What is Remote Browser Isolation
In today's digital landscape, remote browser isolation has emerged as a powerful solution for enhancing cybersecurity and protecting sensitive data. This innovative technology isolates web browsing activities from the local device, creating a secure environment that shields users from potential threats. In this blog post, we will dive into the world of remote browser isolation, exploring its benefits, implementation, and future prospects.
Remote browser isolation, also known as web isolation or browser isolation, is a security approach that separates web browsing activities from the user's device. By executing web sessions in a remote environment, remote browser isolation prevents potentially malicious code or content from infiltrating the user's system. It acts as a barrier between the user and the internet, ensuring a safe and secure browsing experience.
Enhanced Security: One of the primary advantages of remote browser isolation is its ability to mitigate web-based threats. By isolating web content and executing it in a separate environment, any malicious code or malware is contained and unable to affect the user's device. This significantly reduces the risk of cyberattacks such as phishing, drive-by downloads, and zero-day exploits.
Protection Against Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: Zero-day vulnerabilities are software vulnerabilities that are unknown to the vendor and, therefore, unpatched. Remote browser isolation provides a powerful defense against such vulnerabilities by executing web sessions in an isolated environment. Even if a website contains a zero-day exploit, it poses no threat to the user's device as the execution occurs remotely.
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) Security: With the rise of remote work and the increasing use of personal devices for business purposes, remote browser isolation offers a robust security solution. It allows employees to access corporate resources and browse the internet securely, without the need for complex VPN setups or relying solely on endpoint security measures.
Cloud-Based Deployments: Cloud-based remote browser isolation solutions have gained popularity due to their scalability and ease of deployment. These solutions route web traffic to a remote virtual environment, where browsing sessions are executed. The rendered content is then transmitted back to the user's device, ensuring a seamless browsing experience.
On-Premises Deployment: For organizations with specific compliance requirements or highly sensitive data, on-premises remote browser isolation solutions provide an alternative. In this approach, the isolation environment is hosted within the organization's infrastructure, granting greater control and customization options.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, remote browser isolation is expected to play an increasingly important role in cybersecurity strategies. The adoption of this technology is likely to grow, driven by the need for robust protection against web-based attacks. Moreover, advancements in virtualization and cloud technologies will further enhance the performance and scalability of remote browser isolation solutions.
Remote browser isolation is a game-changer in the realm of cybersecurity. By creating a secure and isolated browsing environment, it provides effective protection against web-based threats, zero-day vulnerabilities, and enables secure BYOD practices. Whether implemented through cloud-based solutions or on-premises deployments, remote browser isolation is poised to shape the future of web security, ensuring safer digital experiences for individuals and organizations alike.
Matt Conran
Highlights: What is Remote Browser Isolation
What is Browser Isolation
With browser isolation (remote browsing), internet browsing activity is separated from loading and displaying webpages locally.
Most website visitors load content and code directly from their local browsers. The content and code on the Internet often come from unknown sources (e.g., cloud hosting and web servers), which makes browsing the Internet somewhat risky from a security perspective. Web content is loaded and executed in the cloud by remote browser isolation (RBI), which underpins browser isolation.
Detecting hazardous web content is “outsourced” to remote browsing, like machines monitoring hazardous environments to protect humans. Consequently, users are protected from malicious websites (and the networks they connect to) that carry malware.
Types: Remote Browser Isolation?
Remote browser isolation (RBI), or cloud-hosted browser isolation, involves loading and executing webpages and code on a cloud server far from users’ local devices. Any malicious cookies or downloads are deleted after the user’s browsing session ends.
RBI technology protects users and corporate networks from untrusted browser activity. Users’ web browsing activities are typically conducted on a cloud server controlled by RBI vendors. Through RBI, users can interact with webpages normally without loading the entire website on their local device or browser. User actions, such as mouse clicks, keyboard inputs, and form submissions, are sent to a cloud server for further processing.
1. Enhanced Security: The primary advantage of remote browser isolation is its ability to provide enhanced web security. By isolating the browsing activity in a remote environment, any potential malware, zero-day exploits, or malicious websites are contained within the isolated environment, ensuring they cannot reach the user’s device. This dramatically reduces the risk of successful cyber attacks, as the user’s device remains protected even if a website is compromised.
2. Protection Against Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks are a significant concern for individuals and organizations. Remote browser isolation offers a robust defense against such attacks. By isolating the browsing session, any attempts to trick users into revealing sensitive information through fraudulent websites or email links are ineffective, as the malicious code is contained within the isolated environment.
3. Mitigation of Web-Based Threats: Remote browser isolation effectively mitigates web-based threats by preventing the execution of potentially malicious code on the user’s device. Whether it’s malware, ransomware, or drive-by downloads, all potentially harmful elements are executed within the isolated environment, ensuring the user’s device remains unharmed. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes the potential impact of web-based threats.
4. Compatibility and Ease of Use: One key advantage of remote browser isolation is its compatibility with various platforms and devices. Users can access isolated browsing sessions from any device, including desktops, laptops, and mobile devices, without compromising security. This flexibility ensures a seamless user experience while maintaining high security.
Example Technology: Browser Caching
Understanding Browser Caching
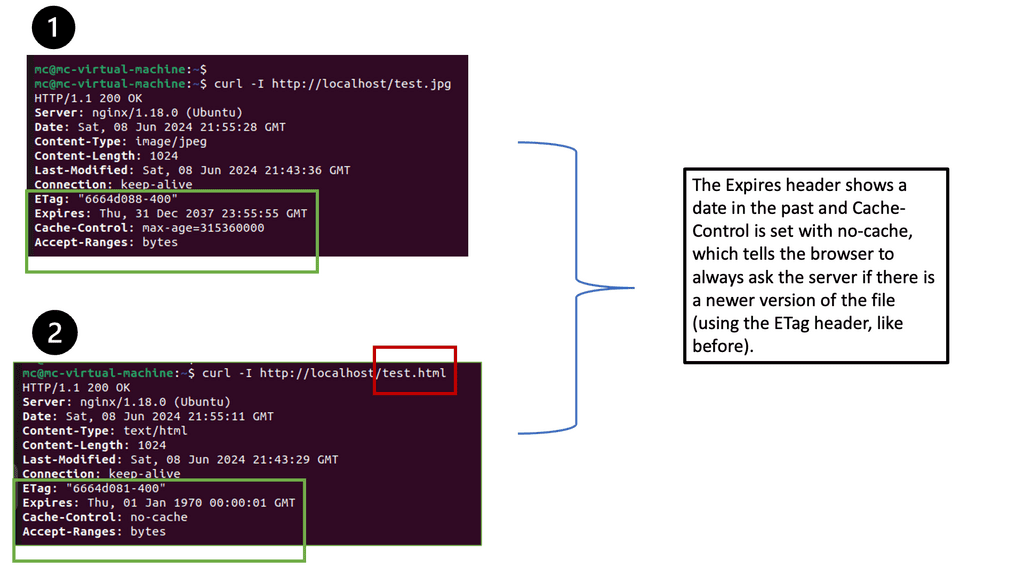
Browser caching is a mechanism that allows web browsers to store static files locally, such as images, CSS files, and JavaScript scripts. When a user revisits a website, the browser can retrieve these cached files from the local storage instead of making a new request to the server. This significantly reduces page load time and minimizes bandwidth usage.
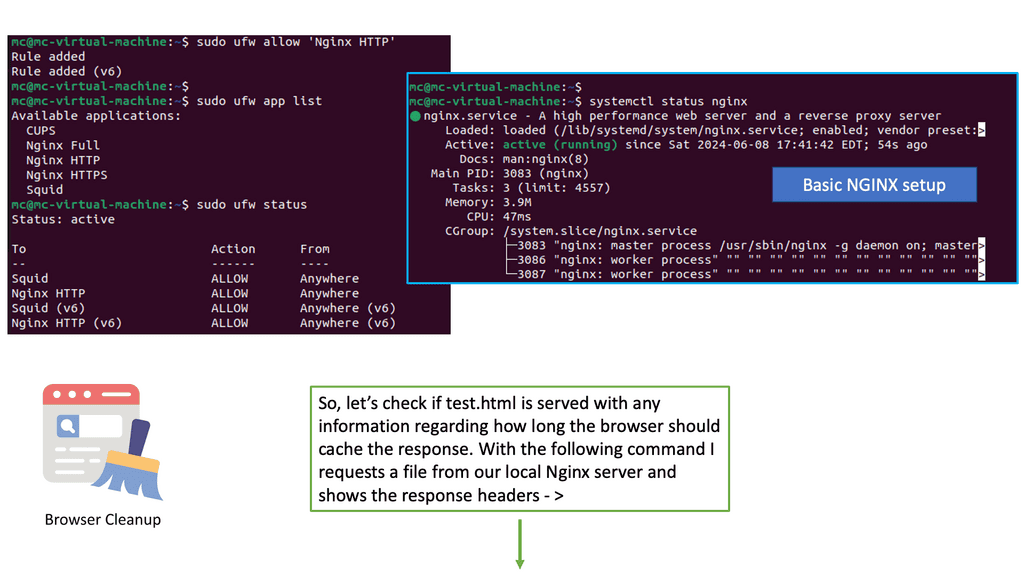
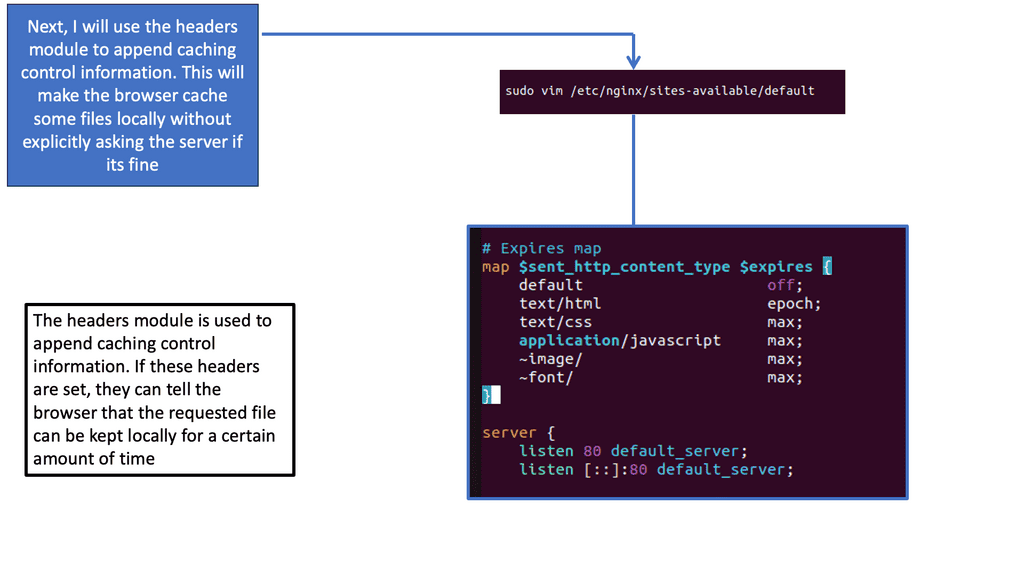
Nginx, a popular web server, offers a powerful module called “header” that enables fine-grained control over HTTP response headers. By utilizing this module, we can easily configure browser caching directives and control cache expiration for different types of files.
Implementing Browser Caching
To start leveraging browser caching with Nginx, we need to modify the server configuration. First, we define the types of files we want to cache, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript. Then, we set the desired expiration time for each file type, specifying how long the browser should keep the cached versions before checking for updates.
While setting a fixed expiration time for cached files is a good start, it’s important to fine-tune our cache expiration strategies based on file update frequency. For static files that rarely change, we can set longer expiration times. However, for dynamic files that are updated frequently, we should use techniques like cache busting or versioning to ensure users always receive the latest versions.
Implementing Remote Browser Isolation:
– Implementing remote browser isolation typically involves deploying a virtualized browsing environment that runs on a server or in the cloud. When a user initiates a web session, the web content is rendered within this isolated environment and securely transmitted to the user’s device as a visual stream, ensuring no potentially harmful code reaches the endpoint.
– Various approaches to implementing remote browser isolation exist, ranging from on-premises solutions to cloud-based services. Organizations can choose the option that best suits their requirements, considering scalability, ease of management, and integration with existing security infrastructure.
The Rise of Threats:
– The majority of attacks originate externally. Why? The Internet can be dirty because we can’t control what we don’t know. Browsing the Internet and clicking on uniform resource identifier (URL) links exposes the enterprise to compromise risks.
– These concerns can be very worrying for individuals who need to use the internet regularly, as they want a safe online browsing experience. Cyber security is becoming an increasingly vital consideration to be aware of when using the internet, with rising cyber-attacks forcing the need for Remote Browser Isolation (RBI).
Before you proceed, you may find the following posts helpful:
What is Remote Browser Isolation
The Challenging Landscape
It is estimated that the distribution of exploits used in cyber attacks by type of application attacked showed over 40% related to browser attacks. Android was next in line with 27% of the attack surface. As a result, we need to provide more security regarding Internet browsing.
Most compromises involve web-based attacks and standard plugins, such as Adobe, supported in the browser. Attacks will always happen, but your ability to deal with them is the key. If you use the Internet daily, check the security of your proxy server.
Challenge: Browser Attacks
Attacking through the browser is too easy, and the targets are too rich. Once an attacker has penetrated the web browser, they can move laterally throughout the network, targeting high-value assets such as a database server. Data exfiltration is effortless these days.
Attackers use social media accounts such as Twitter and even domain name systems (DNS) commonly not inspected by firewalls as file transfer mechanisms. We need to apply the zero trust network design default-deny posture to web browsing. This is known as Remote Browser Isolation.
Remote Browser Isolation: Zero Trust
Neil McDonald, an analyst from Gartner, is driving the evolution of Remote Browser Isolation. This feature is necessary to offer a complete solution to the zero-trust model. The zero-trust model already consists of micro-segmentation vendors that can be SDN-based, network-based appliances (physical or virtual), microservices-based, host-based, container-centric, IaaS built-in segmentation, or API-based. There are also a variety of software-defined perimeter vendors in the zero-trust movement.
So, what is Remote Browser Isolation (RBI)? Remote Browser Isolation starts with a default-deny posture, contains the ability to compromise, reduces the surface area for an attack, and, as sessions are restored to a known good state after each use, it is like having a dynamic segment of 1 for surfing the Internet. Remote browser offerings are a subset of browser isolation technologies that remove the browser process from the end user’s desktop.
You can host a browser on a terminal server and then use the on-device browser to browse to that browser, increasing the security posture. When you use HTML 5 connectivity, the rendering is done in the remote browser.
RBI – Sample Solution
Some vendors are coming out with a Linux-based, proxy-based solution. A proxy – often hosted on sites like https://www.free-proxy-list.net/ – acts as an internet gateway, a middleman for internet interactions. Usually, when you browse the Internet, you go to a non-whitelist site, but if it hasn’t been blacklisted, you will be routed to the remote system.
Real-time Rendering
You could have a small Linux-based solution in the demilitarized zone (DMZ) or the cloud in the proxy-based system. That container with docker container security best practices enabled will do the browsing for you. It will render the information in real time and send it back to the user using HTML5 as the protocol using images. For example, if you are going to a customer relationship management (CRM) system right now, you will go directly to that system as it is whitelisted.
Best Browsing Experience
But when you go to a website that hasn’t been defined, the system will open a small container, and that dedicated container can give you the browsing experience, and you won’t know the difference. As a result, you can mimic a perfect browsing experience without any active code running on your desktop while browsing.
Separating Browsing Activities
Remote browser isolation has emerged as a powerful solution in the fight against web-based cyber threats. Separating browsing activities from the user’s local device provides enhanced security, protects against phishing attacks, mitigates web-based threats, and offers compatibility across different platforms and devices.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, remote browser isolation is set to play a crucial role in safeguarding individuals and organizations from the ever-present dangers of the web.
Closing Points on RBI
Remote Browser Isolation is a security measure designed to protect users from web-based threats by isolating web browsing activities from the local network. Unlike traditional security measures that rely on detecting and blocking threats, RBI assumes that all web content could be potentially harmful. It works by executing web pages in a secure, isolated environment—often in the cloud—thus preventing any malicious content from reaching the user’s device. This proactive approach ensures that even if a web page is infected, the threat remains contained within the isolated environment.
The benefits of Remote Browser Isolation stretch beyond mere threat containment. Firstly, it significantly reduces the risk of phishing attacks, a common method used by cybercriminals. By isolating web pages, users are protected from inadvertently downloading ransomware or malware. Secondly, RBI improves compliance and data protection, essential for industries handling sensitive information. Additionally, it provides a seamless user experience, as the isolation occurs in real-time without noticeable delays, maintaining productivity and efficiency.
Implementing RBI in your organization involves several key steps. Begin by assessing your current cybersecurity posture and identifying areas where RBI can complement existing defenses. Collaborate with IT professionals to ensure a smooth integration process. Training and educating employees about the benefits and functionality of RBI will also enhance adoption rates. Moreover, regularly updating and maintaining the isolation environment is crucial to adapt to evolving cyber threats.
Many organizations across various sectors are already reaping the benefits of Remote Browser Isolation. Financial institutions, for example, utilize RBI to safeguard sensitive customer data from phishing and malware attacks. Educational institutions employ RBI to create a safe browsing environment for students and staff. These success stories highlight the versatility and effectiveness of RBI in enhancing cyber resilience and protecting critical information.
Summary: What is Remote Browser Isolation
In today’s digital landscape, where online threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, ensuring secure browsing experiences is paramount. Remote Browser Isolation (RBI) emerges as an innovative solution to tackle these challenges head-on. In this blog post, we delved into the world of RBI, its key benefits, implementation, and its role in enhancing cybersecurity.
Understanding Remote Browser Isolation
Remote Browser Isolation, also known as Web Isolation, is an advanced security technique that separates web browsing activities from the local device and moves them to a remote environment. By executing web code and rendering web content outside the user’s device, RBI effectively prevents malicious code and potential threats from reaching the user’s endpoint.
The Benefits of Remote Browser Isolation
Enhanced Security: RBI is a robust defense mechanism against web-based attacks such as malware, ransomware, and phishing. By isolating potentially harmful content away from the local device, it minimizes the risk of compromise and protects sensitive data.
Improved Productivity: With RBI, employees can access and interact with web content without worrying about inadvertently clicking on malicious links or compromising their devices. This freedom increases productivity and empowers users to navigate the web without fear.
Compatibility and User Experience: One of the notable advantages of RBI is its seamless compatibility with various devices and operating systems. Regardless of the user’s device specifications, RBI ensures a consistent and secure browsing experience without additional software installations or updates.
Implementing Remote Browser Isolation
Cloud-Based RBI Solutions: Many organizations opt for cloud-based RBI solutions, where web browsing activities are redirected to remote virtual machines. This approach offers scalability, ease of management, and reduced hardware dependencies.
On-Premises RBI Solutions: Some organizations prefer deploying RBI on their own infrastructure, which provides them with greater control over security policies and data governance. On-premises RBI solutions offer enhanced customization options and tighter integration with existing security systems.
Remote Browser Isolation in Action
Secure Web Access: RBI enables users to access potentially risky websites and applications in a safe and controlled environment. This proves particularly useful for industries like finance, healthcare, and government, where sensitive data protection is paramount.
Phishing Prevention: By isolating web content, RBI effectively neutralizes phishing attempts. The isolation prevents potential damage or data loss, even if a user unintentionally interacts with a fraudulent website or email link.
Conclusion:
Remote Browser Isolation stands at the forefront of modern cybersecurity strategies, offering a proactive and practical approach to protect users and organizations from web-based threats. RBI provides enhanced security, improved productivity, and seamless compatibility by isolating web browsing activities. Whether deployed through cloud-based solutions or on-premises implementations, RBI is a powerful tool for safeguarding digital experiences in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
- DMVPN - May 20, 2023
- Computer Networking: Building a Strong Foundation for Success - April 7, 2023
- eBOOK – SASE Capabilities - April 6, 2023



[…] the zero trust movement; software-defined perimeter (SDP) and micro-segmentation. Apparently, the remote browser isolation (RBI) is next in line to be added, and I’m sure there will be more arriving in the near […]