BGP SDN
The networking landscape has significantly shifted towards Software-Defined Networking (SDN) in recent years. With its ability to centralize network management and streamline operations, SDN has emerged as a game-changing technology. One of the critical components of SDN is Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), a routing protocol that plays a vital role in connecting different autonomous systems. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of BGP SDN and its implications for the future of networking.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a dynamic routing protocol that facilitates the exchange of routing information between different networks. It enables the establishment of connections and the exchange of network reachability information across autonomous systems. BGP is the glue that holds the internet together, ensuring that data packets are delivered efficiently across various networks.
Scalability and Flexibility: BGP SDN empowers network administrators with the ability to scale their networks effortlessly. By leveraging BGP's inherent scalability and SDN's programmability, network expansion becomes a seamless process. Additionally, the flexibility provided by BGP SDN allows for the customization of routing policies, enabling network administrators to adapt to changing network requirements.
Traffic Engineering and Optimization: Another significant advantage of BGP SDN is its capability to perform traffic engineering and optimization. With granular control over routing decisions, network administrators can efficiently manage traffic flow, ensuring optimal utilization of network resources. This results in improved network performance, reduced congestion, and enhanced user experience.
Dynamic Path Selection: BGP SDN enables dynamic path selection based on various parameters, such as network congestion, link quality, and cost. This dynamic nature of BGP SDN allows for intelligent and adaptive routing decisions, ensuring efficient data transmission and load balancing across the network.
Policy-Based Routing: BGP SDN allows network administrators to define routing policies based on specific criteria. This capability enables the implementation of fine-grained traffic management strategies, such as prioritizing certain types of traffic or directing traffic through specific paths. Policy-based routing enhances network control and enables the optimization of network performance for specific applications or user groups.
BGP SDN represents a significant leap forward in network management. By combining the robustness of BGP with the flexibility of SDN, organizations can unlock new levels of scalability, control, and optimization. Whether it's enhancing network performance, enabling dynamic path selection, or implementing policy-based routing, BGP SDN paves the way for a more efficient and agile network infrastructure.
Matt Conran
Highlights: BGP SDN
BGP SDN, which stands for Border Gateway Protocol Software-Defined Networking, combines the power of traditional BGP routing protocols with the flexibility and programmability of SDN. It enables network administrators to have granular control over their routing decisions and allows for dynamic and automated network provisioning.
**BGP SDN Centralized Forwarding**
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, network management and optimization have become more critical than ever. With the burgeoning demands for higher bandwidth, lower latency, and greater network reliability, traditional networking methods are increasingly finding themselves inadequate. This is where BGP SDN Centralized Forwarding comes into play, offering a revolutionary approach to network management by combining the strengths of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN).
**Understanding BGP and SDN**
Before delving into the centralized forwarding aspect, it’s crucial to understand the foundational components: BGP and SDN. BGP, a robust and mature protocol, has been the cornerstone of the internet’s routing infrastructure for decades. It is responsible for making core routing decisions and ensuring data packets find their way across the networks of different organizations. On the other hand, SDN is a modern paradigm that separates the control plane from the data plane, allowing for more agile and flexible network management. By integrating these two technologies, we can create a more efficient and manageable network.
**The Need for Centralized Forwarding**
Traditional BGP implementations operate in a distributed manner, which, while reliable, can lead to inefficiencies and complexities in network management. Centralized forwarding through SDN changes this by offering a holistic view and control over the network. This centralized approach allows network administrators to implement policies and changes from a single point, reducing complexities and potential errors. This is especially beneficial in large-scale networks where consistent and efficient routing decisions are imperative.
Key BGP SDN Considerations:
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability: BGP SDN brings unmatched flexibility to network operators. By decoupling the control plane from the data plane, it allows for dynamic rerouting and network updates without disrupting the overall network operation. This flexibility also enables seamless scalability as networks grow or evolve over time.
Improved Network Performance and Efficiency: With BGP SDN, network administrators can optimize traffic flow by dynamically adjusting routing decisions based on real-time network conditions. This intelligent traffic engineering ensures efficient resource utilization, reduced latency, and improved overall network performance.
Simplified Network Management: By leveraging programmability, BGP SDN simplifies network management tasks. Network administrators can automate routine configuration changes, implement policies, and troubleshoot network issues more efficiently. This leads to significant time and cost savings.
Rapid Deployment of New Services: BGP SDN enables faster service deployment by allowing administrators to define routing policies and service chaining through software. This eliminates the need for manual configuration changes on individual network devices, reducing deployment time and potential human errors.
Improved Network Security: BGP SDN provides enhanced security features by allowing fine-grained control over network access and traffic routing. It enables the implementation of robust security policies, such as traffic isolation and encryption, to protect against potential threats.
BGP-based SDN
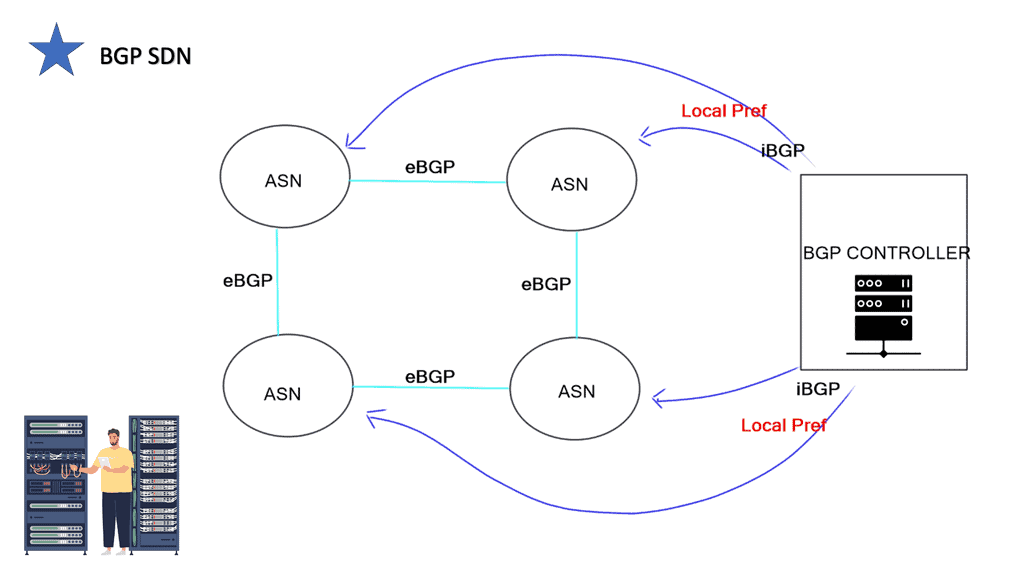
BGP SDN, also known as BGP-based SDN, is an approach that leverages the strengths of BGP and SDN to enhance network control and management. Unlike traditional networking architectures, where individual routers make routing decisions, BGP SDN centralizes the control plane, allowing for more efficient routing and dynamic network updates. By separating the control plane from the data plane, operators can gain greater visibility and control over their networks.
BGP SDN offers a range of features and benefits that make it an attractive choice for network operators. First, it provides enhanced scalability and flexibility, allowing networks to adapt to changing demands and traffic patterns. Second, operators can easily define and modify routing policies, ensuring optimal traffic distribution across the network.
Another notable feature is the ability to enable network programmability. Using APIs and controllers, network operators can dynamically provision and configure network services, making deploying new applications and services easier. This programmability also opens doors for automation and orchestration, simplifying network management and reducing operational costs.
Use Cases of BGP SDN: BGP SDN has found applications in various domains, from data centers to wide-area networks. In data centers, it enables efficient load balancing, traffic engineering, and rapid service deployment. It also allows for the creation of virtual networks, enabling secure multi-tenancy and resource isolation.
BGP SDN brings benefits such as traffic engineering and improved network resilience in wide-area networks. It enables dynamic path selection, optimizes traffic flows, and reduces congestion. Additionally, BGP SDN can enable faster network recovery during failures, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
BGP vs SDN:
BGP, also known as the routing protocol of the Internet, plays a vital role in facilitating communication between autonomous systems (AS). It enables the exchange of routing information and determines the best path for data packets to reach their destinations. With its robust and scalable design, BGP has become the go-to protocol for inter-domain routing.
SDN, on the other hand, is a paradigm shift in network architecture. SDN centralizes network management and allows for programmability and flexibility by decoupling the control plane from the forwarding plane. With SDN, network administrators can dynamically control network behavior through a centralized controller, simplifying network management and enabling rapid innovation.
Synergizing BGP and SDN
When BGP and SDN converge, the result is a potent combination that transcends the limitations of traditional networking. SDN’s centralized control plane empowers network operators to control BGP routing policies dynamically, optimizing traffic flow and enhancing network performance. By leveraging SDN controllers to manipulate BGP attributes, operators can quickly implement traffic engineering, load balancing, and security policies.
The Role of SDN:
In contrast to the decentralized control logic that underpins the construction of the Internet as a complex bundle of box-centric protocols and vertically integrated solutions, software-defined networking (SDN) advocates the separation of control logic from hardware and its centralization in software-based controllers. Introducing innovative applications and incorporating automatic and adaptive control into these fundamental tenets can ease network management and enhance user experience.
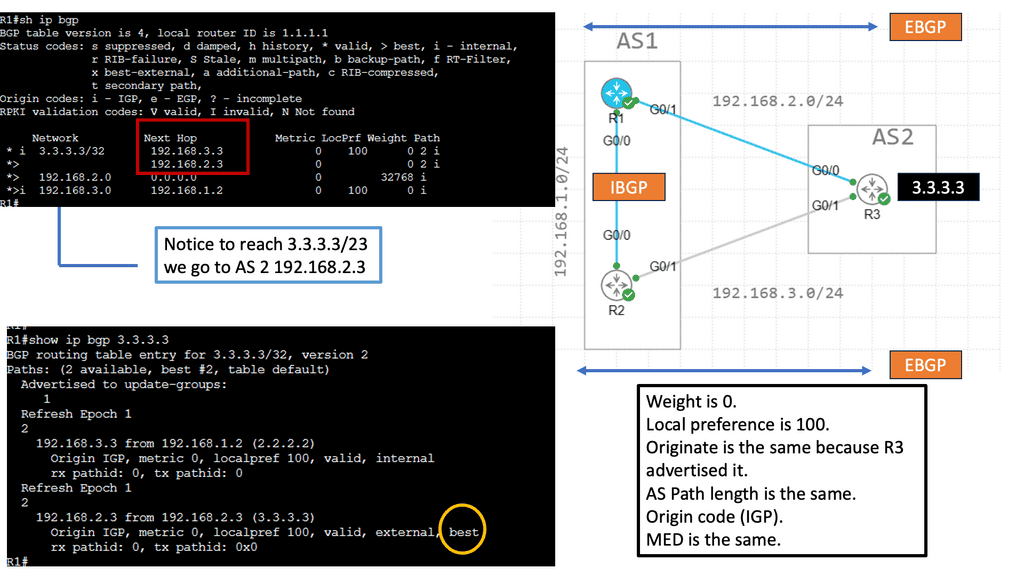
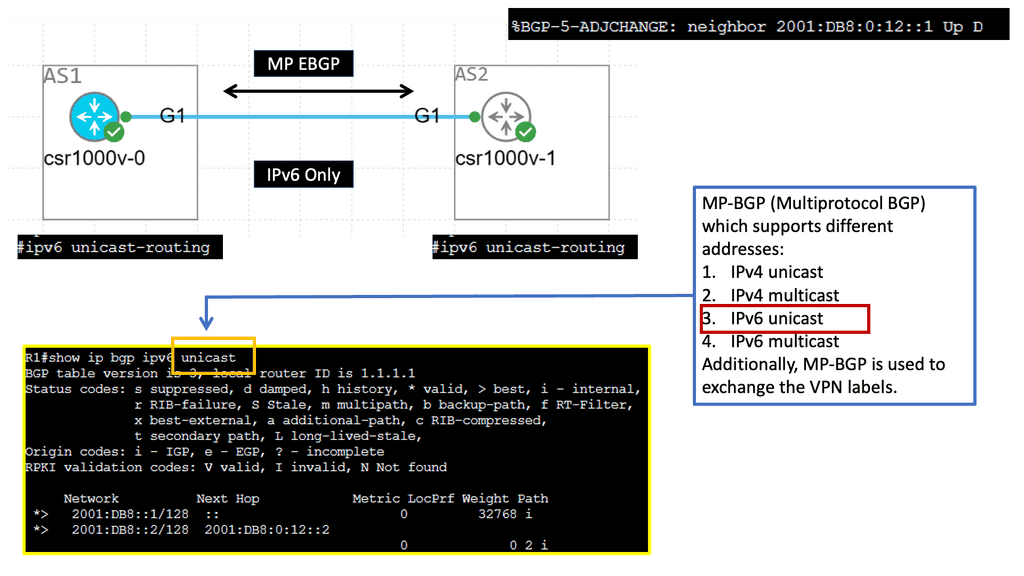
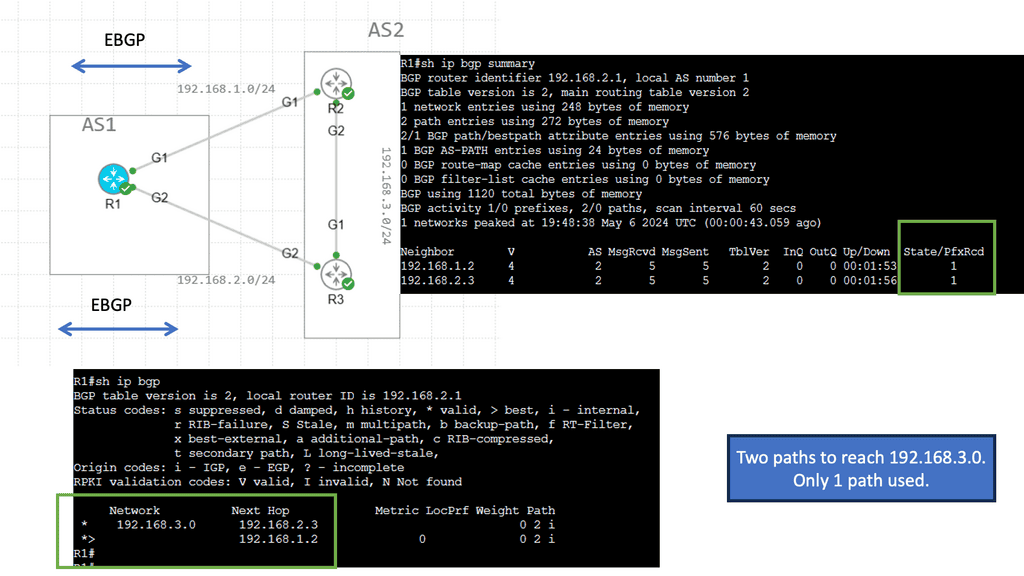
Recap Technology: EBGP over IBGP
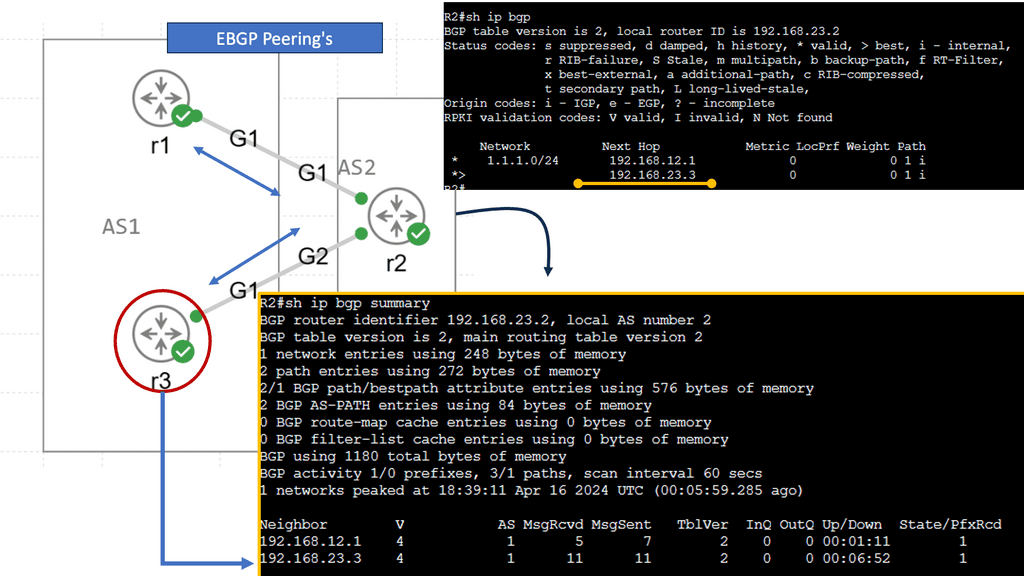
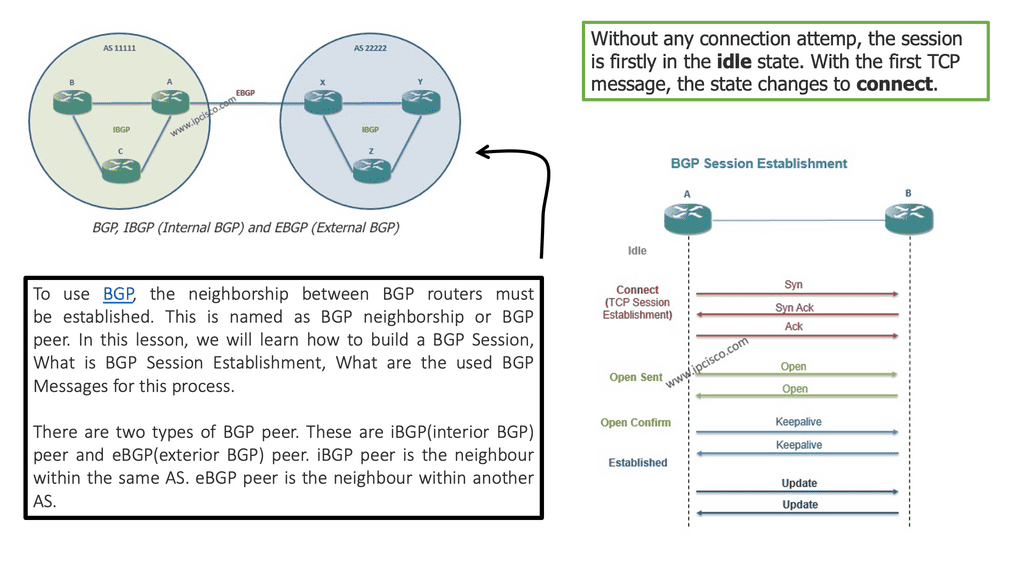
EBGP, or External Border Gateway Protocol, is a routing protocol typically used between different autonomous systems (AS). It facilitates the exchange of routing information between these AS, allowing efficient data transmission across networks. EBGP’s primary characteristic is that it operates between routers in different AS, enabling interdomain routing.
IBGP, or Internal Border Gateway Protocol, operates within a single autonomous system (AS). It establishes peering relationships between routers within the same AS, ensuring efficient routing within the network. Unlike EBGP, IBGP does not involve exchanging routes between different AS; instead, it focuses on sharing routing information between routers within the same AS.
While both EBGP and IBGP serve to facilitate routing, there are crucial differences between them. One significant distinction lies in the scope of their operation. EBGP connects routers across different AS, making it ideal for interdomain routing. On the other hand, IBGP connects routers within the same AS, providing efficient intradomain routing.
EBGP is commonly used by internet service providers (ISPs) to exchange routing information with other ISPs, ensuring global reachability. It enables autonomous systems to learn about and select the best paths to reach specific destinations. IBGP, on the other hand, helps maintain synchronized routing information within an AS, preventing routing loops and ensuring efficient internal traffic flow.
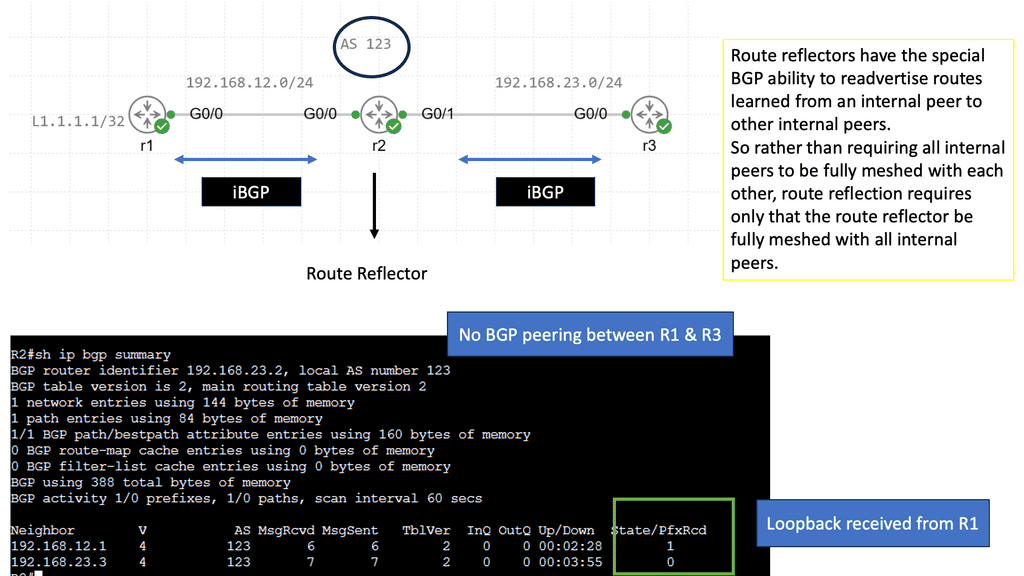
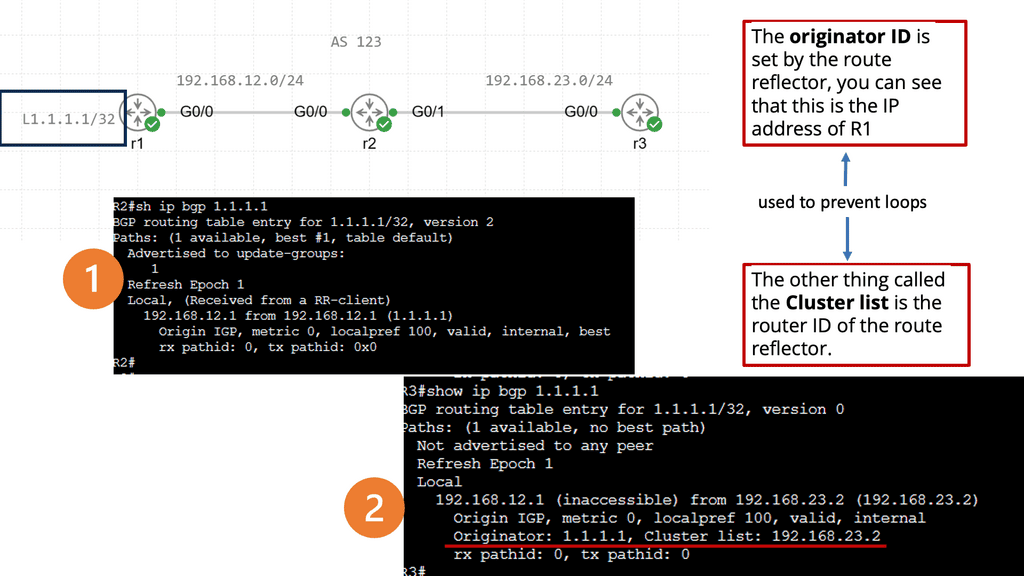
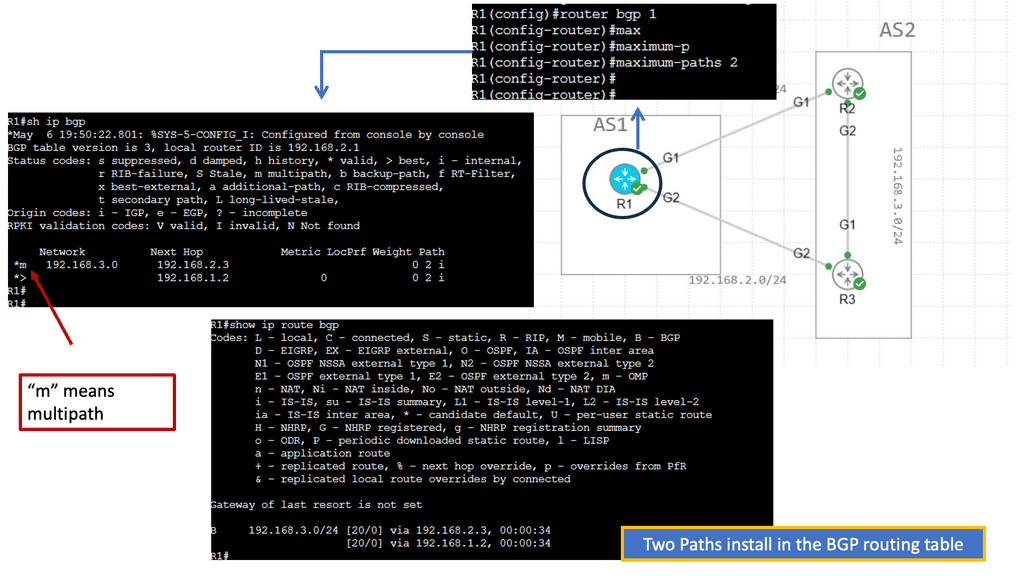
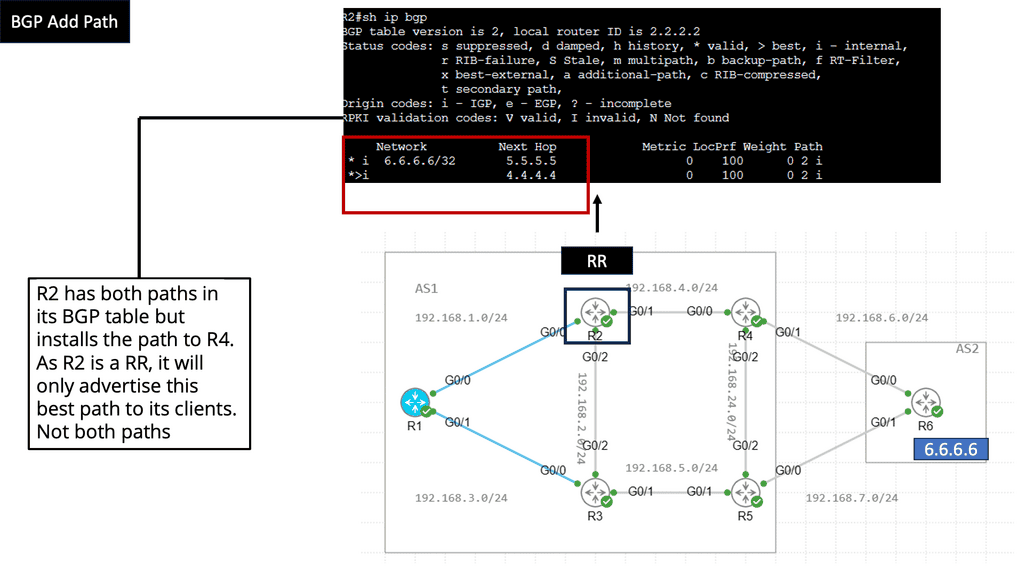
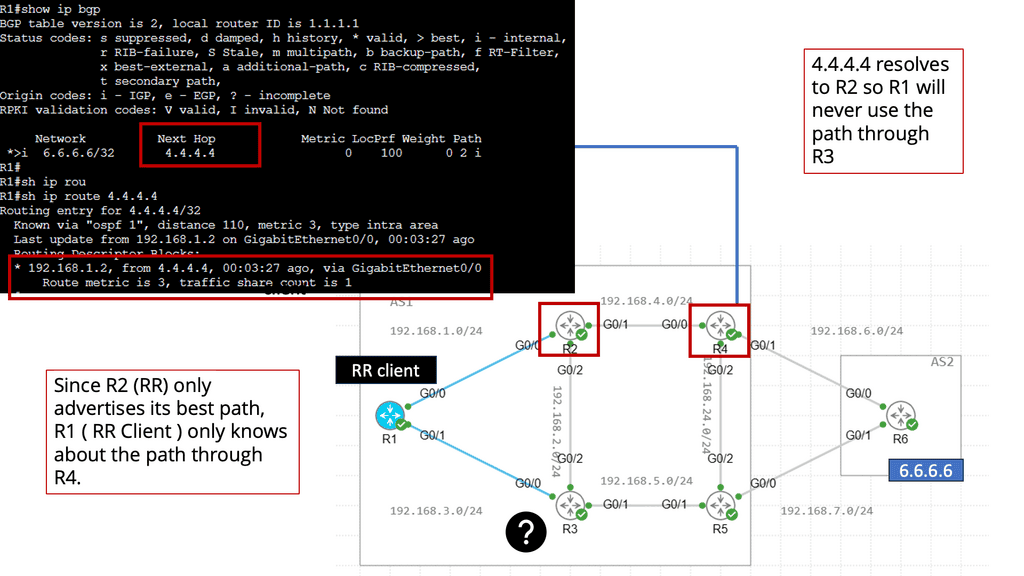
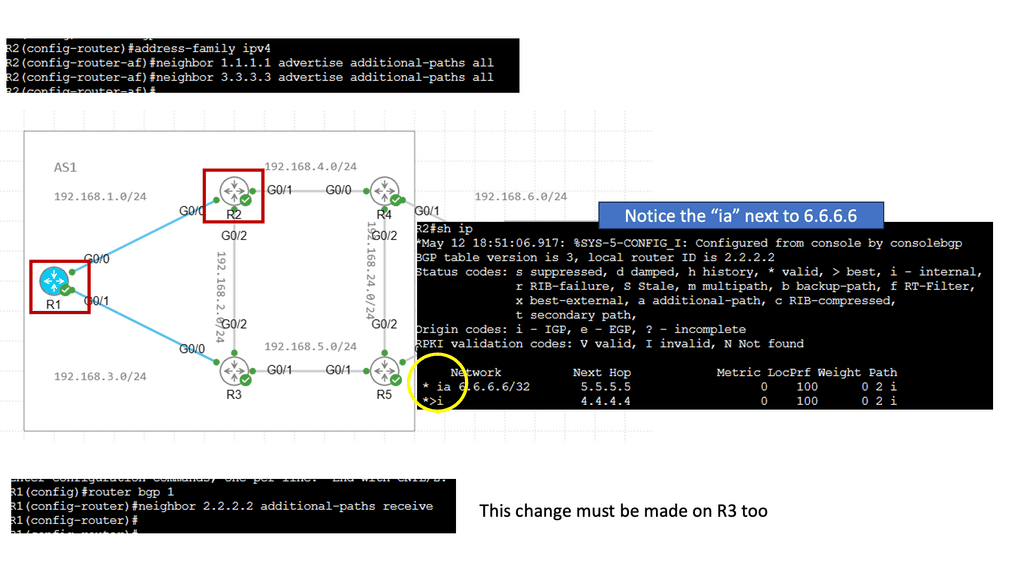
Recap Technology: BGP Route Reflection
Understanding BGP Route Reflection
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is a crucial routing protocol in large-scale networks. However, route propagation can become cumbersome and resource-intensive in traditional BGP setups. BGP route reflection offers an elegant solution by reducing the number of full-mesh connections needed in a network.
By implementing BGP route reflection, network administrators can achieve significant advantages. Firstly, it reduces resource consumption by eliminating the need for every router to maintain full mesh connectivity. This leads to improved scalability and reduced overhead. Additionally, it enhances network stability and convergence time, ensuring efficient routing updates.
To implement BGP route reflection, several key steps need to be followed. Firstly, identify the routers that will act as route reflectors in the network. These routers should have sufficient resources to handle the increased routing information. Next, configure the route reflectors and their respective clients, ensuring proper peering relationships. Finally, monitor and fine-tune the route reflection setup to optimize performance.
Challenges to Networking
Over the past few years, there has been a growing demand for a new approach to networking to address the many issues associated with current networks. According to the SDN approach, networking operations can be simplified, network management can be optimized, and innovation and flexibility can be introduced.
According to Kim and Feamster (2013), four key reasons can be identified for the problems encountered in managing existing networks:
(1) Complex and low-level network configuration: Network configuration is a distributed task typically configured vendor-specific at the low level. Moreover, network operators constantly change configurations manually due to the rapid growth of the network and changing networking conditions, adding complexity and introducing additional configuration errors to the configuration process.
(2) Growing complexity and dynamic network state: networks are becoming increasingly complex and more extensive. Moreover, as mobile computing trends continue to develop and network virtualization (Bari et al. 2013; Alam et al. 2020) and cloud computing (Zhang et al. 2010; Sharkh et al. 2013; Shamshirband et al. 2020) become more prevalent, the networking environment becomes even more dynamic as hosts are constantly moving, arriving and departing due to the flexibility offered by virtual machine migration, which results in a rapid and significant change of traffic patterns and network conditions.
(3) Exposed complexity: today’s large-scale networks are complicated by distributed low-level network configuration interfaces that expose great complexity. Many control and management features are implemented in hardware, which generates this complexity.
(4) Heterogeneous: Current networks contain many heterogeneous network devices, including routers, switches, and middleboxes of various kinds. As a result, network management becomes more complex and inefficient because each appliance has its proprietary configuration tools.
Because legacy networks’ static, inflexible architecture is ill-suited to cope with today’s increasingly dynamic networking trends and meet modern users’ QoE expectations, network management is becoming increasingly challenging. As a result, complex, high-level policies must be adopted to adapt to current networking environments, and network operations must be automated to reduce the tedious work of low-level device configuration.
Traffic Engineering
Networks with multiple Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Autonomous Systems (ASNs) under the same administrative control implement traffic engineering with policy configurations at border edges. Policies are applied on multiple routers distributedly, which can be hard to manage and scale. Any per-prefix traffic engineering changes may need to occur on various devices and levels.
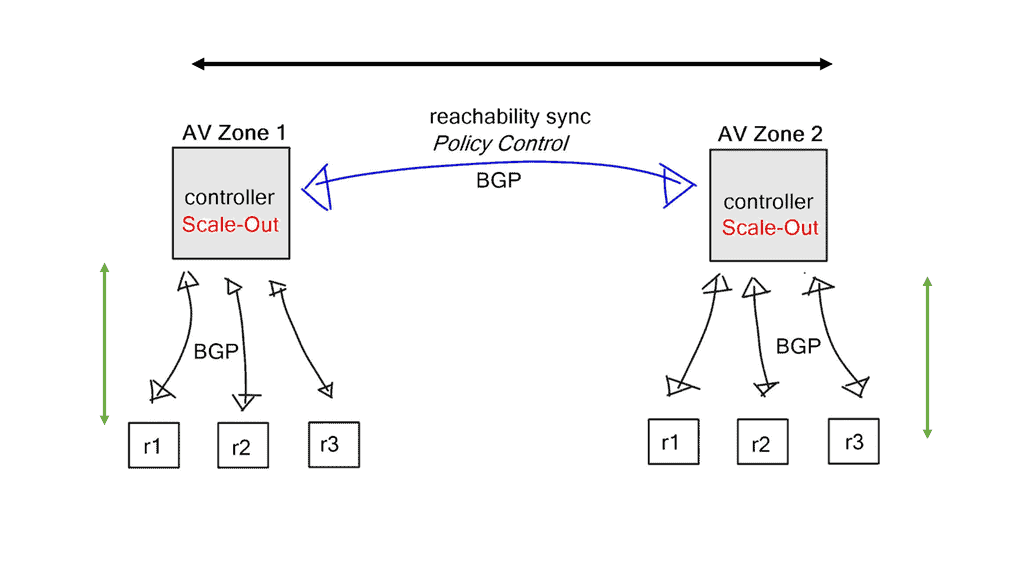
A new BGP Software-Defined Networking (SDN) solution introduced by P. Lapukhov and E. Nkposong proposes a centralized routing model. It introduces the concept of a BGP SDN controller, also known as an SDN BGP controller with a routing control platform. No protocol extensions or additional protocols are needed to implement the SDN architecture. BGP is employed to push down new routes and peers iBGP with all existing BGP routers.
BGP-only Network
A BGP-only network has many advantages, and this solution promotes a more stable Layer 3-only network, utilizing one control plane protocol – BGP. BGP captures topology discovery and links up/down events. BGP can push different information to different BGP speakers, while an IGP has to flood the same LSA throughout the IGP domain.
For additional pre-information, you may find the following helpful:
BGP SDN
BGP Peering Session Overview
In BGP terminology, a BGP neighbor relationship is called a peer relationship, unlike OSPF and EIGRP, which implement their transport mechanism. In place of TCP, BGP utilizes BGP TCP port 179 as its transport protocol. A BGP peering session can only be established between two routers after a TCP session has been established between them. Selecting a BGP session consists of establishing a TCP session and exchanging BGP-specific information to establish a BGP peering session.
A TCP session operates on a client/server model. On a specific TCP port number, the server listens for connection attempts. Upon hearing the server’s port number, the client attempts to establish a TCP session. Next, the client sends a TCP synchronization (TCP SYN) message to the listening server to indicate that it is ready to send data.
Upon receiving the client’s request, the server responds with a TCP synchronization acknowledgment (TCP SYN-ACK) message. Finally, the client acknowledges receipt of the SYN-ACK packet by sending a simple TCP acknowledgment (TCP ACK). TCP segments can now be sent from the client to the server. As part of this process, TCP performs a three-way handshake.
So, how does BGP work? BGP is a path-vector protocol that stores routes in the Routing Information Bases (RIBs). The RIB within a BGP speaker consists of three parts:
- The Adj-RIB-In,
- The Loc-RIB,
- The Adj-RIB-Out.
The Adj-RIB-In stores routing information learned from the inbound UPDATE messages advertised by peers to the local router. The routes in the Adj-RIB-In define routes that are available to the path decision process. The Loc-RIB contains routing information the local router selected after applying policy to the routing information in the Adj-RIB-In.
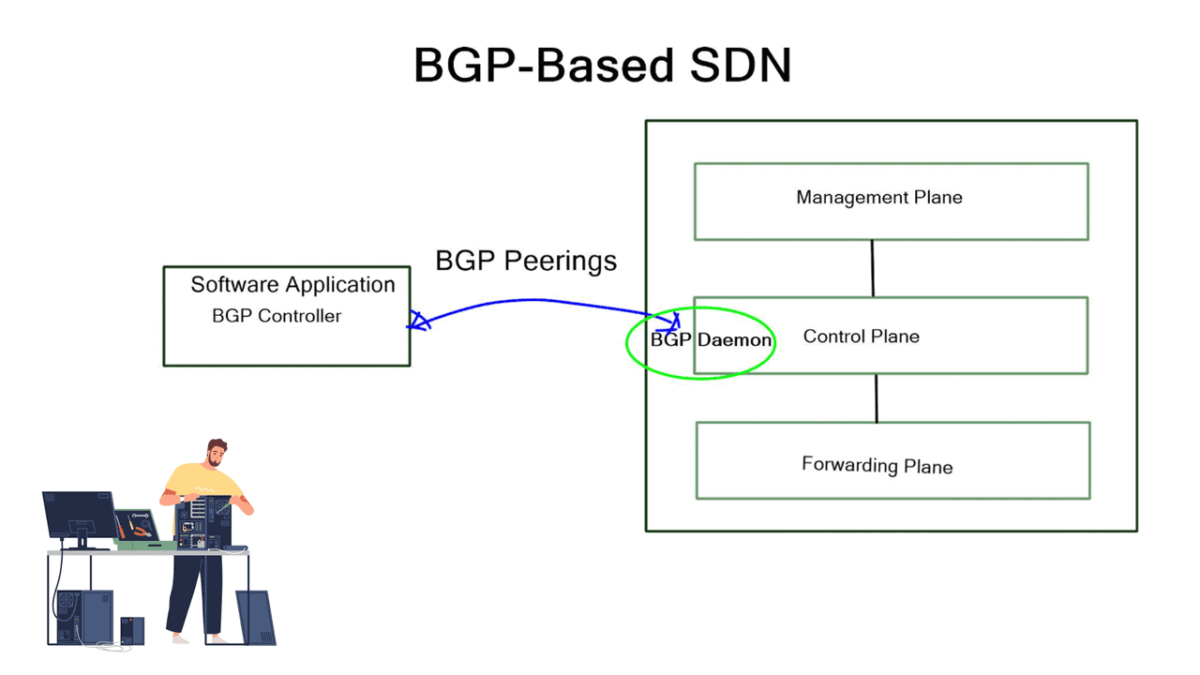
The Emergence of BGP in SDN:
Software-defined networking (SDN) introduces a paradigm shift in managing and operating networks. Traditionally, network devices such as routers and switches were responsible for handling routing decisions. However, with the advent of SDN, the control plane is decoupled from the data plane, allowing for centralized management and control of the network.
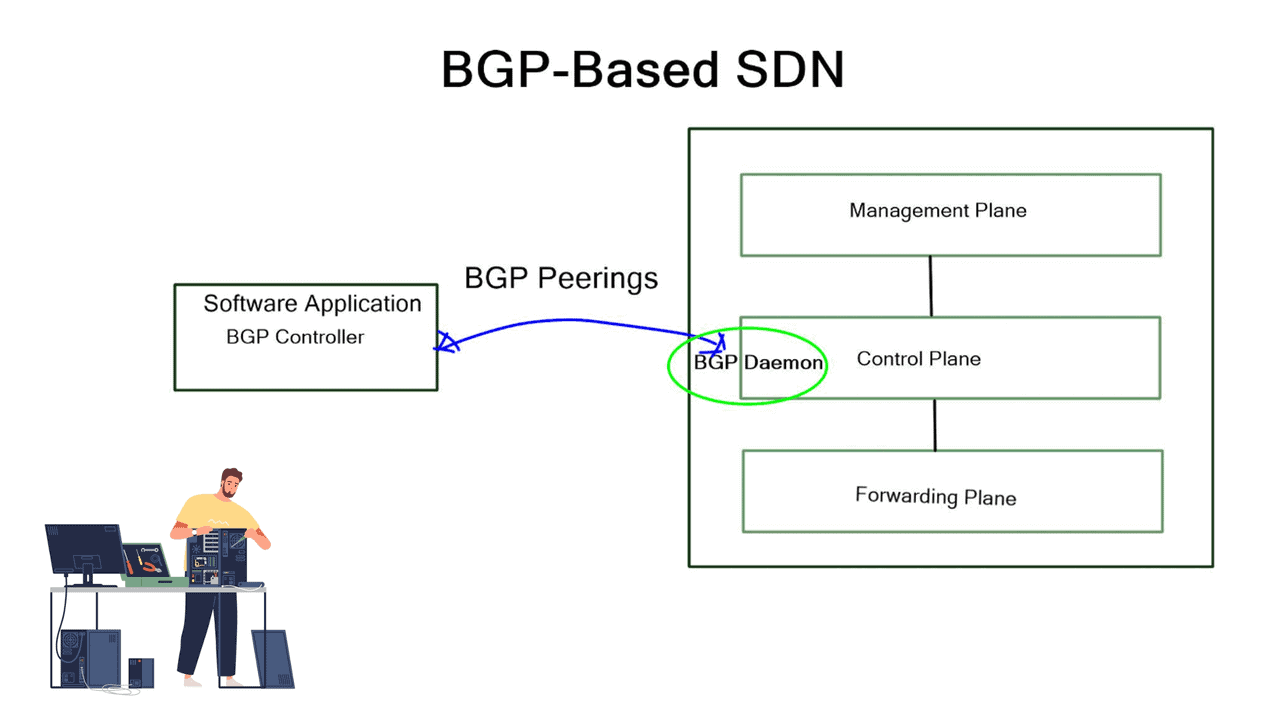
BGP plays a crucial role in the SDN architecture by acting as a control protocol that enables communication between the controller and the network devices. It provides the intelligence and flexibility required for orchestrating network policies and routing decisions in an SDN environment.
Layer-2 and Layer-3 Technologies
Traditional forwarding routing protocols and network designs comprise a mix of Layer 2 and 3 technologies. Topologies resemble trees with different aggregation levels, commonly known as access, aggregation, and core. IP routing is deployed at the top layers, while Layer 2 is in the lower tier to support VM mobility and other applications requiring Layer 2 VLANs to communicate.
Fully routed networks are more stable as they confine the Layer 2 broadcast domain to certain areas. Layer 2 is segmented and confined to a single switch, usually used to group ports. Routed designs run Layer 3 to the Top of the Rack (ToR), and VLANs should not span ToR switches. As data centers grow in size, the stability of IP has been preferred over layer 2 protocols.
- A key point: Traffic patterns
Traditional traffic patterns leave the data center, known as north-to-south traffic flow. In this case, conventional tree-like designs are sufficient. Upgrades consist of scale-out mechanisms, such as adding more considerable links or additional line cards. However, today’s applications, such as Hadoop clusters, require much more server-to-server traffic, known as east-to-west traffic flow.
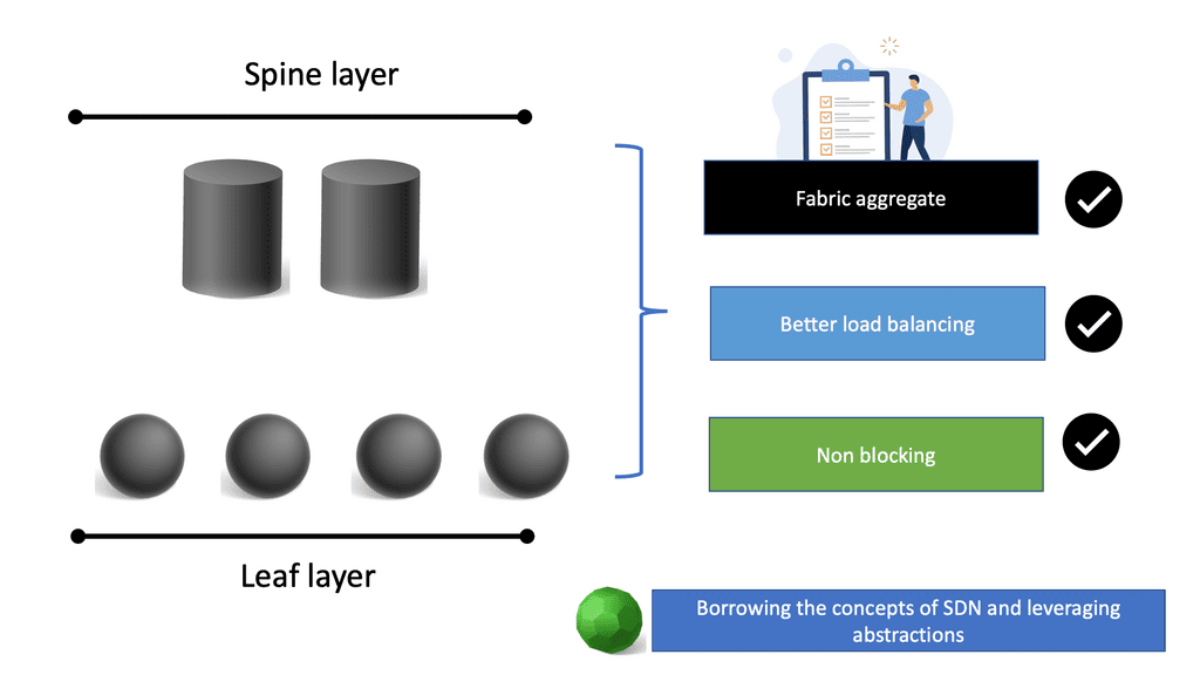
Scaling up traditional tree topologies to match these traffic demands is possible but not an optimum way to run your network. A better choice is to scale your data center horizontally with a CLOS topology ( leaf and spine ), not a tree topology.
Leaf and spine topologies permit equidistant endpoints and horizontal scaling, resulting in a perfect combination for optimum east-to-west traffic patterns. So, what layer 3 protocol do you use for your routing design? An Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP), such as ISIS or OSPF? Or maybe BGP? BGP’s robustness makes it a popular Layer 3 protocol for reducing network complexity.
How BGP works with BGP SDN: Centralized forwarding
What is BGP protocol in networking? Regarding internal data structures, BGP is less complex than a link-state IGP. Instead of forming adjacency maintenance and controls, it runs all its operations over Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and uses TCP’s robust transport mechanism.
BGP has considerably less flooding overhead than IGPs, with a single flooding domain propagation scope. For these reasons, BGP is great for reducing network complexity and is selected as this SDN solution’s singular control plane mechanism.
Peter has written a draft called “Centralized Routing Control in BGP Networks Using Link-State Abstraction,” which discusses the use case of BGP for centralized routing control in the network.
The main benefit of the architecture is centralized rather than distributed control. There is no need to configure policies on multiple devices. All changes are made with an API in the controller.
A link-state map
The network looks like a collection of BGP ASN, and the entire routing is done with BGP only. First, BGP builds a link-state map of the network in the controller memory.
Then, they use BGP to discover the topology and notice link-up and link-down events. Instead of installing a 5-tuple that can install flows based on the entire IP header, the BGP SDN solution offers destination-based forwarding only. For additional granularity, implement BGP flow spec, RFC 55745, entitled “Dissemination of Flow Specification Rules.”
Routing Control Platform
The proposed method was inspired by the Routing Control Platform (RCP). The RCP platform uses a controller-based function and selects BGP routes for the routers in an AS using a complete view of the available routes and IGP topology. The RCP platform has properties similar to those of the BGP SDN solution.
Both run iBGP peers to all routers in the network and influence the default topology by changing the controller and pushing down new routes. However, a significant difference is that the RCP has additional IGP peerings. It’s not a BGP-only network. BGP SDN promotes a single control plane of BGP without any IGPs.
BGP detects health, builds a link-state map, and represents the network to a third-party application as multiple topologies. You can map prefixes to different topologies and change link costs from the API.
Multi-Topology view
The agent builds the link-state database and presents a multi-topology view of this data to the client applications. You may clone this topology and give certain links higher costs, mapping some prefixes to this new non-default topology. The controller pushes new routes down with BGP.
The peering is based on iBGP, so new routes are set with a better Local Preference, enabling them to be selected higher in the BGP path decision process. It is possible to do this with eBGP, but iBGP can be more accessible. With iBGP, you don’t need to care about the next hops.
BGP and OpenFlow
What is OpenFlow? BGP works like OpenFlow and pushes down the forwarding information. It populates routes in the forwarding table. Instead of using BGP in a distributed fashion, they centralize it. One main benefit of using BGP over OpenFlow is that you can shut the controller down, and regular BGP operation continues on the network.
But if you transition to an OpenFlow configuration, you cannot roll back as quickly as you could with BGP. Using BGP inband has great operational benefits. It is a great design by P. Lapukhov. There is no need to deploy BGP-LS or any other enhancements to BGP.
Closing Points on BGP SDN
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN). BGP has long been the backbone of internet routing, while SDN is redefining how we manage and configure networks. But what happens when these two paradigms intersect? The convergence of BGP and SDN centralized forwarding presents an exciting frontier in network management, offering enhanced flexibility and control.
BGP is the protocol that holds the internet together by deciding the best paths for data to travel from source to destination across autonomous systems. It’s like the GPS for the internet, ensuring data packets find their way. However, traditional BGP lacks agility, often requiring manual configuration and offering limited adaptability to rapid network changes. This rigidity can lead to inefficiencies and delays, particularly in large-scale networks.
Enter SDN, a transformative approach that decouples the network control plane from the data plane, allowing for centralized management of network resources. SDN introduces a layer of abstraction that provides network administrators with the flexibility to program and configure network behavior dynamically, using software-based controllers. This means that network policies can be adjusted on the fly, responding swiftly to changing demands and conditions.
Combining BGP with SDN centralized forwarding brings the best of both worlds. SDN controllers can leverage BGP for routing decisions while maintaining centralized control over network policies and configurations. This synergy allows for automated, real-time optimization of routing paths, better resource allocation, and improved network resilience. In this hybrid model, networks become more efficient, scalable, and responsive to the needs of modern applications and services.
While the integration of BGP and SDN centralized forwarding offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges. Compatibility issues between legacy systems and modern SDN architectures can arise, requiring careful planning and execution. Additionally, security considerations must be addressed to protect the centralized control plane from potential threats. However, the potential benefits—such as enhanced performance, reduced operational costs, and greater adaptability—make overcoming these hurdles worthwhile.
Summary: BGP SDN
In the ever-evolving networking world, two key technologies have emerged as game-changers: Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN). In this blog post, we delved into the intricacies of these powerful tools, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and impact on the networking landscape.
Understanding BGP
BGP, an exterior gateway protocol, plays a crucial role in enabling communication between different autonomous systems on the internet. It allows routers to exchange information about network reachability, facilitating efficient routing decisions. With its robust path selection mechanisms and ability to handle large-scale networks, BGP has become the de facto protocol for inter-domain routing.
Exploring SDN
SDN, on the other hand, represents a paradigm shift in network architecture. SDN centralizes network management and provides a programmable and flexible infrastructure by decoupling the control plane from the data plane. SDN empowers network administrators to dynamically configure and manage network resources through controllers and open APIs, leading to greater automation, scalability, and agility.
The Synergy Between BGP and SDN
While BGP and SDN are distinct technologies, they are not mutually exclusive. They can complement each other to enhance network performance and efficiency. SDN can leverage BGP’s routing capabilities to optimize traffic flows and improve network utilization. Conversely, BGP can benefit from SDN’s centralized control, enabling faster and more adaptive routing decisions.
Benefits and Challenges
The adoption of BGP and SDN brings numerous benefits to network operators. BGP provides stability, scalability, and fault tolerance in inter-domain routing, ensuring reliable connectivity across the internet. SDN offers simplified network management, quick provisioning, and the ability to implement security policies at scale. However, implementing these technologies may also present challenges, such as complex configurations, interoperability issues, and security concerns that need to be addressed.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, BGP and SDN have revolutionized the networking landscape, offering unprecedented control, flexibility, and efficiency. BGP’s role as the backbone of inter-domain routing, combined with SDN’s programmability and centralized management, paves the way for a new era of networking. As technology advances, a deep understanding of BGP and SDN will be essential for network professionals to adapt and thrive in this rapidly evolving domain.