IPv6 RA
In the realm of IPv6 network configuration, ICMPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) plays a crucial role. As the successor to ICMPv4 Router Discovery Protocol, ICMPv6 RA facilitates the automatic configuration of IPv6 hosts, allowing them to obtain network information and effectively communicate within an IPv6 network. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of ICMPv6 R-Advertisement, its importance, and its impact on network functionality.
ICMPv6 Router Advertisement is a vital component of IPv6 network configuration, specifically designed to simplify configuring hosts within an IPv6 network. Routers periodically send RAs to notify neighboring IPv6 hosts about the network's presence, configuration parameters, and other relevant information.
IPv6 Router Advertisement, commonly referred to as RA, plays a crucial role in the IPv6 network configuration process. It is a mechanism through which routers communicate essential network information to neighboring devices. By issuing periodic RAs, routers efficiently manage network parameters and enable automatic address configuration.
RA is instrumental in facilitating the autoconfiguration process within IPv6 networks. When a device receives an RA, it can effortlessly derive its globally unique IPv6 address. This eliminates the need for manual address assignment, simplifying network management and reducing human error.
One of the key features of IPv6 RA is its support for Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC). With SLAAC, devices can generate their own IPv6 address based on the information provided in RAs. This allows for a decentralized approach to address assignment, promoting scalability and ease of deployment.
Beyond address autoconfiguration, RA also serves as a conduit for configuring various network parameters. Routers can advertise the network prefix, default gateway, DNS server addresses, and other relevant information through RAs. This ensures that devices on the network have the necessary details to establish seamless communication.
By leveraging RA, network administrators can optimize network efficiency and performance. RAs can convey parameters like hop limits, MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) sizes, and route information, enabling devices to make informed decisions about packet forwarding and path selection. This ultimately leads to improved network responsiveness and reduced latency.
IPv6 Router Advertisement is a fundamental component of IPv6 networks, playing a pivotal role in automatic address configuration and network parameter dissemination. Its ability to simplify network management, enhance efficiency, and accommodate the growing number of connected devices makes it a powerful tool in the modern networking landscape. Embracing the potential of IPv6 RA opens up a world of seamless connectivity and empowers organizations to unlock the full capabilities of the Internet of Things (IoT).
Matt Conran
Highlights: IPv6 RA
IPv6 RA ( Router Advertisements )
– IPv6 RA stands for Router Advertisement, an essential component of the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) in IPv6. Its primary purpose is to allow routers to announce their presence and provide vital network configuration information to neighboring devices.
– IPv6 RA serves as the cornerstone for IPv6 autoconfiguration, enabling devices on a network to obtain an IPv6 address and network settings automatically. By broadcasting router advertisements, routers inform neighboring devices about network prefixes, hop limits, and other relevant parameters. This process simplifies network setup and management, eliminating the need for manual configuration.
**Periodically sending router advertisements**
– IPv6 RA operates by periodically sending router advertisements to the local network. These advertisements contain crucial information such as the router’s link-local address, network prefixes, and flags indicating specific features like the presence of a default router or stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC). Devices on the network listen to these advertisements and utilize the provided information to configure their IPv6 addresses and network settings accordingly.
– One remarkable aspect of IPv6 RA is its ability to enhance network efficiency. By employing Route Optimization and Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) techniques, IPv6 RA ensures optimal routing and prevents address conflicts, leading to a more streamlined and reliable network infrastructure.
**Unraveling Router Advertisement Preference**
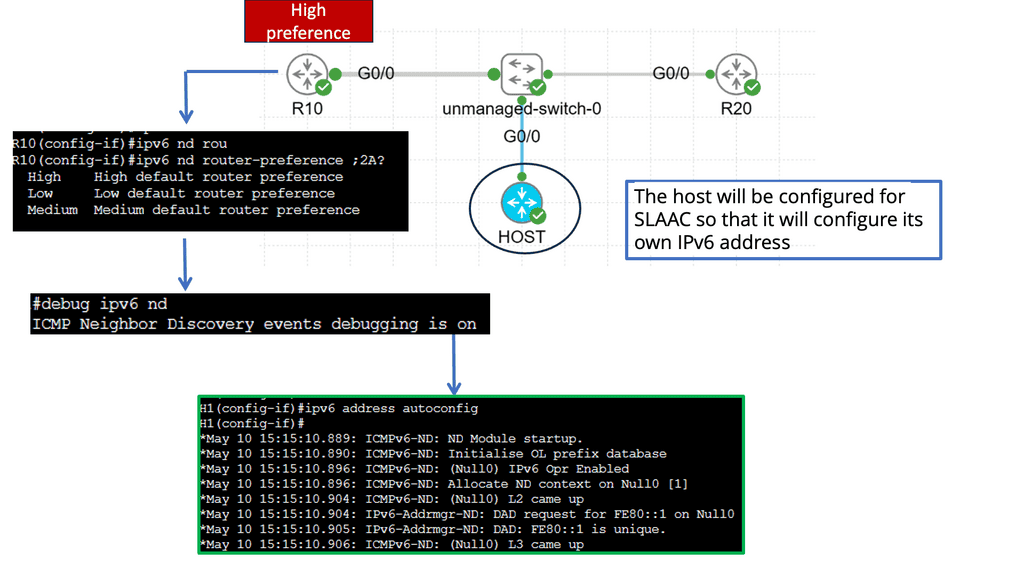
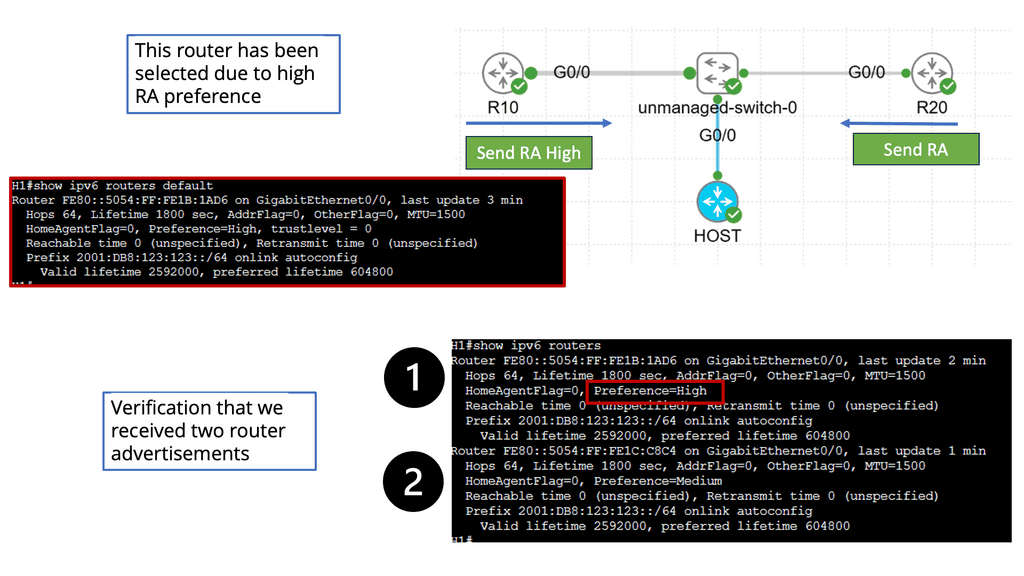
A: – Router Advertisement Preference determines the behavior of IPv6 hosts when multiple routers are present on a network segment. It helps hosts decide which router’s advertisements to prioritize and use for address configuration and default gateway selection. Understanding the different preference levels and their implications is crucial for maintaining a well-functioning IPv6 network.
B: – High-preference routers (e.g., with a preference value of 255) are typically designated as default gateways, while low-preference routers (e.g., with a preference value of 1) are considered backup gateways. We explore the benefits and trade-offs of having multiple routers with varied preference levels in a network environment.
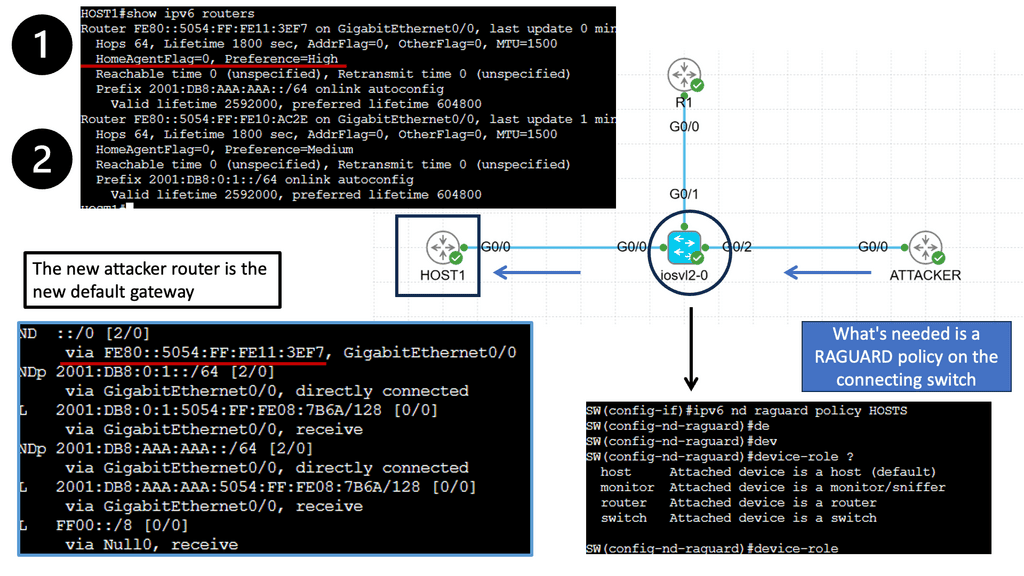
Understanding IPv6 RA Guard
IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) Guard is a feature designed to protect networks from rogue router advertisements. By filtering and inspecting RA messages, RA Guard prevents unauthorized and potentially harmful router advertisements from compromising network integrity.
RA Guard operates by analyzing RA messages and validating their source and content. It verifies the legitimacy of router advertisements, ensuring they originate from authorized routers within the network. By discarding malicious or unauthorized RAs, RA Guard mitigates the risk of rogue routers attempting to redirect network traffic.
To implement IPv6 RA Guard, network administrators need to configure it on relevant network devices, such as switches or routers. This can typically be achieved through command-line interfaces or graphical user interfaces provided by network equipment vendors. Understanding the specific implementation requirements and compatibility across devices is essential to ensuring seamless integration.
How does IPv6 RA work
- RA Message Format
Routers send RA messages periodically, providing vital information to neighboring devices. The message format consists of various fields, including the ICMPv6 type, code, checksum, and options like the prefix, MTU, and hop limit. Each field serves a specific purpose in conveying essential network details.
- RA Advertisement Intervals
RA messages are sent at regular intervals determined by the router. These intervals are defined by the Router Advertisement Interval Option (RAIO), which specifies the time between successive RA transmissions. The intervals can vary depending on network requirements, but routers typically aim to balance timely updates and network efficiency.
- Prefix Advertisement
One of RA’s primary functions is to advertise network prefixes. Routers inform hosts about the available network prefixes and their associated attributes by including the Prefix Information Option (PIO) in the RA message. This allows hosts to autoconfigure their IPv6 addresses using the advertised prefixes.
RA messages can also include other configuration parameters, such as the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) and hop limit. The MTU option informs hosts about the maximum packet size they should use for optimal network performance. The hop limit option specifies the default maximum number of hops for packets destined for a particular network.
- Neighbor Discovery in ICMPv6
When a Router Solicitation message is received, IPv6 routers send ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages every 200 seconds. RA messages suggest to devices on the segment how to obtain address information dynamically, and they provide their own IPv6 link-local addresses as default gateways.
ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery has some benefits, but it also has some drawbacks. The clients are responsible for determining whether the primary default gateway has failed until the Router Lifetime timer has expired. A NUD client determines that the primary default gateway is down after about 40 seconds.
Failover can be improved by modifying two timers: the Router Advertisement interval and the Router Lifetime duration. By default, RA messages are sent out every 200 seconds with a Router Lifetime of 1800 seconds.
IPv6 Core Considerations
It would be best if you considered the following before implementing Neighbor Discovery as a first-hop failover method:
- The client’s behavior depends on the operating system when the Router Lifetime timer expires.
- When the RA interval is increased, every device on the network must process the RA messages more frequently.
- Instead of processing RA messages every 200 seconds, clients will now need to process them every second. This can be a problem when there are thousands of virtual machines (VMs) in a data center.
- The router may also have to generate more RA messages and possibly process more RS messages as a result of this issue. Having multiple interfaces on a router can easily result in a lot of CPU processing.
- According to load balancing, a client chooses its default gateway based on which RA message it receives first. Due to the lack of load balancing provided by Neighbor Discovery, one router can perform a significant amount of packet forwarding.
IPv6: At the Network Layer
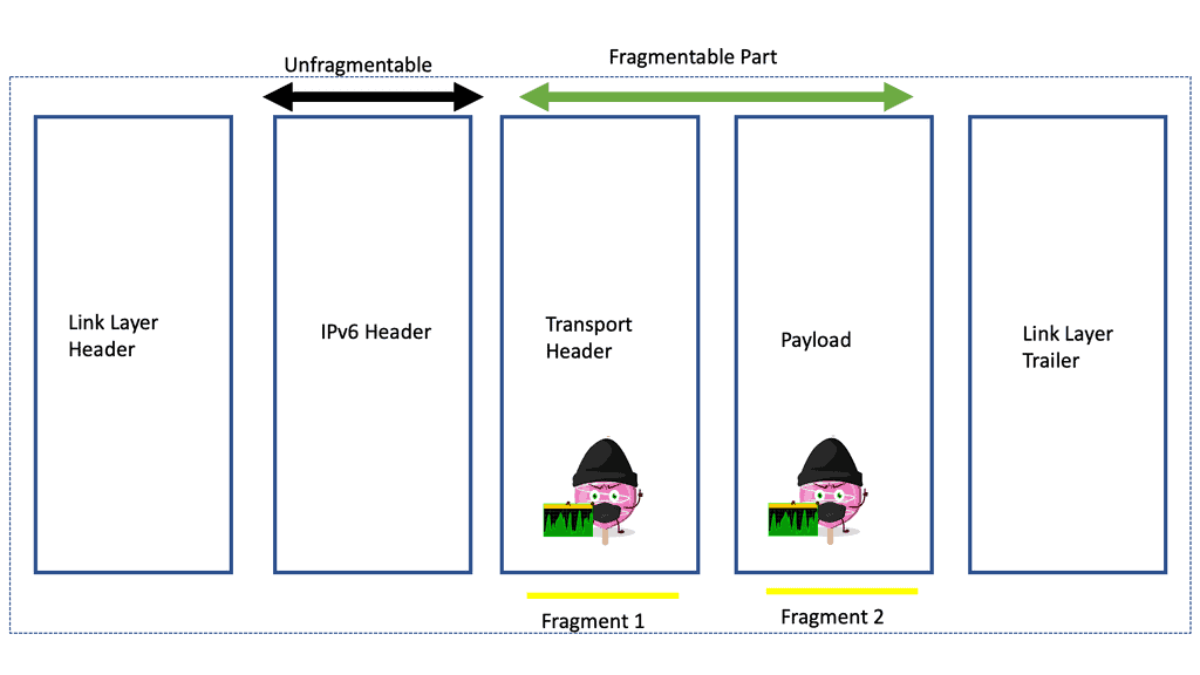
IPv6 is a Network-layer replacement for IPv4. Before we delve into IPv6 high availability, the different IPv6 RA ( router advertisement ), and VRRPv3, you should first consider that IPv6 does not solve all the problems experienced with IPv4 and will still have security concerns with, for example, the drawbacks and negative consequences that can arise from a UDP scan and IPv6 fragmentation.
Also, issues experienced with multihoming and Network Address Translation ( NAT ) still exist in IPv6. Locator/ID Separation Protocol (LISP) solves the problem of multihoming, not IPv6, and Network Address Translation ( NAT ) is still needed for IPv6 load balancing. The main change with IPv6 is longer addresses. We now have 128 bits to play with instead of 32 with IPv4.
Additional Address Families
Increasing bits means we cannot transport IPv6 packets using existing routing protocols—some protocols like ISIS, EIGRP, and BGP support address families offering multiprotocol capabilities. Protocols supporting families made enabling IPv6 with IPv6 extended address families easy. However, other protocols, such as OSPF, were too tightly coupled with IPv4, and a complete protocol redesign was required to support IPv6, including new LSA types, flooding rules, and internal packet formats.
Before you proceed, you may find the following post helpful:
IPv6 RA
IPv6 is the newest Internet protocol (IP) version developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The common theme is that IPv6 helps address the IPv4 address depletion due to prolonged use. But IPv6 is much more than just a lot of addresses.
The creators of IPv6 took the possibility to improve IP and related protocols; IPv6 is now enabled by default on every central host operating system, including Windows, Mac OS, and Linux. In addition, all mobile operating systems are IPv6-enabled, including Google Android, Apple iOS, and Windows Mobile.
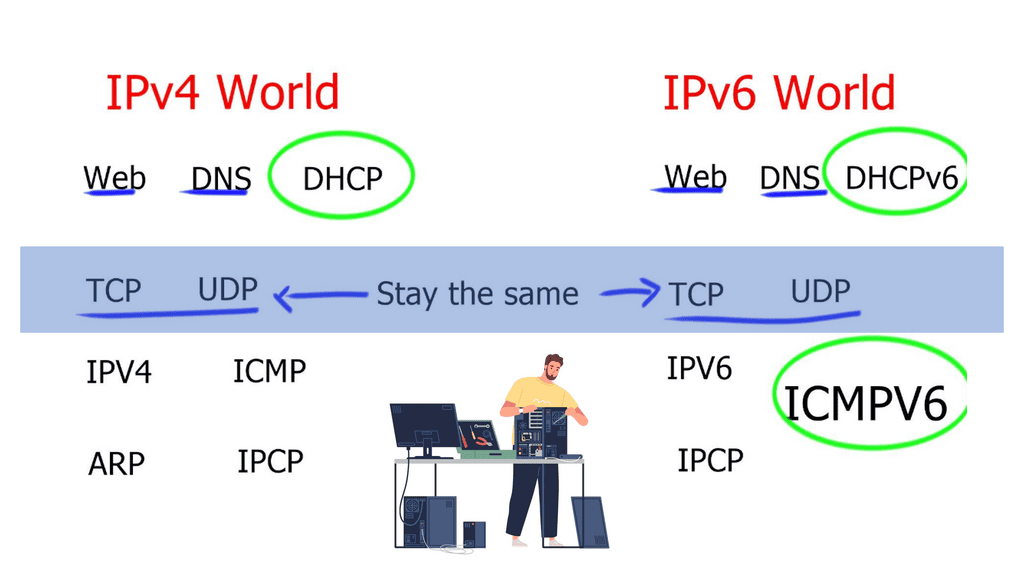
IPv6 and ICMPv6
IPv6 uses Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 ( ICMPv6 ) and acts as a control plane for the v6 world. Then we have IPv6 Neighbor Discovery ( ND ) replacing IPv4 Address Resolution Protocol ( ARP ). We now have IPv6 IPCP in PPP’s IPCP. IPCP in IPv6 does not negotiate the endpoint address as it does with IPv4 IPCP. IPv6 IPCP is just negotiating the use of protocols.
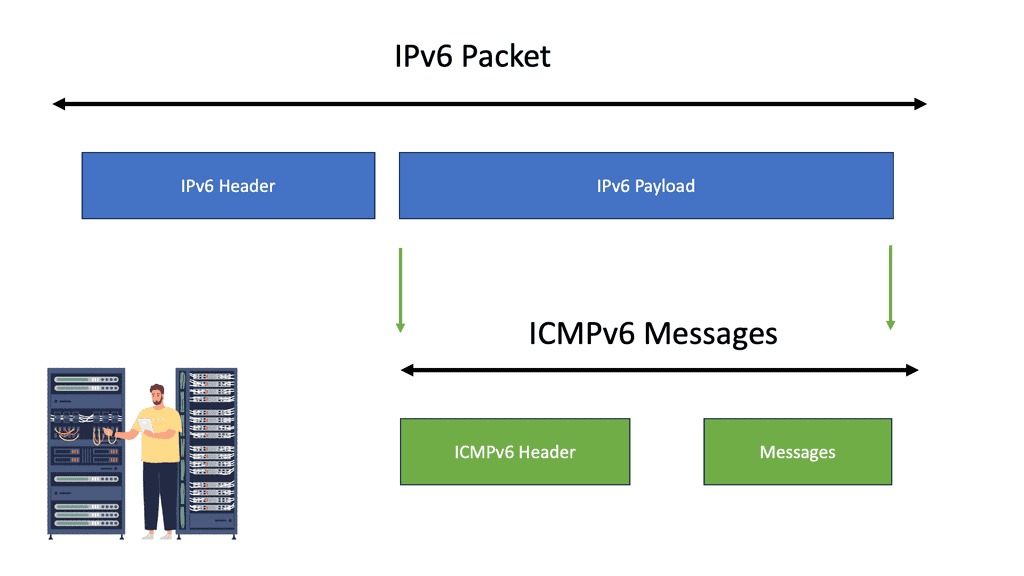
ICMPv6, an extension of ICMPv4, is an integral part of the IPv6 protocol suite. It primarily sends control messages and reports error conditions within an IPv6 network. ICMPv6 operates at the network layer of the TCP/IP model and aids in the diagnosis and troubleshooting of network-related issues.
Functions of ICMPv6:
- Neighbor Discovery:
One of the essential functions of ICMPv6 is neighbor discovery. In IPv6 networks, devices use ICMPv6 to determine the link-layer addresses of neighboring devices. This process helps efficiently route packets and ensures the accurate delivery of data across the network.
- Error Reporting:
ICMPv6 serves as a vital tool for reporting errors in IPv6 networks. When a packet encounters an error during transmission, ICMPv6 generates error messages to inform the sender about the issue. These error messages assist network administrators in identifying and resolving network problems promptly.
- Path MTU Discovery:
Path Maximum Transmission Unit (PMTU) refers to the maximum packet size that can be transmitted without fragmentation across a network path. ICMPv6 aids in path MTU discovery by allowing devices to determine the optimal packet size for efficient data transmission. This ensures that packets are not unnecessarily fragmented, reducing network overhead.
- Multicast Listener Discovery:
ICMPv6 enables devices to discover and manage multicast group memberships. By exchanging multicast-related messages, devices can efficiently join or leave multicast groups, allowing them to receive or send multicast traffic across the network.
- Redirect Messages:
In IPv6 networks, routers use ICMPv6 redirect messages to inform devices of a better next-hop address for a particular destination. This helps optimize the routing path and improve network performance.
- ICMPv6 Router Advertisement:
IPv6 RA is an essential mechanism for configuring hosts in an IPv6 network. By providing critical network information, such as prefixes, default routers, and configuration parameters, RAs enable hosts to autonomously configure their IPv6 addresses and establish seamless communication within the network. Understanding the intricacies of ICMPv6 R-Advertisement is vital for network administrators and engineers, as it forms the cornerstone of IPv6 network configuration and ensures the efficient functioning of modern networks.
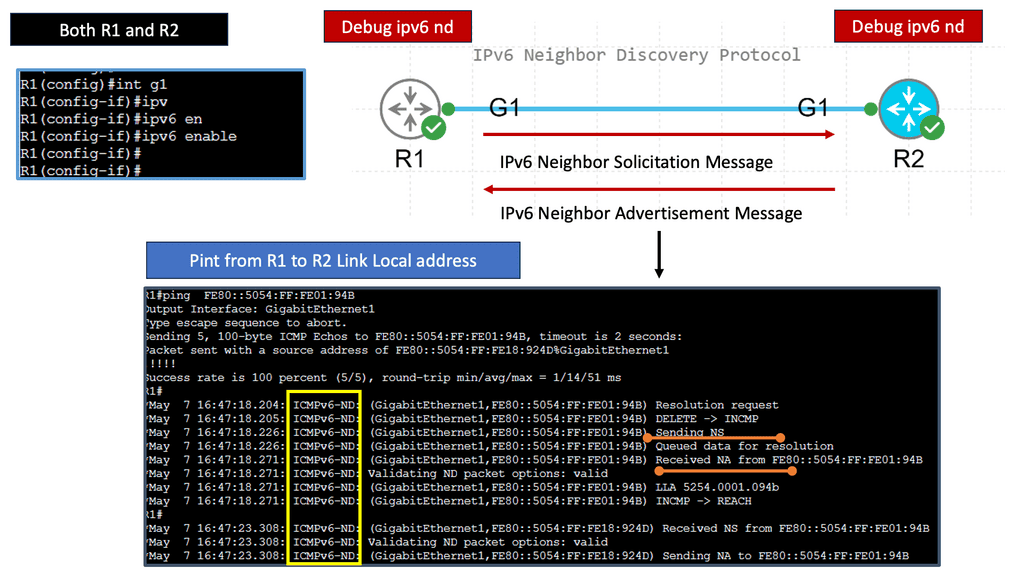
Guide on ICMPv6
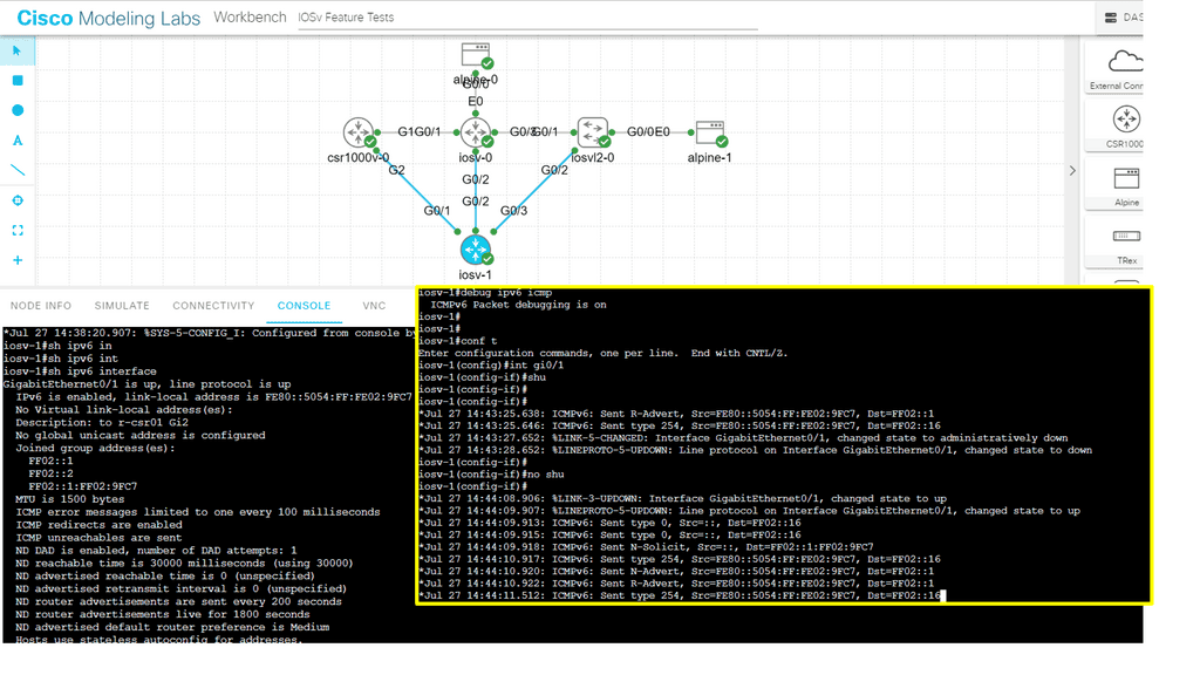
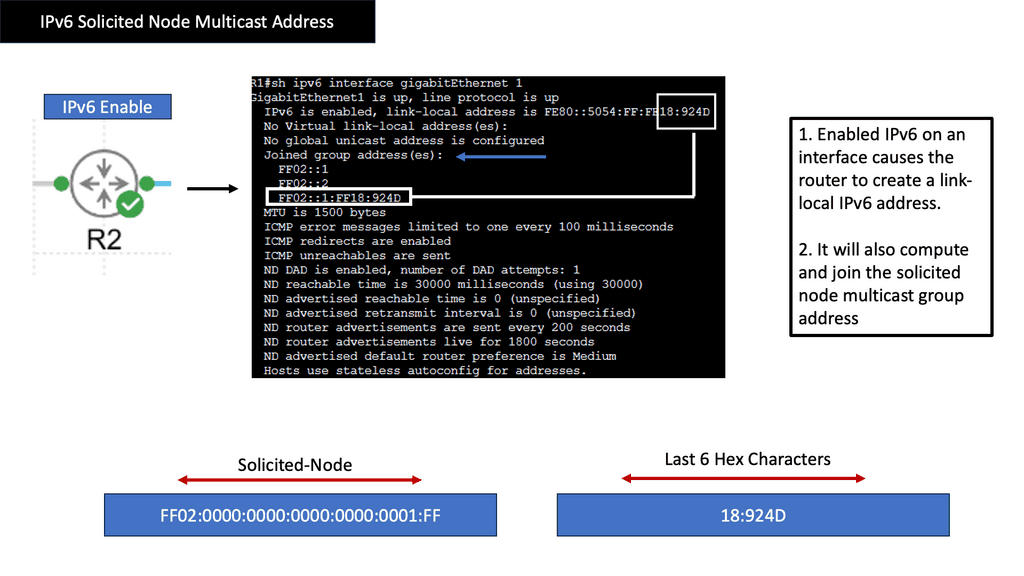
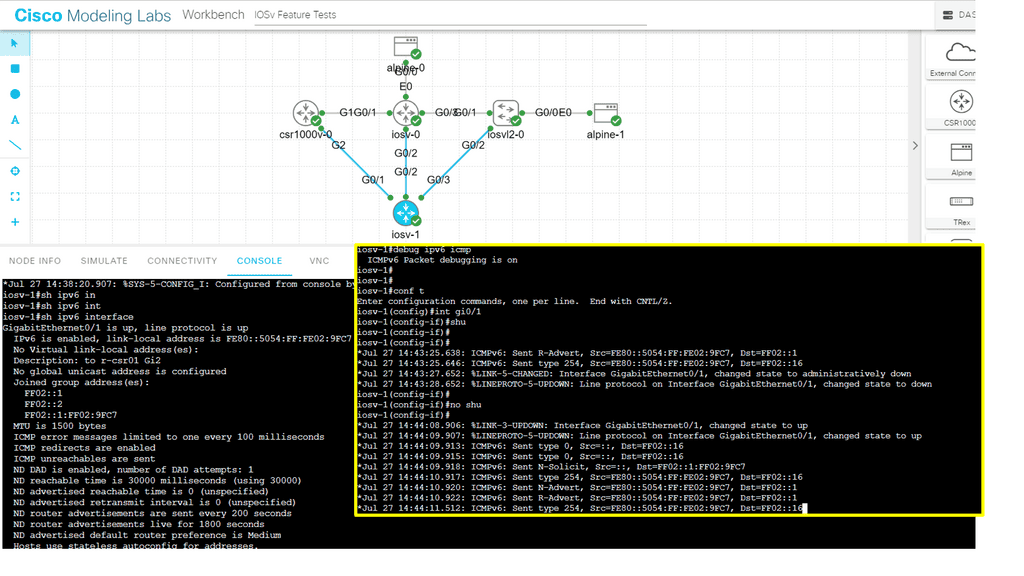
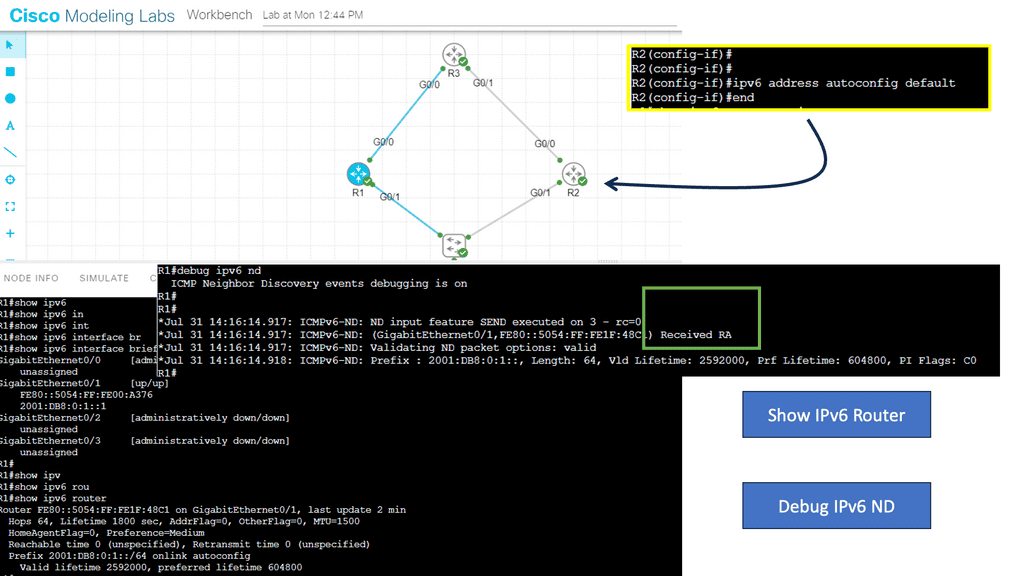
In the following lab, we demonstrate ICMPv6 RA messages. I have enabled IPv6 with the command ipv6 enable and left everything else to the defaults. IPv6 is not enabled anywhere else on the network. Therefore, when I do a shut and no shut on the IPv6 interfaces, you will see that we are sending ICMPv6 RA but not receiving it.

What is ICMPv6 Router Advertisement?
ICMPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) is a crucial component of the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) in IPv6 networks. Its primary function is to allow routers to advertise their presence and provide essential network configuration information to neighboring devices. Unlike its IPv4 counterpart, ICMPv6 RA is an integral part of the IPv6 protocol suite and plays a vital role in the auto-configuration of IPv6 hosts.
Key Features and Benefits:
1. Stateless Address Autoconfiguration: ICMPv6 RA enables the automatic configuration of IPv6 addresses for hosts within a network. By broadcasting periodic RAs, routers inform neighboring devices about the network prefix, allowing hosts to generate their unique IPv6 addresses accordingly. This stateless address autoconfiguration eliminates the need for manual address assignment, simplifying network administration.
2. Default Gateway Discovery: Routers use ICMPv6 RAs to advertise as default gateways. Hosts within the network listen to these advertisements and determine the most suitable default gateway based on the information provided. This process ensures efficient routing and enables seamless connectivity to external networks.
3. Prefix Information: ICMPv6 RAs include vital network prefixes and length information. This information is crucial for hosts to generate their IPv6 addresses and determine the appropriate subnet for communication. By advertising the prefix length, routers enable hosts to configure their subnets and ensure proper network segmentation.
4. Router Lifetime: RAs contain a router lifetime parameter that specifies the validity period of the advertised information. This parameter allows hosts to determine the duration for which the router’s information is valid. Hosts can actively seek updated RAs upon expiration to ensure uninterrupted network connectivity.
5. Duplicate Address Detection (DAD): ICMPv6 RAs facilitate the DAD process, which ensures the uniqueness of generated IPv6 addresses within a network. Routers indicate whether an address should undergo DAD by including the ‘A’ flag in RAs. This process prevents address conflicts and ensures the network’s integrity.
Guide on IPv6 RA
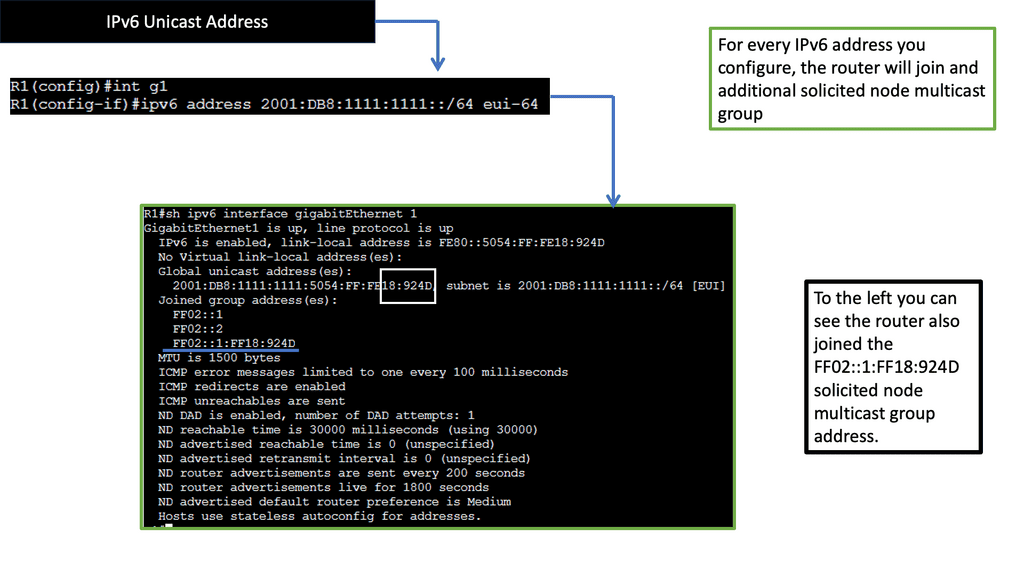
Hosts can use Router advertisements to automatically configure their IPv6 address and set a default route using the information they see in the RA. With the command ipv6 address autoconfig default we are setting an IPv6 address along with a default route.
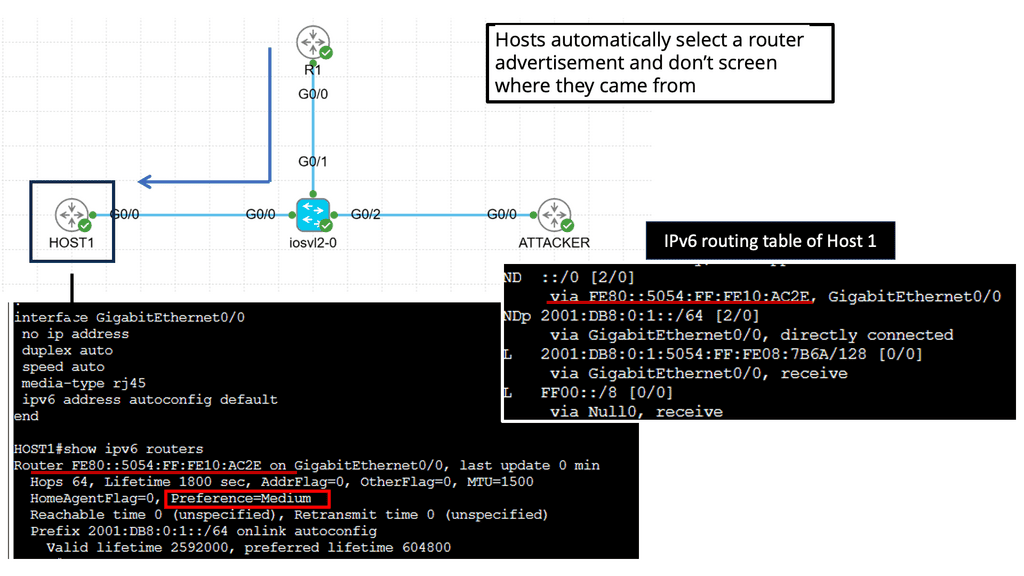
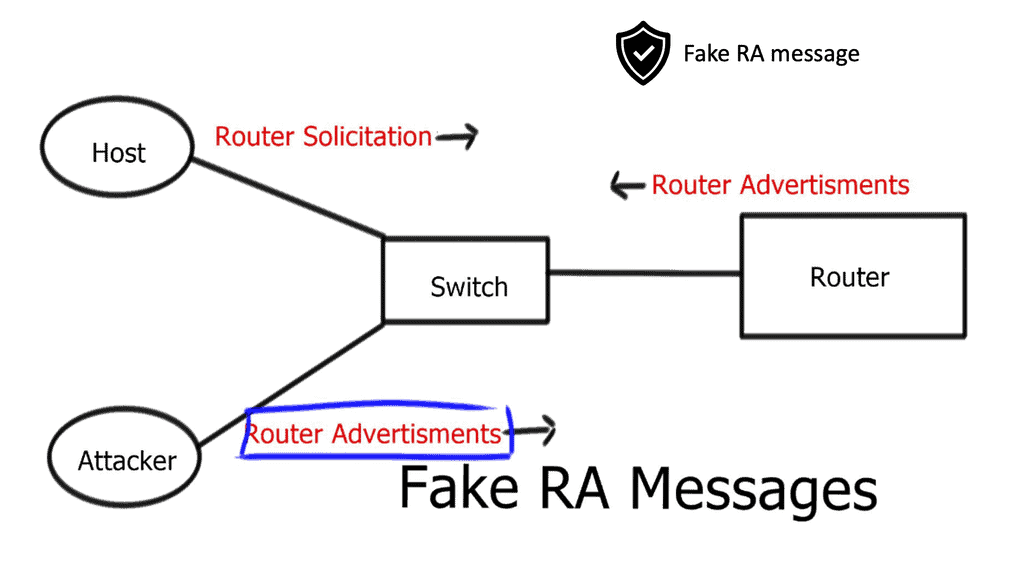
However, hosts automatically select a router advertisement and don’t care where it originated. This is how it was meant to be, but it does introduce a security risk since any device can send router advertisements, and your hosts will happily accept it.
IPv6 Best Practices & IPv6 Happy Eyeballs
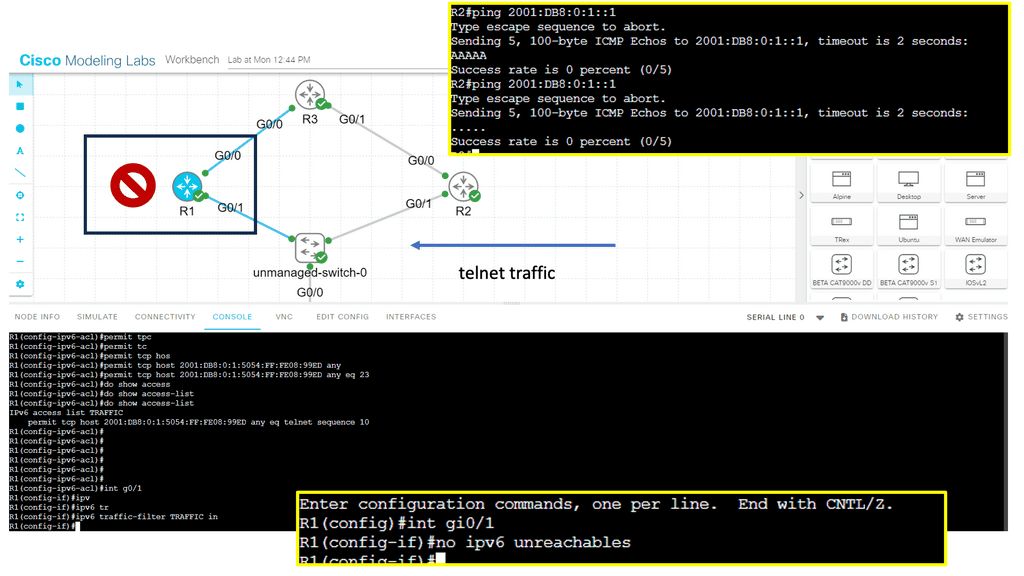
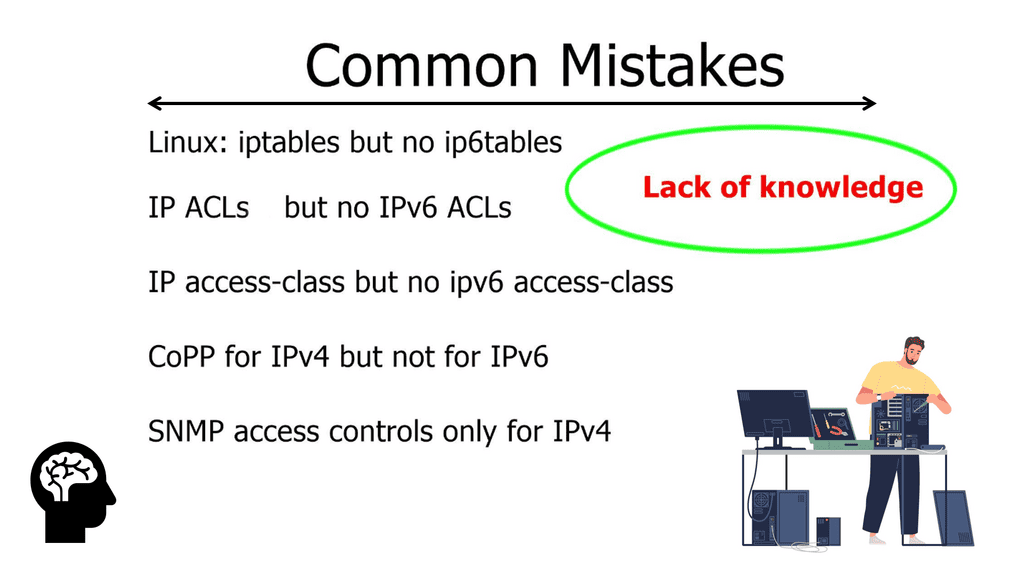
There are a few things to keep in mind when deploying mission-critical applications in an IPv6 environment. Significant problems arise from deployments of multiprotocol networks, i.e., dual stacking IPv4 and IPv6 on the same host. Best practices are quickly forgotten when you deploy IPv6. For example, network implementations forget to add IPv6 access lists to LAN interfaces and access-lists VTY lines to secure device telnet access, leading to IPv6 attacks.
Consistently implement IPv6 first-hop security mechanisms such as IPv6 RA guard and source address validation. In an IPv4 world, we have an IP source guard, ARP guard, and DHCP snooping. Existing IPv4 security measures have corresponding IPv6 counterparts; you must make the switches support these mechanisms. In virtual worlds, all these features are implemented on the hypervisor.
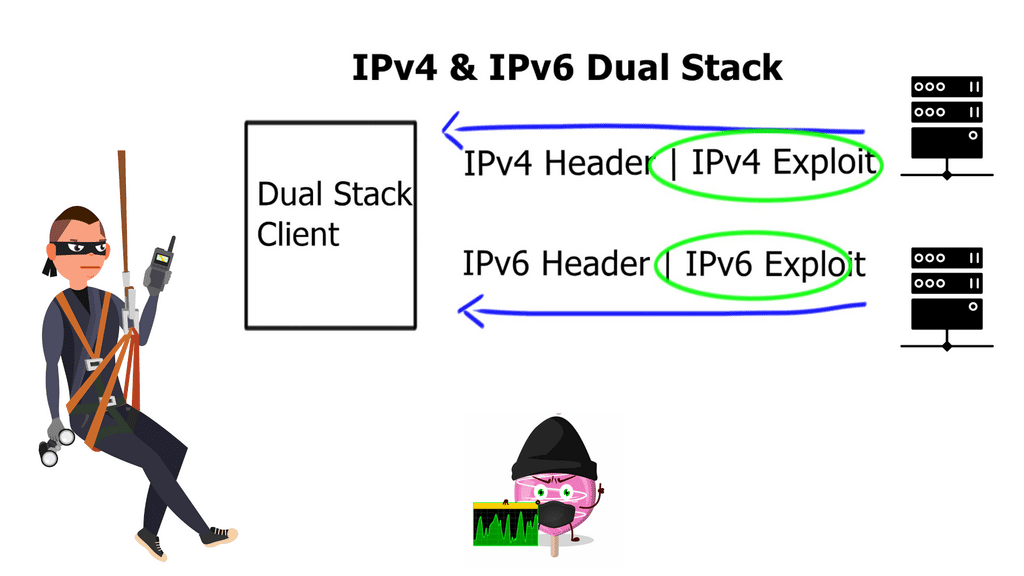
The first issue with dual-stack networks
The first problem we experience with dual-stack networks is that the same application can run over IPv4 and IPv6, and application transports (either IPv4 & or IPv6 transports) could change dynamically without any engineering control, i.e., application X is available over IPv4 one day and dynamically changes to IPv6 the next day. The dynamic change between IPv4 and IPv6 transports is known as the effect of the happy eyeball. Different operating systems (Windows and Linux) may react differently to this change, and no single operating system reacts in the same way.
Having IPv4 and IPv6 sessions established ( almost ) in parallel introduces significant layers of complexity to network troubleshooting and is non-deterministic. Therefore, designers should always attempt to design with simplicity and determinism in mind.
IPv6 high availability and IPv6 best practices
Avoid dual stack at all costs due to its non-deterministic and happy eyeballs effect. Instead, disable IPv6 unless needed or ensure that the connected switches only pass IPv4 and not IPv6.
High availability and IPv6 load balancing are not just network functions. They go deep into the application architecture and structures. Users should get the most they can, regardless of the operational network. The issue is that we have designed an end-to-end network because we usually do not control the first hop between the user and the network—for example, a smartphone connecting to 4G to download a piece of information.
We do not control the initial network entry points. Application developers are changing the concepts of high availability methods within the Application. New applications are now carrying out what is known as graceful degradation to be more resilient to failures. In scenarios with no network, graceful degradation permits some local action for users. For example, if the database server is down, users may still be able to connect but not perform any writing to the database.
IPv6 load balancing: First hop IPv6 High Availability mechanism
You can configure static or automatic configuration with Stateless Address Autoconfiguration ( SLAAC ) or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol ( DHCP ). Many prefer to use SLAAC. But for security or legal reasons, you need to know exactly what address you are using for what client forces you down the path of DHCPv6. In addition, IPv6 security concerns exist, and clients may set addresses manually and circumvent DHCPv6 rules.
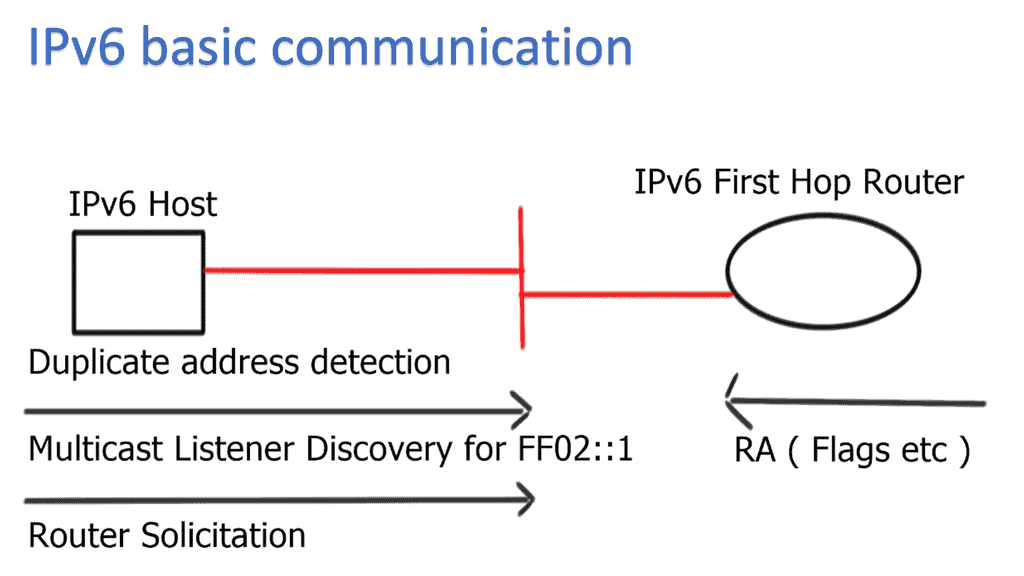
IPv6 basic communication:
Whenever a host starts, it creates an IPv6 link-local address from the Media Access Control Address ( MAC ) interface. First, nodes attempt to determine if anyone else is trying to use that address, and duplicate address detection ( DAD ) is carried out. Then, the host sends out Router Solicitation ( RS ) from its link-local to determine the routes on the network. All IPv6 routers respond with IPV6 RA (Router Advertisement).
IPv6 best practices and IPv6 Flags
Every IPv6 prefix has several flags. One type of flag configured with all prefixes is the “A” flag. “A” flag enables hosts to generate their IPv6 address on that link. If the “A” flag is set, the server may create another IPv6 address ( in addition to a static address ).
They result in servers having link-local, static, and auto-generated addresses. Numerous IPv6 addresses will not affect inbound sessions as inbound sessions can accept traffic on all IPv6 addresses. However, complications may arise when the server establishes sessions outbound, which can be unpredictable. To ensure this does not happen, ensure the A flag is cleared on IPv6 subnets.
IPv6 RA messages
RA messages can also indicate more information available, for example, when the IPv6 host sends a DHCP information request. This is indicated with the “O” flag in the RA message. Usually, I need to find out who the DNS server is.
Every prefix has “A” and “L” flags. When the “L” flag is set, two hosts can communicate directly, even if they are not on the same subnet (the router is advertising two subnets ), allowing them to communicate directly.
For example, if Host A and Host B are on the same or in different subnets and the routing device advertises the subnet without the “L” flag, the absence of the L flag tells the hosts not to communicate directly. All traffic goes via the router even if both hosts are in the same subnet.
If you are running an IPv4-only subnet and an intruder compromises the network and starts to send RA messages, all servers will auto-configure. The intruder can advertise as an IPv6 default router and IPv6 DNS server. Once the IPv6 attackers hit the default routers, they own the subnet and can do whatever they want with that traffic. With the “L” flag cleared, all the traffic will go through the intruder’s device. Intercepts everything.
First Hop IPv6 High Availability
IPv6 load balancing and VRRPv3
Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation ( MLAG ) and switch stack technology are identical to IPv4 and IPv6—there are no changes to Layer 2 switches. It would be best if you implemented changes at Layer 3. Routers advertise their presence with IPv6 RA messages, and host behavior will vary from one Operating System to the other. It will use the first valid RA message received and the load balance between all first-hop routers.
RA-based failures are appropriate for convergence of around 2 to 3 seconds. Is it possible to tweak this by setting RA timers? The minimum RA interval is 30 msec, and the minimum RA lifetime is 1 second. Avoid low timer values as RA-based failover consumes CPU cycles to process.
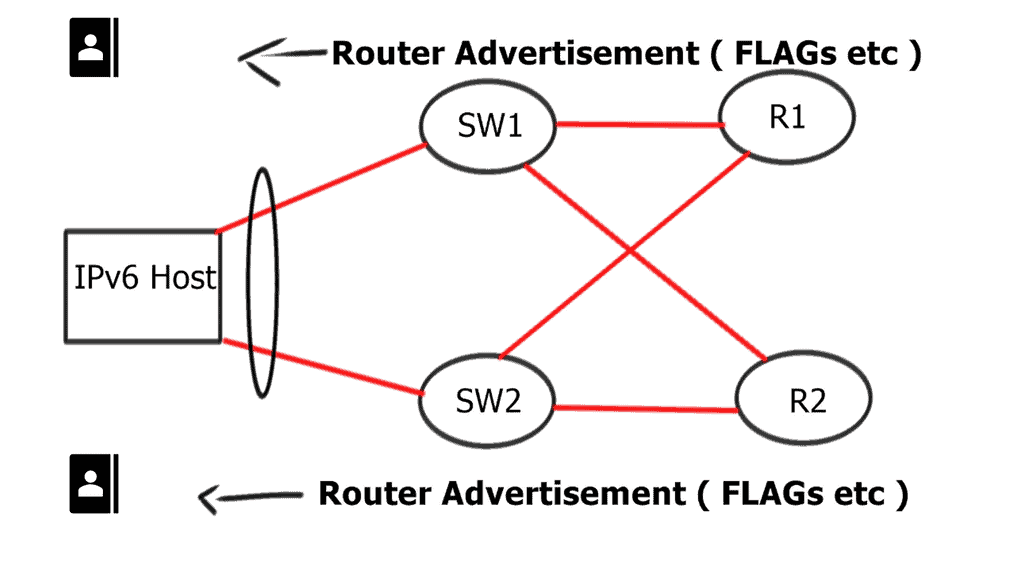
If you have stricter-convergence requirements, implement HSRP or VRRPv3 as the IPv6 first-hop redundancy protocol. It works the same way as it did in version 2. The master is the only one sending RA messages. All hosts send traffic to the VRRP IP address, which is resolved to the VRRP MAC address. Sub-second convergence is possible.
Load balancing between two boxes is possible. You could configure two VRRPv3 groups to server-facing subnets using the old trick. The implementation includes multiple VRRPv3 groups configured on the same interface with multiple VRRPv3 masters ( one per group ). Instead of having one VRRPv3 Master sending out RA advertisements, we now have various masters, and each Master sends RA messages with its group’s IPv6 and virtual MAC address.
The host will receive two RA messages and can do whatever the OS supports. Arista EOS has a technology known as Virtual ARP: both Layer 3 devices will listen to the same IPv6 MAC address, and whichever one gets the packet will process it.
Essential Functions and Features of ICMPv6 RA:
1. Prefix Information: RAs contain prefix information that allows hosts to autoconfigure their IPv6 addresses. This information includes the network prefix, length, and configuration flags.
2. Default Router Information: ICMPv6 RAs also provide information about the network’s default routers. This allows hosts to determine the best path for outbound traffic and ensures smooth communication with other nodes on the network.
3. MTU Discovery: ICMPv6 RAs assist in determining the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) for hosts, enabling efficient packet delivery without fragmentation.
4. Other Configuration Parameters: RAs can include additional configuration parameters such as DNS server addresses, network time protocol (NTP) server addresses, and other network-specific information.
ICMPv6 RA Configuration Options:
1. Managed Configuration Flag (M-Flag): The M-Flag indicates whether hosts should use stateful address configuration methods, such as DHCPv6, to obtain their IPv6 addresses. When set, hosts will rely on DHCPv6 servers for address assignment.
2. Other Configuration Flag (O-Flag): The O-Flag indicates whether additional configuration information, such as DNS server addresses, is available via DHCPv6. When set, hosts will use DHCPv6 to obtain this information.
3. Router Lifetime: The router lifetime field in RAs specifies the duration for which the router’s information should be considered valid. Hosts can use this value to determine how long to rely on a router for network connectivity.
ICMPv6 RA and Neighbor Discovery:
ICMPv6 RA is closely tied to the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), which facilitates the discovery and management of neighboring nodes within an IPv6 network. RAs play a significant role in the NDP process, ensuring proper address autoconfiguration, router selection, and network reachability.
ICMPv6 Router Advertisement is essential to IPv6 networking, enabling efficient auto-configuration and seamless connectivity. By leveraging ICMPv6 RAs, routers can efficiently advertise network configuration information, including address prefix, default gateway, and router lifetime.
Hosts within the network can then utilize this information to generate IPv6 addresses and ensure proper network segmentation. Understanding the significance of ICMPv6 Router Advertisement is crucial for network administrators and IT professionals working with IPv6 networks, as it forms the backbone of automatic address configuration and routing within these networks.
Closing Points: IPv6 RA
IPv6 Router Advertisement is a pivotal component of the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). Operating within the Internet Control Message Protocol for IPv6 (ICMPv6), RAs are essential messages sent by routers to announce their presence and provide necessary network parameters to IPv6 hosts. These advertisements carry critical information such as network prefixes, default gateway addresses, and link-layer address options, enabling hosts to configure themselves automatically and seamlessly integrate into the network.
One of the most significant advantages of IPv6 is its ability to facilitate stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC). Through Router Advertisements, hosts can generate their own IP addresses by appending a network prefix, received via RA, to a unique interface identifier. This eliminates the need for manual IP configuration or reliance on DHCP servers, streamlining the process of connecting devices to a network and enhancing overall efficiency.
While IPv6 Router Advertisements simplify network configuration, they also introduce potential security vulnerabilities. Attackers can exploit RA messages to perform malicious activities such as address spoofing or man-in-the-middle attacks. To mitigate these threats, network administrators must implement robust security measures such as RA Guard, Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND), and proper network segmentation to ensure a secure networking environment.
To harness the full potential of IPv6 RAs, it is essential to adhere to best practices. This includes regularly updating router firmware, configuring RA parameters to suit network needs, and monitoring network traffic for any suspicious RA activities. By doing so, network administrators can achieve optimal network performance, scalability, and security.
Summary: IPv6 RA
ICMPv6 RA (Internet Control Message Protocol Version 6 Router Advertisement) stands out as a crucial component in the vast realm of networking protocols. This blog post delved into the fascinating world of ICMPv6 RA, uncovering its significance, key features, and benefits for network administrators and users alike.
Understanding ICMPv6 RA
ICMPv6 RA, also known as Router Advertisement, plays a vital role in IPv6 networks. It facilitates the automatic configuration of network interfaces, enabling devices to obtain network addresses, prefixes, and other critical information without manual intervention.
Key Features of ICMPv6 RA
ICMPv6 RA offers several essential features that contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of IPv6 networks. These include:
1. Neighbor Discovery: ICMPv6 RA helps devices identify and communicate with neighboring devices on the network, ensuring seamless connectivity.
2. Prefix Advertisement: By providing prefix information, ICMPv6 RA enables devices to assign addresses to interfaces automatically, simplifying network configuration.
3. Router Preference: ICMPv6 RA allows routers to specify their preference level, assisting devices in selecting the most appropriate router for optimal connectivity.
Benefits of ICMPv6 RA
The utilization of ICMPv6 RA brings numerous advantages to network administrators and users:
1. Simplified Network Configuration: With ICMPv6 RA, network devices can automatically configure themselves, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing the risk of human errors.
2. Efficient Address Assignment: By providing prefix information, ICMPv6 RA enables devices to generate unique addresses effortlessly, promoting efficient address assignment and avoiding address conflicts.
3. Seamless Network Integration: ICMPv6 RA ensures smooth network integration by facilitating the discovery and communication of neighboring devices, enhancing overall network performance and reliability.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, ICMPv6 RA plays a crucial role in the world of networking, offering significant benefits for network administrators and users. Its ability to simplify network configuration, facilitate address assignment, and ensure seamless network integration makes it an indispensable tool in the realm of IPv6 networks.