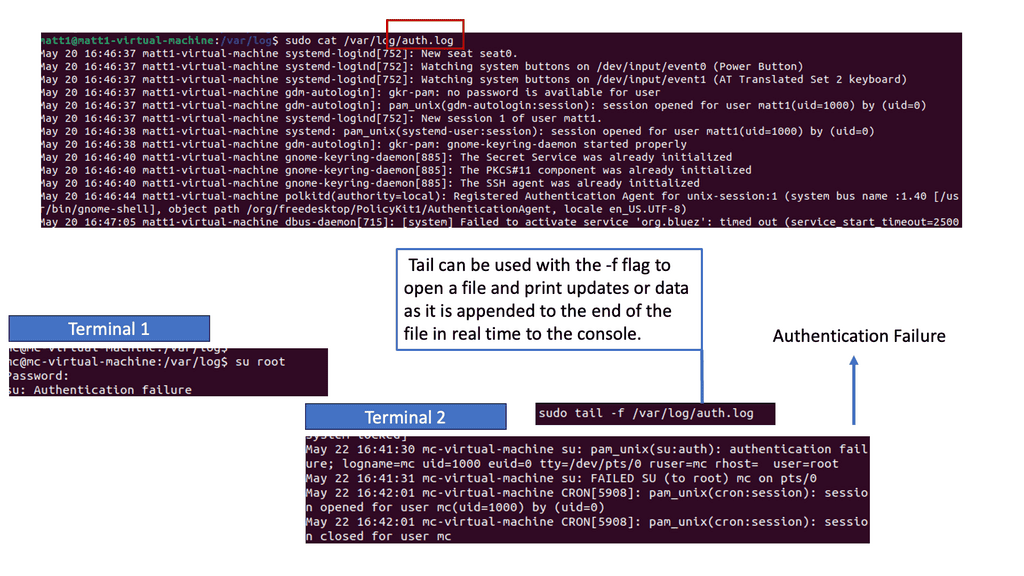
Example: Detecting Threats in Logs
Understanding syslog and auth.log
Syslog is a standard protocol for message logging, allowing devices to send log messages to a centralized server. Auth.log, on the other hand, Auth.log is a specific log file that records authentication-related events on Unix-like systems. Familiarizing ourselves with these logs is the first step toward effective security event detection.
Syslog messages can provide valuable insights into security events. By examining their content and structure, we can identify anomalies, such as repeated failed login attempts, suspicious network connections, or unexpected system reboots. Various log analysis tools, like Splunk and ELK stack, offer powerful features to aid this process.
Auth.log is a goldmine for detecting potential security breaches. This log file captures authentication-related events, such as successful logins, failed login attempts, and user privilege escalations. By carefully monitoring auth.log, security analysts can spot unauthorized access attempts, brute-force attacks, or unusual user behavior, enabling them to take timely action to mitigate potential threats.
Starting Cisco Umbrella CASB
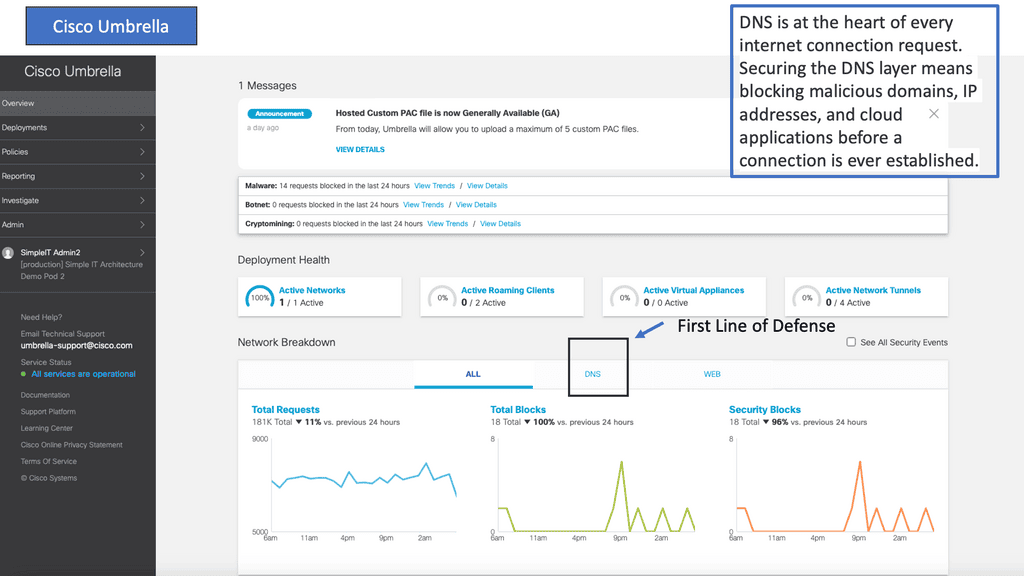
You can use Cisco Umbrella CASB to discover your actual usage of cloud services through multiple means, such as network monitoring, integration with existing network gateways and monitoring tools or even monitoring Domain Name System (DNS) queries. The CASB solution provides this form of discovery service.
This is the first step to CASB security, understanding both sanctioned and shadow I.T. Once the different services are discovered, a CASB solution can monitor activity on approved services through two standard deployment options.
First, we have an API connection or inline (man-in-the-middle) interception. Some vendors offer a multimode approach. Both deployment modes have their advantages and disadvantages.
The CASB alone is far from a silver bullet and works in combination with other security functions. The power of Cisco Umbrella CASB depends on its Data Loss Prevention (DLP) capabilities, which can be either part of the CASB solution or an external service, depending on the CASB security vendor’s capabilities. The Cisco Umbrella has an inline DLP engine.
Data Loss Prevention
After the Discovery is performed, CASB security can be used as a preventative control to block access to SaaS products. This functionality, however, is being quickly replaced through the integration of DLP. DLP systems inspect network traffic, leaving your systems looking for sensitive data. Traffic carrying unauthorized data is terminated to protect it from loss and leakage.
Through integration with a DLP service, you can continue to allow access to a SaaS product but control what is being done within that SaaS product. For example, if somebody uses Twitter, you can restrict specific keywords or statements from being sent to the platform.
So, for example, if you’re using an application like Salesforce in the cloud and have a policy that you’re not allowed to copy customers or download customer databases from Salesforce, the CASB solution can enforce that and monitor if someone attempts to download or violate the policies.
Example: Sensitive Data Protection
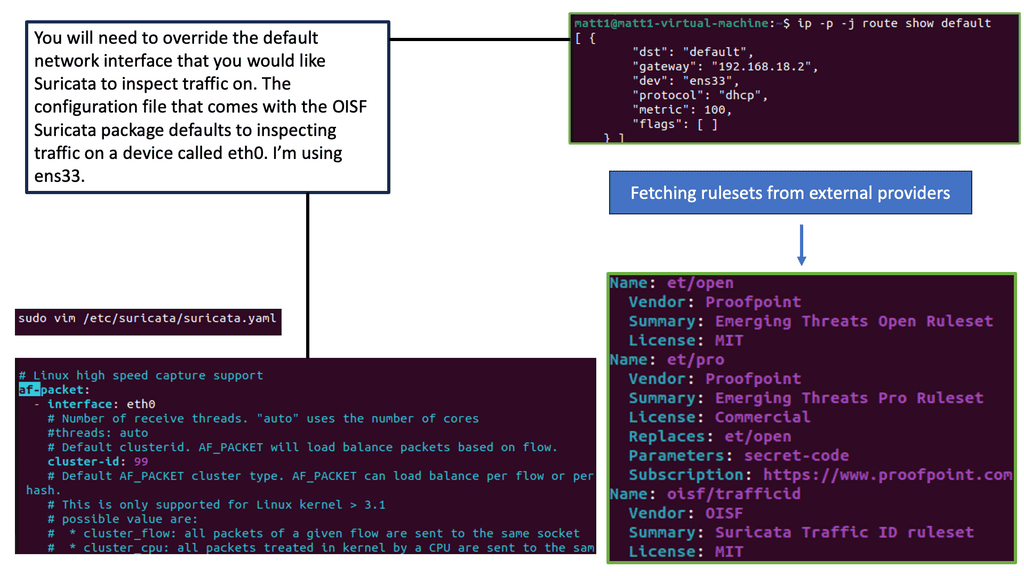
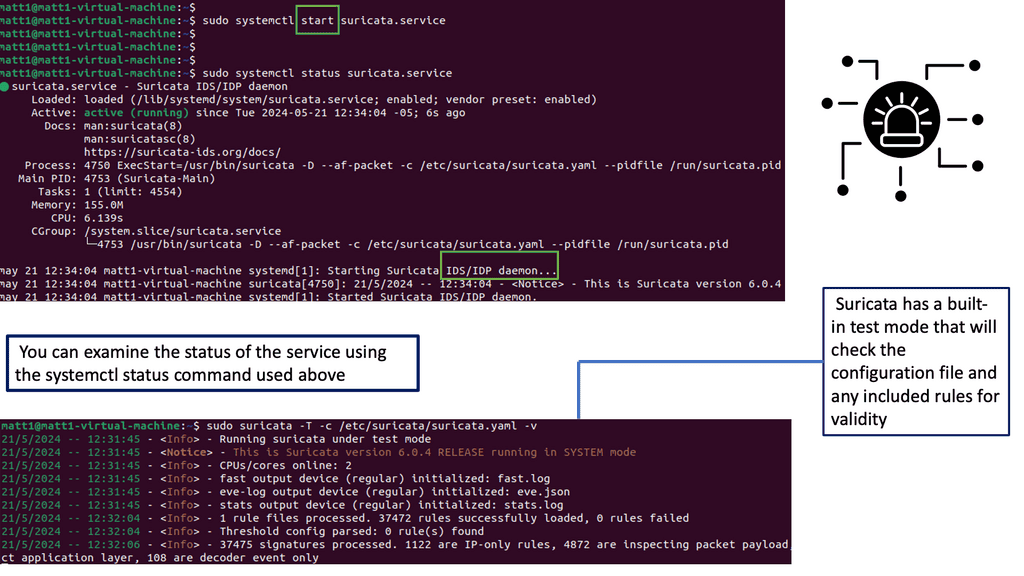
Example Technology: IPS IDS
Suricate IPS/IDS has a range of powerful features, making it a formidable defense mechanism for your network. Some of its notable features include:
1. Intrusion Detection: Suricate continuously scans network traffic, analyzing it for any signs of malicious behavior or suspicious activities. It can identify various attacks, such as DDoS attacks, SQL injections, and malware intrusions.
2. Intrusion Prevention: Suricate IPS is a proactive shield that prevents potential threats from infiltrating your network. It can block malicious packets, unauthorized access attempts, and suspicious traffic patterns, effectively neutralizing potential risks.
3. Real-time Alerting: Suricate instantly alerts network administrators or security teams whenever it detects a potential threat. These alerts provide valuable insights and allow for immediate response and mitigation, minimizing the impact of an attack.
Cisco Umbrella CASB: SASE Capabilities
Cisco Umbrella’s CASB, DLP, and Umbrella remote browser isolation (RBI) offering is a core part of Cisco’s overall SASE strategy. The value of CASB security is from its capability to give insight into cloud application use across cloud platforms and identify unsanctioned use.
CASBs use auto-discovery to detect cloud applications and identify high-risk applications and users. In addition, they include DLP functionality and the capability to detect and provide alerts when abnormal user activity occurs to help stop internal and external threats. This enables Cisco Umbrella to expose shadow I.T. by providing the capability to detect and report on the cloud applications used across your environment.
Now, we have a central place for all applications. Cisco Umbrella CASB looks at all your cloud applications and puts them in a single box, on a single pane of glass, that you can manage and look at what’s happening, but that functionality has to exist already. So, instead of going to a hundred different applications and cloud providers, you just go to one system, and your CASB solution handles everything.
Pillar1: Visibility
The CASB security should detect all cloud services, assign each a risk ranking, and identify all users and third-party apps able to log in. More often than there are a lot of power users, such as finance, that have access to large data sets. So, files are shared and exposed within the content of files used, and apps are installed.
This is generally due to a slight majority of users controlling most applications. So, these users, who are a small number, introduce a considerable amount of security risk. In addition, these users often collaborate with several external parties, which will be cloud-based sharing, not to mention sharing with non-corporate email addresses.
**A key point: Understanding risk**
The first thing you want to do is understand the risk. Here, you can identify risky applications by gaining visibility on any shadow I.T. These apps that admins have no control or visibility into are being used in their environment that they need to protect.
You can also investigate what identities use these applications and why they are used. How do you gain visibility? You may wonder how you get all this data. A few sources can be used to discover the data we will discuss.
Applications in your environment can be displayed in different categories and break down risk based on other criteria. For example, there is business risk, usage risk, and vendor compliance. Each risk category has different factors used to make up the risk categories. Cisco Umbrella CASB integrates with Cisco Talos, which helps you get the reputation information by looking at the Host domain and URL associated with informing you if the app has a good reputation.
Pillar2: Discovery
To gain visibility, we have to perform Discovery. The discovery process involves pulling in and logging data out of other security products and then analyzing the information. All of the capabilities to discover apps work out of the box. You only need to set the user traffic to the Umbrella system. The first is DNS, which we can also discover with the Secure Web Gateway (SWG) proxy and a cloud-delivered firewall.
These SASE engines offer a unique view of sanctioned and unsanctioned applications. So, if you send traffic through one of these Cisco Umbrella engines, it can collect this data automatically. Also, Cisco Umbrella has a Layer 7 application Firewall that can provide information such as application protocols, giving you information on the top-used protocols per application.
Native proxy, Firewall, and DNS logs.
The Umbrella has several components of engines that help with Discovery, such as native proxy, Firewall, and DNS logs. So, the user can be determined when every engine picks up the traffic, such as DNS or Firewall levels. This will give you a holistic view of the application, such as the risk associated with it and the identity on a per-app basis. So, now we can have a broader look at risk to understand cloud apps and traffic going to, for example, Malware hosts and going C&C command servers, and if any ToR endpoints are running on your network.
Pillar 3: Data Security and Control
When dealing with any systematic issue, prevention is critical, with a focus on data protection. A good start would be to define which applications are risky. From there, you can build a workflow and data sets that you need to protect from, for example, data leakage. Once Discovery is performed along with risk assessment, you can prevent unwanted applications in your environment, which is the first step in enforcement.
The first component is the CASB security, followed by DLP to enforce controls. We are creating DLP policies to prevent data leakage. The CASB should be able to identify and control sensitive information. So here, we have DLP features and the capability to respond to classification labels on content.
There is a component called granular control, in which you can allow access to special applications but control different actions for specific applications and users. For example, you can enable access to the app but block uploads.
You can then tie this to an identity so only your finance team can upload it. You can allow, secure, and also isolate. The CASB DLP can operate natively and in conjunction with enterprise DLP products via Internet Content Adaptation Protocol (ICAP) or REST API integration.
A standard DLP engine for the on-premise and cloud locations will eliminate policy duplication. This Cisco Umbrella solution opts for an inline DLP engine without the need to service chain to an additional appliance.
Pillar 4: Inline Data Loss Prevention
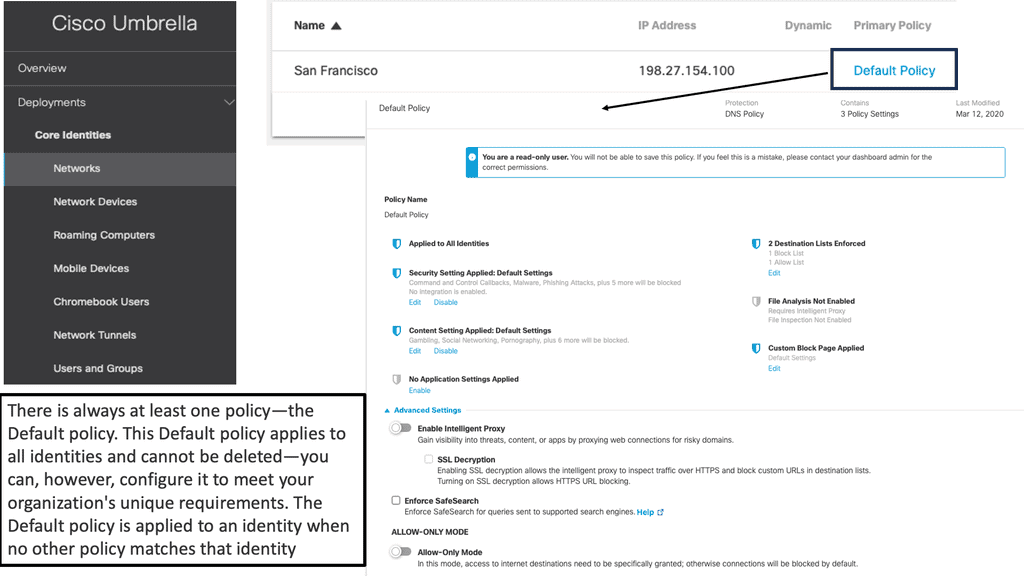
The Data Loss Prevention policy monitors content classified as personally identifiable or sensitive information. When necessary, content is blocked from an upload or a post. With Cisco DLP, there is only one data loss prevention policy.
Rules are added to the policy to define what traffic to monitor (identities and destinations), the data classifications required, and whether content should be blocked or only monitored. For example, an office may want to monitor its network for file uploads that include credit card numbers because the uploads breach company privacy and security policies. A rule that scans the network and uploads to domains can block these files.
Cisco Umbrella: 80 pre-built data Identifiers
There are two primary functions of DLP. The first piece identifies and classifies sensitive data; the second is the actions to take. Cisco Umbrella has robust DLP classification with over 80 pre-built data identifiers that are aligned with detailed reporting on every DLP report. So, working with DLP, you have first to select data classification.
This is where you start your DLP and have different identities for the data. If you are concerned with financial data sets and want to examine credit card numbers, you can choose a list of predicted identifiers. Then, you can add your customizations.
Cisco umbrella DLP engine also supports regular expressions that support pattern patterns. This allows you to match any pattern. So we have a custom action and pre-built and then apply this to a DLP policy. As you know, there is only one data loss prevention policy.
Rules are added to the policy to define what traffic to monitor (identities and destinations), the data classifications required, and whether content should be blocked or only monitored.
**Starting a SASE Project**
A) – SASE DLP Starting Points
As a starting point, when considering DLP, there are a couple of best practices to follow. First, you must “train” a DLP to understand sensitive data and what is not. Especially with DLP, you should have it in monitoring-only mode and not be aggressive and block. You want to understand what is happening before you start to block.
Sometimes, you want to understand more about data and data ID and where it moves. Second, a DLP cannot inspect encrypted traffic; if it does, check the performance hit. Third, some cloud SDKs and APIs may encrypt portions of data and traffic, which will interfere with the success of a DLP implementation.
B) – SASE Best Practices
As a best practice with Cisco Umbrella, you can start with the pre-built identifiers and create custom dictionaries to monitor your organization’s specific keywords and phrases. Then, you can create specific rules based on users, groups, devices, and locations for which you want to watch data. Finally, you can choose which destination and apps you like to monitor; many organizations choose only to monitor when creating DLP rules and then enable block over time.
C) – Cisco Umbrella CASB starting points
Consider the following recommendations when starting a project that consists of CASB functionality. First, discover sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud services and then access the cloud risk based on cloud service categories. This includes all cloud services and cloud plug-ins. Once this information has been gained, it can be measured, along with risk. This can then be compared to the organization’s risk tolerance.
Next, identify and protect sensitive information. Once you find all sensitive information in the cloud, you can classify it and then apply controls to control its movement, such as DLP. For example, additional protections can be used if sensitive data is moved from the cloud services to a local unmanaged laptop.
D) – SASE Detect and Mitigate Threats.
You can access the user’s behavior and any deviations that may signal out-of-normal activity. The CASB is one of many solutions that should be used here—more mature products with advanced detection, such as Splunk User Behavior Analytics (UBA). For example, trust decreases once a significant deviation from the baseline is noticed. You could implement step-down privileges or more extreme courses, therefore changing the level of access. In addition, it would be helpful to track all data’s movement and detect and eliminate Malware. And then have an implementation strategy for remediation.
Summary: Cisco Umbrella SASE
In today’s digital landscape, businesses are rapidly adopting cloud technologies to drive innovation and enhance productivity. However, this shift towards the cloud also introduces new security challenges. Enter Cisco Umbrella CASB, a comprehensive cloud access security broker solution that empowers organizations to safely navigate their cloud journey while ensuring data protection and compliance.
Understanding Cisco Umbrella CASB
Cisco Umbrella CASB is a robust platform that provides visibility, control, and protection across all cloud applications and services utilized by an organization. It offers a centralized console to manage cloud access, enforce security policies, and detect potential threats. With its advanced capabilities, Cisco Umbrella CASB enables businesses to embrace the cloud securely.
Key Features and Benefits
a) Cloud Application Visibility: Cisco Umbrella CASB offers deep visibility into cloud applications and services being used within an organization. It provides valuable insights into user activities, data transfers, and potential risks, allowing administrators to make informed decisions.
b) Policy Enforcement: With granular policy controls, Cisco Umbrella CASB enables organizations to define and enforce security policies tailored to their specific needs. It ensures that data is accessed, shared, and stored within the cloud according to predefined guidelines, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
c) Threat Detection and Response: By leveraging advanced threat intelligence and machine learning, Cisco Umbrella CASB proactively identifies and mitigates potential threats within cloud environments. It alerts administrators about anomalous activities, suspicious behavior, or policy violations, enabling swift incident response.
Seamless Integration and Scalability
Cisco Umbrella CASB seamlessly integrates with existing security infrastructure, including firewalls, proxies, and endpoint security solutions. This integration allows businesses to leverage their existing investments while extending comprehensive cloud security capabilities. Additionally, the solution scales effortlessly as organizations expand their cloud footprint, ensuring continuous protection.
Real-World Use Cases
a) Data Loss Prevention: Cisco Umbrella CASB helps prevent sensitive data leakage by monitoring and controlling data transfers within cloud applications. It enables organizations to set up policies that restrict the sharing of confidential information or personally identifiable data, reducing the risk of data loss incidents.
b) Compliance and Governance: With its robust auditing and reporting capabilities, Cisco Umbrella CASB assists organizations in meeting regulatory compliance requirements. It provides detailed logs and insights into user activities, ensuring transparency and accountability in cloud usage.
Conclusion
Cisco Umbrella CASB is a game-changer in the realm of cloud security. Its comprehensive feature set, seamless integration, and scalability make it an invaluable asset for organizations aiming to secure their cloud journey. By harnessing the power of Cisco Umbrella CASB, businesses can unlock the true potential of the cloud while safeguarding their critical assets and maintaining compliance.