Dynamic Workload Scaling ( DWS )
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses strive to deliver high-quality services while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency. To achieve this, organizations are increasingly adopting dynamic workload scaling techniques. This blog post will explore the concept of dynamic workload scaling, its benefits, and how it can help businesses optimize their operations.
- Adjustment of resources
Dynamic workload scaling refers to the automated adjustment of computing resources to match the changing demands of a workload. This technique allows organizations to scale their infrastructure up or down in real time based on the workload requirements. By dynamically allocating resources, businesses can ensure that their systems operate optimally, regardless of varying workloads.
- Defined Thresholds
Dynamic workload scaling is all about monitoring and distributing traffic at user-defined thresholds. Data centers are under pressure to support the ability to burst new transactions to available Virtual Machines ( VM ). In some cases, the VMs used to handle the additional load will be geographically dispersed, with both data centers connected by a Data Center Interconnect ( DCI ) link. The ability to migrate workloads within an enterprise hybrid cloud or in a hybrid cloud solution between enterprise and service provider is critical for business continuity for planned and unplanned outages.
Before you proceed, you may find the following post helpful:
- Network Security Components
- Virtual Data Center Design
- How To Scale Load Balancer
- Distributed Systems Observability
- Active Active Data Center Design
- Cisco Secure Firewall
Dynamic Workloads |
|
Back to basics with OTV.
Overlay Transport Virtualization (OTV) is an IP-based technology to provide a Layer 2 extension between data centers. OTV is transport agnostic, indicating that the transport infrastructure between data centers can be dark fiber, MPLS, IP routed WAN, ATM, Frame Relay, etc.
The sole prerequisite is that the data centers must have IP reachability between them. OTV permits multipoint services for Layer 2 extension and separated Layer 2 domains between data centers, maintaining an IP-based interconnection’s fault-isolation, resiliency, and load-balancing benefits.
Unlike traditional Layer 2 extension technologies, OTV introduces the Layer 2 MAC routing concept. The MAC-routing concept enables a control-plane protocol to advertise the reachability of Layer 2 MAC addresses. As a result, the MAC-routing idea has enormous advantages over traditional Layer 2 extension technologies that traditionally leveraged data plane learning, flooding Layer 2 traffic across the transport infrastructure.
Cisco and Dynamic Workloads
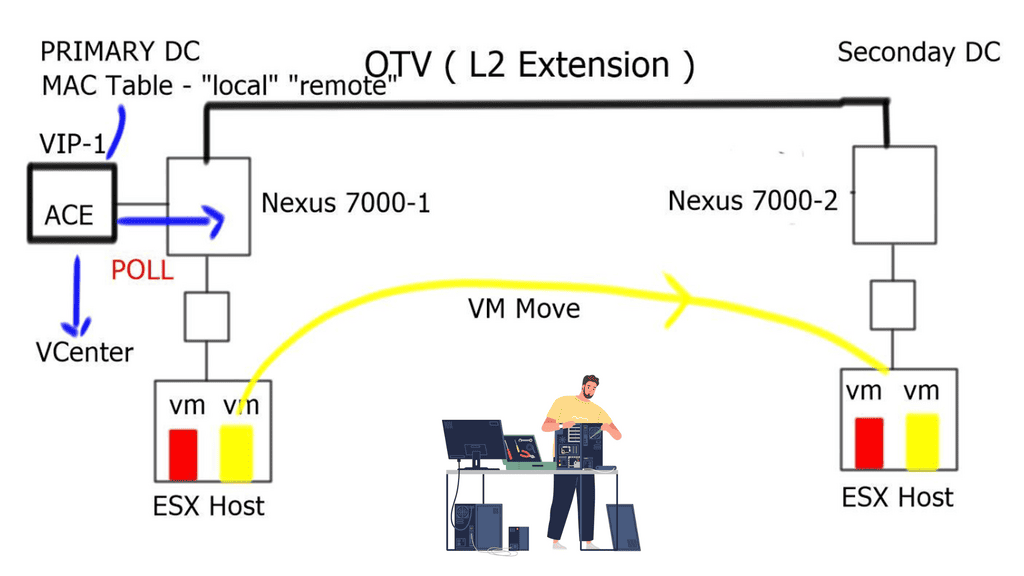
A new technology introduced by Cisco, called Dynamic Workload Scaling ( DWS ), satisfies the requirement of dynamically bursting workloads based on user-defined thresholds to available resource pools ( VMs ). It is tightly integrated with Cisco Application Control Engine ( ACE ) and Cisco’s Dynamic MAC-in-IP encapsulation technology known as Overlay Transport Virtualization ( OTV ), enabling resource distribution across Data Center sites. OTV provides the LAN extension method that keeps the virtual machine’s state as it passes locations, and ACE delivers the load-balancing functionality.
Dynamic workload scaling: How does it work?
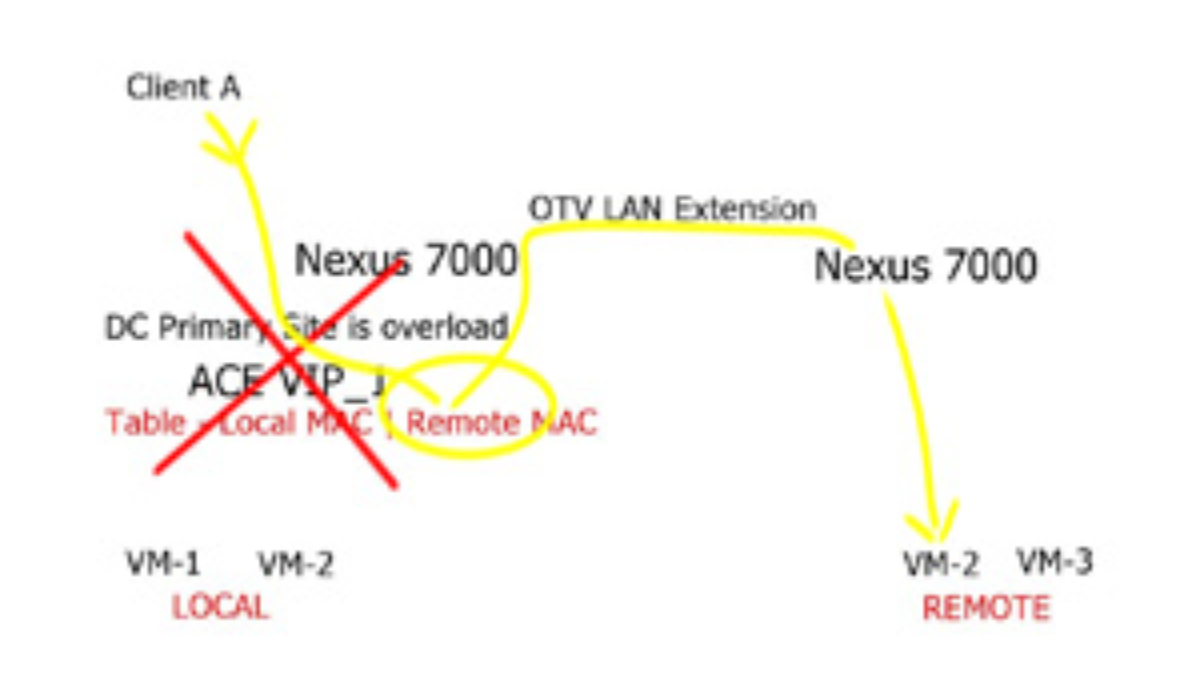
- DWS monitors the VM capacity for an application and expands that application to another resource pool during periods of peak usage. We provide a perfect solution for distributed applications among geographically dispersed data centers.
- DWS uses the ACE and OTV technologies to build a MAC table. It monitors the local MAC entries and those located via the OTV link to determine if a MAC entry is considered “Local” or “Remote.”
- The ACE monitors the utilization of the “local” VM. From these values, the ACE can compute the average load of the local Data Center.
- DWS uses two APIs. One is to monitor the server load information polled from VMware’s VCenter, and another API is to poll OTV information from the Nexus 7000.
- During normal load conditions, when the data center is experiencing low utilization, the ACE can load incoming balance traffic to the local VMs.
- However, when the data center experiences high utilization and crosses the predefined thresholds, the ACE will add the “remote” VM to its load-balancing mechanism.
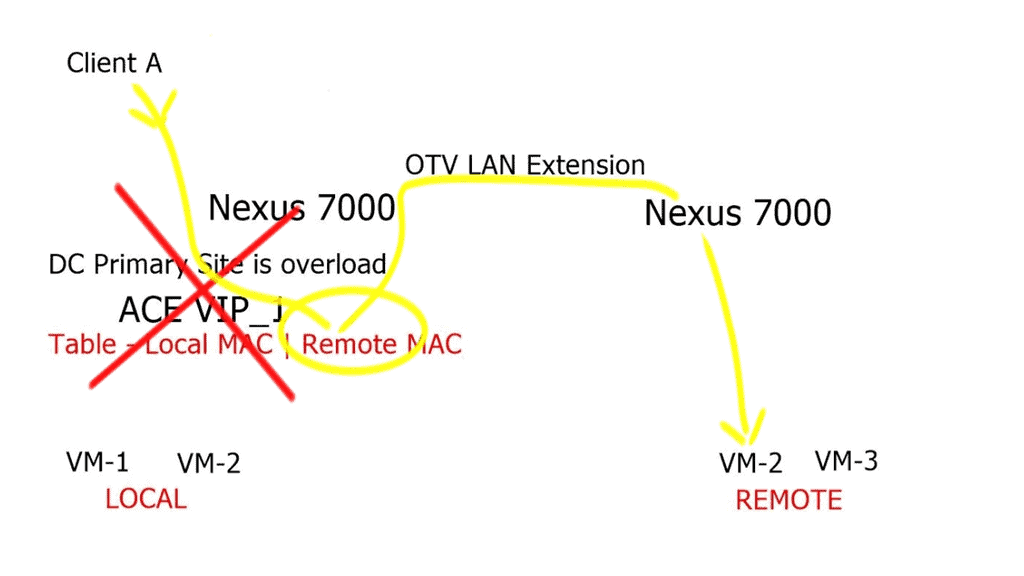
Dynamic workload scaling: Design considerations
During congestion, the ACE adds the “remote” VM to its load-balancing algorithm. The remote VM placed in the secondary data center could add additional load on the DCI. Essentially hair-pining traffic for some time as ingress traffic for the “remote” VM continues to flow via the primary data center. DWS should be used with Locator Identity Separation Protocol ( LISP ) to enable automatic move detection and optimal ingress path selection.
Benefits of Dynamic Workload Scaling:
1. Improved Efficiency:
Dynamic workload scaling enables businesses to allocate resources precisely as needed, eliminating the inefficiencies associated with over-provisioning or under-utilization. Organizations can optimize resource utilization and reduce operational costs by automatically scaling resources up during periods of high demand and scaling them down during periods of low demand.
2. Enhanced Performance:
With dynamic workload scaling, businesses can effectively handle sudden spikes in workload without compromising performance. Organizations can maintain consistent service levels and ensure smooth operations during peak times by automatically provisioning additional resources when required. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and retention.
3. Cost Optimization:
Traditional static infrastructure requires businesses to provision resources based on anticipated peak workloads, often leading to over-provisioning and unnecessary costs. Dynamic workload scaling allows organizations to provision resources on demand, resulting in cost savings by paying only for the resources utilized. Additionally, by scaling down resources during periods of low demand, businesses can further reduce operational expenses.
4. Scalability and Flexibility:
Dynamic workload scaling allows businesses to scale their operations as needed. Whether expanding to accommodate business growth or handling seasonal fluctuations, organizations can easily adjust their resources to match the workload demands. This scalability and flexibility enable businesses to respond quickly to changing market conditions and stay competitive.
Dynamic workload scaling has emerged as a crucial technique for optimizing efficiency and performance in today’s digital landscape. By dynamically allocating computing resources based on workload requirements, businesses can improve efficiency, enhance performance, optimize costs, and achieve scalability. Implementing robust monitoring systems, automation, and leveraging cloud computing services are critical steps toward successful dynamic workload scaling. Organizations can stay agile and competitive and deliver exceptional customer service by adopting this approach.
Key Features of Cisco Dynamic Workload Scaling:
Intelligent Automation:
Cisco’s dynamic workload scaling solutions leverage intelligent automation capabilities to monitor real-time workload demands. By analyzing historical data and utilizing machine learning algorithms, Cisco’s automation tools can accurately predict future workload requirements and proactively scale resources accordingly.
Application-Aware Scaling:
Cisco’s dynamic workload scaling solutions are designed to understand the unique requirements of different applications. By utilizing application-aware scaling, Cisco can allocate resources based on the specific needs of each workload, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing resource wastage.
Seamless Integration:
Cisco’s dynamic workload scaling solutions seamlessly integrate with existing IT infrastructures, allowing businesses to leverage their current investments. This ensures a smooth transition to dynamic workload scaling without extensive infrastructure overhauls.
Conclusion:
In today’s dynamic business environment, efficiently managing and scaling workloads is critical for organizational success. Cisco’s dynamic workload scaling solutions provide businesses with the flexibility, performance optimization, and cost savings necessary to thrive in an ever-changing landscape. By leveraging intelligent automation, application-aware scaling, and seamless integration, Cisco empowers organizations to adapt and scale their workloads effortlessly. Embrace Cisco’s dynamic workload scaling and unlock the full potential of your business operations.