Nuage Networks: SD-WAN
Traditional WANs hinder business operations and don’t meet the demands of today’s applications. A new emerging WAN architecture called SD-WAN replaces existing WANs with a business-aware approach to networking. This approach is now thoroughly adopted by Nuage Networks, and their SD-WAN solution solves the limitations of conventional WANs.
Nuage Networks SD-WAN offers a centralized solution, adding intelligence to the WAN in forwarding, policy, and monitoring. Nuage understands all the existing WAN pitfalls, and their SD-WAN solution enables policy-based traffic forwarding. If you make routing aware of the application, you can steer traffic down different links based on business logic, not just destination-based forwarding. This is a two-part post – Part 1 introduces the challenges of traditional WAN, and Part 2 (this post) describes Nuage Networks SD-WAN solution.
For additional pre-information, you may find the following helpful:
WAN edge into the data center
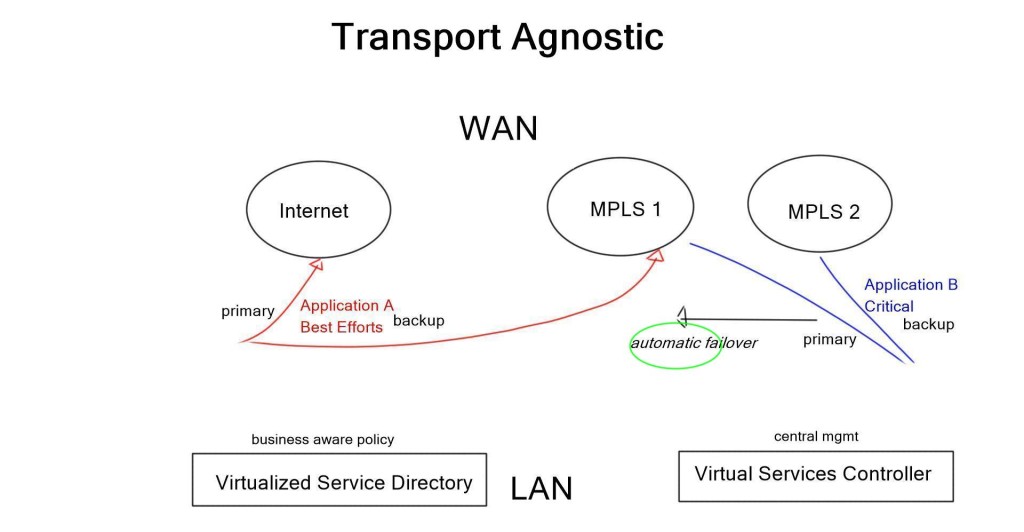
Nuage Networks are one of the first companies to incorporate the WAN edge into the data center, enabling one large network fabric and management entity. The entire solution is Virtualized Network Services (VNS), which uses many components from the existing Virtualized Service Platform (VSP). The WAN is no longer managed with complex control planes, Policy Based Routing (PBR), IP SLA, enhanced object tracking, and per-link QoS configurations. As the WAN is now combined with the internal data center, it can be managed as one entity via a central controller, known as Virtualized Services Controller (VSC), and a policy engine, known as Virtualized Service Directory (VSD).
A central viewpoint can now set policy based on business logic. Policies are then pushed down to the end nodes, Network Service Gateways (NSG), to carry out data plane forwarding. All these components combined create an overlay network – a network built on top of another. Overlay networking provides flexible topologies, allowing the application to control the network, not the network controlling the application.
Design Principles
Nuage’s SD-WAN solution might be new, but the control plane functions have been lifted from the 15-year-old source code of the 7750 SR Alcatel-Lucent routers. This provides network engineers with the comfort of knowing the IP stack is robust and proven in some of the largest global networks.
Nuage employs intelligent product design principles and does not try to reinvent the wheel. They use proven and field-tested protocols as much as possible. Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) and Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) are employed to form the Layer 2 & Layer 3 overlay. For scale-out controller clustering, MP-BGP is implemented between controllers.
MP-BGP is an enhancement to native BGP. BGP supports only unicast IPv4, while MP-BGP supports a wide variety of protocols. It is extensible and can carry a wide variety of information. The data plane NSG nodes are based on the popular Open vSwitch but optimized for enhanced performance. For optimized flow forwarding, Nuage decided to implement OpenFlow with proprietary extensions.
Nuage Networks SD-WAN transforms the WAN into a business-aware network, mapping application requirements to the network. This allows the creation of independent topologies per application. For example, mission-critical applications may use expensive leased lines, while lower-priority applications can use inexpensive best-effort Internet links. Previously, the application had to match and “fit” into the network, but with a Nuage SD-WAN, the application now controls the network topology. Multiple independent topologies per application is a key drivers for SD-WAN.
“Nuage Networks sponsor this post. All thoughts and opinions expressed are the authors.”
- DMVPN - May 20, 2023
- Computer Networking: Building a Strong Foundation for Success - April 7, 2023
- eBOOK – SASE Capabilities - April 6, 2023