CASB Tools
In today's digital landscape, cloud-based technologies have become essential for organizations of all sizes. However, with the convenience and flexibility of the cloud comes the need for robust security measures. Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) tools have emerged as a vital solution for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring regulatory compliance. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of CASB tools and how they can help organizations secure their cloud environment effectively.
CASB tools act as a security intermediary between cloud service providers and end-users, offering visibility, control, and protection for cloud-based applications and data. These tools enable organizations to monitor and manage cloud usage, detect potential threats, and enforce security policies. By providing a centralized platform, CASB tools empower businesses to gain granular insights into their cloud environment and take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
1. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): CASB tools employ advanced analytics to detect anomalous user behavior, identifying potential insider threats or compromised accounts.
2. Data Loss Prevention (DLP): With DLP capabilities, CASB tools monitor data movement within the cloud environment, preventing unauthorized access, sharing, or leakage of sensitive information.
3. Encryption and Tokenization: CASB tools offer encryption and tokenization techniques to protect data both at rest and in transit, ensuring that even if data is compromised, it remains unreadable and unusable.
4. Access Control and Identity Management: CASB tools integrate with Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems, allowing organizations to enforce multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and ensure compliance with security policies.
1. Enhanced Visibility: CASB tools provide deep visibility into cloud usage, allowing organizations to identify potential risks, shadow IT, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
2. Improved Cloud Security: By monitoring user activities, enforcing security policies, and detecting potential threats in real-time, CASB tools significantly enhance cloud security posture.
3. Compliance and Governance: CASB tools assist organizations in meeting regulatory compliance requirements, such as GDPR or HIPAA, by providing data protection controls, encryption, and audit capabilities.
4. Incident Response and Forensics: In the event of a security incident, CASB tools enable quick incident response and forensic
CASB tools have become indispensable for organizations seeking to secure their cloud environment effectively. By offering comprehensive visibility, control, and protection capabilities, these tools enable businesses to embrace the advantages of the cloud while mitigating potential risks. As cloud adoption continues to grow, investing in CASB tools is a strategic move to ensure data security, regulatory compliance, and peace of mind.
Matt Conran
Highlights: CASB Tools
**Key Functions of CASB Tools**
CASB tools are multifaceted, offering a range of functions that help organizations secure their cloud environments. These tools primarily focus on four core areas: Visibility, Compliance, Data Security, and Threat Protection. Visibility allows organizations to gain insights into which cloud services are being accessed and by whom. Compliance ensures that cloud operations meet industry standards and regulations. Data Security involves data loss prevention (DLP) and encryption, while Threat Protection focuses on identifying and mitigating potential threats in real-time.
**Why Your Business Needs a CASB Solution**
The necessity of CASB tools for businesses cannot be overstated. As more companies migrate to cloud-based applications and services, the potential for data breaches and compliance violations increases. CASB tools provide comprehensive security coverage, allowing organizations to confidently leverage cloud technology without compromising on security. By offering granular control over cloud usage and detailed monitoring capabilities, businesses can protect sensitive information and uphold their reputation in the industry.
**Choosing the Right CASB Tool for Your Organization**
Selecting the appropriate CASB solution for your organization can be a daunting task given the myriad of options available. It’s essential to evaluate your specific security needs and business objectives. Consider factors such as ease of integration, scalability, user experience, and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, check if the CASB supports the cloud services your business uses and offers robust reporting and analytics features. Consulting with security experts can also provide valuable insights into making the best choice for your company.
Cloud Security Components
a) CASB, a critical cloud security component, acts as a gatekeeper between your organization and your cloud services. It provides visibility and control over data stored in the cloud, ensuring compliance, preventing threats, and enabling secure access for your users. By monitoring user activities, CASB helps identify and mitigate risks associated with cloud usage.
b) CASB offers a wide range of features that enhance the security of your cloud environment. These include real-time cloud activity monitoring, user behavior analytics, data loss prevention, encryption, and access controls. With CASB, you gain better visibility into cloud usage patterns, identify potential vulnerabilities, and enforce security policies to protect your data.
c) One of CASB’s primary functions is to secure cloud applications. Whether you use popular platforms like Office 365, Salesforce, or AWS, CASB provides granular control over user access and activities. It helps prevent unauthorized access, ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, and safeguards against data leakage.
CASB Core Features:
1. Visibility and Control: CASB tools offer comprehensive visibility into cloud applications and services being used within an organization. They provide detailed insights into user activities, data transfers, and application dependencies, allowing businesses to monitor and manage their cloud environment effectively. With this information, organizations can create and enforce access policies, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access critical data and applications.
2. Data Loss Prevention: CASB tools help prevent data leakage by monitoring and controlling data movement within the cloud. They employ advanced techniques such as encryption, tokenization, and data classification to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Additionally, CASB tools enable businesses to set up policies that detect and prevent data exfiltration, ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
3. Threat Protection: CASB tools are vital in identifying and mitigating cloud-based threats. They leverage machine learning algorithms and behavioral analytics to detect anomalous user behavior, potential data breaches, and malware infiltration. By continuously monitoring cloud activities, CASB tools can quickly detect and respond to security incidents, minimizing the impact of potential violations.
4. Compliance and Governance: Maintaining compliance with industry regulations is a top priority for organizations across various sectors. CASB tools provide the necessary controls and monitoring capabilities to help businesses meet compliance requirements. They assist in data governance, ensuring data is stored, accessed, and transmitted securely according to applicable regulations.
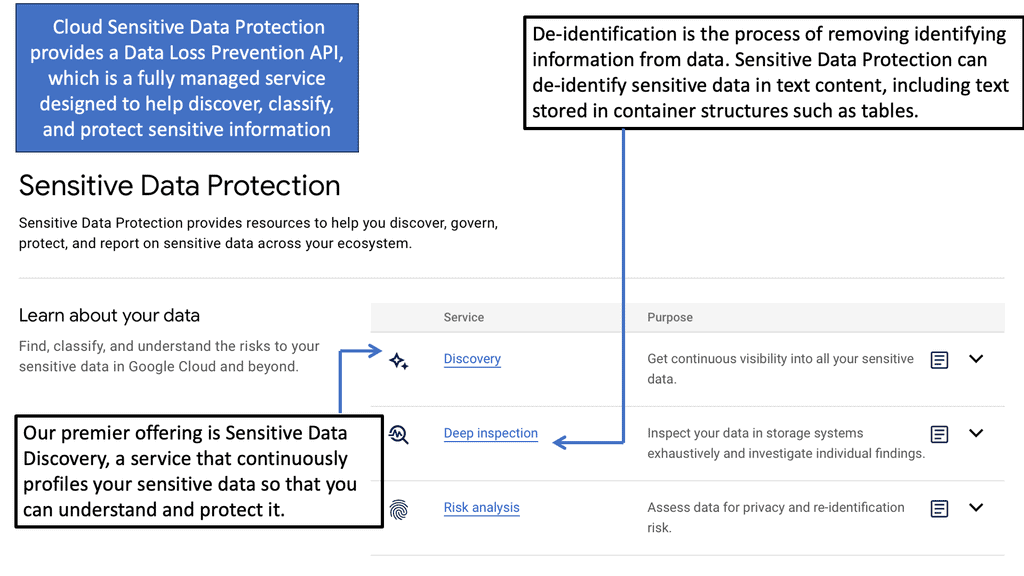
Example Security Technology: Sensitive Data Protection
**Understanding Google Cloud’s Security Framework**
Google Cloud offers a comprehensive security framework designed to protect data at every level. This framework includes encryption, identity and access management, and network security tools that work in tandem to create a secure environment. By encrypting data both in transit and at rest, Google Cloud ensures that your information remains confidential and inaccessible to unauthorized users. Additionally, their identity and access management services provide granular control over who can access specific data, further minimizing the risk of data breaches.
**The Role of Machine Learning in Data Protection**
One of the standout features of Google Cloud’s security offerings is the integration of machine learning technologies. These advanced tools help detect and respond to threats in real-time, allowing for proactive data protection measures. By analyzing patterns and behaviors, machine learning algorithms can identify potential vulnerabilities and suggest solutions before a breach occurs. This predictive approach to data security is a game-changer, providing businesses with the peace of mind that their sensitive data is continuously monitored and protected.
Understanding CASB Tools
CASB tools, short for Cloud Access Security Broker tools, act as a crucial intermediary between your organization and cloud service providers. Their primary objective is to ensure the security and compliance of data and applications when accessing cloud services. By enforcing security policies, monitoring cloud activities, and providing real-time threat detection, CASB tools offer a comprehensive security framework for your cloud environment. CASB tools come equipped with a wide array of features designed to tackle various security challenges in the cloud. These include:
1. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Leveraging machine learning algorithms, CASB tools analyze user behavior patterns to detect anomalies and identify potential threats or unauthorized access attempts.
2. Data Loss Prevention (DLP): CASB tools employ advanced DLP mechanisms to prevent sensitive data from being leaked or mishandled. They monitor data transfers, apply encryption, and enforce policies to protect data.
3. Shadow IT Discovery: CASB tools provide visibility into unauthorized cloud applications and services used within an organization. This helps IT administrators gain control over data sharing and mitigate potential risks.
Implementing CASB tools offers numerous benefits to organizations of all sizes. Some notable advantages include:
1. Enhanced Security: CASB tools provide a unified security framework that extends visibility and control over cloud services, ensuring consistent security policies and protecting against data breaches and cyber threats.
2. Compliance and Governance: CASB tools assist organizations in meeting regulatory requirements by monitoring and enforcing compliance policies across cloud applications and services.
3. Improved Productivity: By offering secure access to cloud platforms and preventing unauthorized activities, CASB tools enable employees to collaborate seamlessly and utilize cloud services without compromising security.
**CASB Selection**
When selecting a CASB tool, it is essential to consider its compatibility with your existing cloud infrastructure. Integration capabilities with popular cloud service providers, such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, are crucial for seamless deployment and management. Additionally, the CASB solution’s scalability and ease of deployment are factors to consider to ensure minimal disruption to your existing cloud environment.
Secure cloud-based applications and services with Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB). These solutions, typically deployed between cloud service consumers and providers, allow organizations to enforce security policies and gain visibility into cloud usage.
1. Visibility
Both managed and unmanaged cloud services require visibility and control. Instead of allowing or blocking all cloud services, cloud brokerage should enable IT to say “yes” to valuable services while controlling access to their activities. For users on unmanaged devices, this could mean offering Web-only email access instead of a sanctioned suite like Microsoft 365. A “no sharing outside the company” policy could also be enforced across an unsanctioned service category.
Security is the primary focus of cloud access security brokers, but they can also help you understand cloud spending. With a CASB, you can discover all cloud services in use, report on your cloud spend, and uncover redundancies in functionality and license costs. In addition to protecting your business and finances, a CASB can provide valuable information.
2. Compliance
Moving data and systems to the cloud requires organizations to consider compliance. If these compliance standards are ignored, data breaches can be costly and dangerous, as they ensure the safety of personal and corporate data.
If you are a healthcare organization concerned about HIPAA or HITECH compliance, a retail company concerned about PCI compliance, or a financial services organization concerned about FFIEC and FINRA compliance, cloud access security brokers can help ensure compliance. Through a CASB, you can keep your company in compliance with industry-specific data regulations and avoid costly data breaches.
3. Data Security
Accuracy can be achieved by using highly sophisticated cloud DLP detection mechanisms like document fingerprinting and reducing the detection surface area (user, location, activity, etc.). A cloud access security broker (CASB) should provide IT with the option to move suspected violations to their on-premises systems for further analysis when sensitive content is discovered in the cloud or on its way there.
CASBs can act as gatekeepers and facilitate the detection and prevention of malicious activity before it escalates. They can carry out more profound research on threat observations. CASBs are IT and business practices experts and take a skilled approach to enhancing an organization’s security.
4. Threat Protection
Organizations should ensure their employees are not introducing or propagating cloud malware and threats by using cloud storage services and their associated sync clients and services. An employee trying to share or upload an infected file should be able to scan and remediate threats in real-time across internal and external networks. In addition, this means detecting and preventing unauthorized access to cloud services and data, which can assist in identifying compromised accounts.
CASBs can protect organizations from cloud threats and malware. Your company must avoid threats that combine prioritized static and dynamic malware analysis for advanced threat intelligence. Proper threat protection can help protect you from threats that originate from or are propagated through cloud services.
**Network Security Components**
Recently, when I spoke to Sorell Slaymaker, we agreed that every technology has its own time and place. Often, a specific product set is forcefully molded to perform all tasks. This carries along with its problems. For example, no matter how modified the Next-Gen firewall is, it cannot provide total security. As you know, we need other products for implementing network security, such as a proxy or a cloud access security broker (CASB API) to work alongside the Next-Gen firewall and zero trust technologies, such as single packet authorization to complete the whole picture.
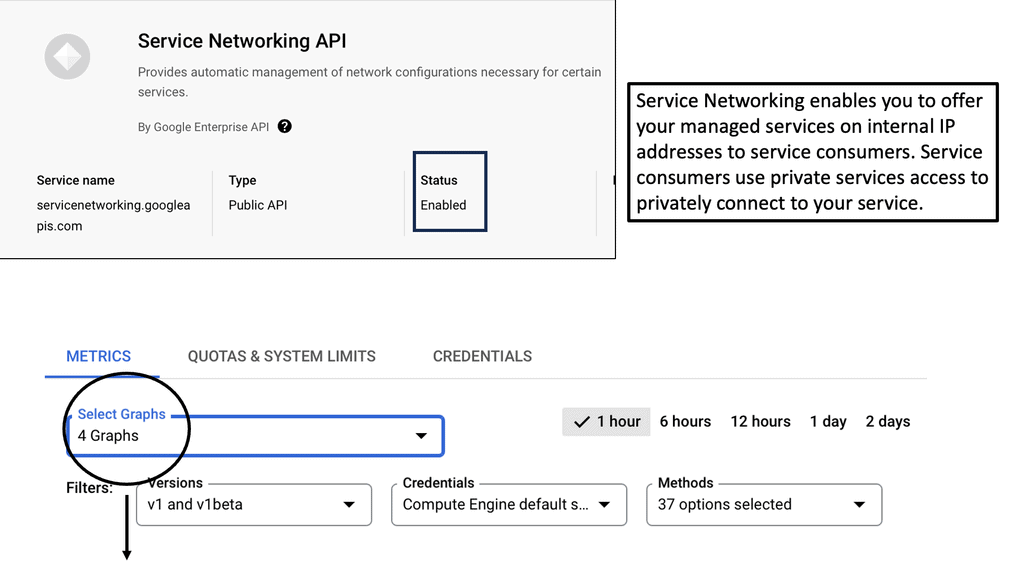
Example API Technology: Service Networking API
### Key Features of Google Cloud’s Service Networking APIs
Google Cloud’s Service Networking APIs provide a suite of powerful features designed to simplify the management of network services. One of the standout features is the ability to create private connections between services, ensuring secure and efficient communication. Additionally, they support automated IP address management, which reduces the risk of IP conflicts and simplifies network configuration. These features, combined with Google’s global infrastructure, provide a scalable and reliable solution for any organization looking to enhance its networking capabilities.
### Benefits of Using Service Networking APIs
The benefits of utilizing Service Networking APIs on Google Cloud are numerous. Firstly, they provide enhanced security by allowing private communications between services without exposing them to the public internet. This is crucial for businesses that handle sensitive data and require stringent security measures. Secondly, the APIs facilitate seamless scalability, allowing businesses to grow their network infrastructure effortlessly as their needs evolve. Lastly, they offer cost efficiency by optimizing network resource usage, leading to potential savings on infrastructure expenses.
Before you proceed, you may find the following posts helpful
CASB Tools
A cloud access security broker (CASB) allows you to move to the cloud safely. It protects your cloud users, data, and apps that can enable identity security. With a CASB, you can more quickly combat data breaches while meeting compliance regulations.
For example, Cisco has a CASB in its SASE Umbrella solution that exposes shadow IT by enabling the detection and reporting of cloud applications across your organization. For discovered apps, you can view details on the risk level and block or control usage to manage cloud adoption better and reduce risk.
Introducing CASB API Security
Network security components are essential for safeguarding business data. As most data exchange is commonplace in business, APIs are also widely leveraged. An application programming interface (API) is a standard way of exchanging data between systems, typically over an HTTP/S connection. An API call is a predefined way of obtaining access to specific types of information kept in the data fields.
However, with the acceleration of API communication in the digital world, API security and CASB API mark a critical moment as data is being passed everywhere. The rapid growth of API communication has resulted in many teams being unprepared. Although performing API integrations is easy, along with that comes the challenging part of ensuring proper authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA).
When you initiate an API, there is a potential to open up calls to over 200 data fields. Certain external partners may need access to some, while others may require access to all.
That means a clear and concise understanding of data patterns, and access is critical for data loss prevention. Essentially, bad actors are more sophisticated than ever, and simply understanding data authorization is not enough to guard the castle of your data. A lack of data security can cause massive business management and financial losses.
CASB Tools: The challenge
Many enterprise security groups struggle to control shadow IT. One example is managing all Amazon Web Services (AWS) accounts, where AWS employs tools like Macie for API management. However, these tools work well only for AWS accounts for which Macie is turned on. Enterprises can have hundreds of test and development accounts with a high risk of data leakage, of which the security teams are unaware.
Also, containers and microservices often use transport layer security (TLS) connections to establish secure connectivity, but this falls short in several ways. Examining the world of API security poses the biggest challenge that needs to be solved in the years to come. So what’s the solution?
CASB Tools and CASB API: The Way Forward
Let’s face it! The digital economy is run by APIs, which permit the exchange of data that needs to be managed. API security tools have become a top priority with the acceleration of API communication. We don’t want private, confidential, and regulated data to leave that is not supposed to go, and we need to account for data that does go. If you don’t have something in the middle and encrypt just the connections, data can flow in and out without any governance and compliance.
API Security Tools
Ideally, a turnkey product that manages API security in real-time independent of the platform—in the cloud, hybrid, or on-premise—is the next technological evolution of the API security tool market. Authentically, having an API platform across the entire environment and enforcing real-time security with analytics empowers administrators to control data movements and access. Currently, API security tools fall into three different types of markets.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers: The CASB API security is between an enterprise and the cloud-hosted services, such as O365, SFDC, ADP, or another enterprise
- API Management Platforms: They focus on creating, publishing, and protecting an API. Development teams that create APIs consumed internally and externally rely on these tools as they write applications. You can check out the Royal Cyber blog to learn about API management platforms like IMB API Connect, MuleSoft, Apigee API, and MS Azure API.
- Proxy Management focuses on decrypting all enterprise traffic, scanning, and reporting anomalies. Different solutions are typically used for various types of traffic, such as web and email. Chat is an example.
Cloud Access Security Brokers
The rise of CASB occurred due to inadequacies of the traditional WAF, Web Security Gateway, and Next-Gen Firewalls product ranges. The challenge with these conventional products is that they work more as a service than at the data level.
They operate at the HTTP/S layer, usually not classifying and parsing the data. Their protection target is different from that of a CASB. Let’s understand it more closely. If you parse the data, you can classify it. Then, you have rules to define the policy, access, and the ability to carry out analytics. As the CASB solutions mature, they will become more automated.
They can automatically discover API, map, classify, and learn intelligently. The CASBs provide a central location for policy and governance. They sit as a boundary between the entities. They are backed by the prerequisite to decrypt the traffic, TLS, or IPSec. After decrypting, they read, parse, and then re-encrypt the traffic to send it on its way.
Tokenization
When you are in the middle, you need to decrypt the traffic and then parse it to examine and classify all the data. Once it is classified, if there are specific susceptible data, be it private, confidential, or regulated, you can tokenize or redact it at a field and file level. Many organizations previously created a TLS or IPsec connection between themselves and the cloud provider or third-party network.
However, they didn’t have strict governance or compliance capabilities to control and track the data going in and out of the organization. TLS or IPsec is the only point-to-point encryption; the traffic is decrypted once you reach the end location. As a result, sensitive data is then available, which could be in an unsecured network.
Additional security controls are needed so that the data has an extra level of encryption when the connections are complete. TLS or IPSec is for the data in motion, and tokenization is for the data at rest. We have several ways to secure data, and tokenization is one of them. Others include encryption with either provider-managed keys or customer BYOK.
We also have different application-layer encryption. Tokenization substitutes the sensitive data element with a non-sensitive equivalent, a token. As a result, the third party needs additional credentials to see that data.
However, when you send the data out to a 3rd party, you add another layer of encryption by putting in a token instead of a specific number like the social security number. Redact means that the data is not allowed to leave the enterprise.
CASB API Security
For API security, AAA is at an API layer. This differs from the well-known AAA model used for traditional network access control (NAC). Typically, you allow IP addresses and port numbers in the network world. In an API world, we are at the server and service layer.
– Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a common add-on feature for CSBs. Once you parse and classify the data, you can govern it. Here, the primary concern is what data can be left, who can access it, and when. DLP is an entire market, whereas the CASB will be specific to specific APIs.
– It would be best if you often had a different DLP solution, for example, to scan your Word documents. Some vendors bundle DLP and CASB. We see this with the Cisco Umbrella, where the CASB and DLP engines are on the same platform.
– Presently, the next-generation CASBs are becoming more application-specific. They now have the specific capability for Office 365 and SalesForce. The market constantly evolves; it will integrate with metadata management over time.
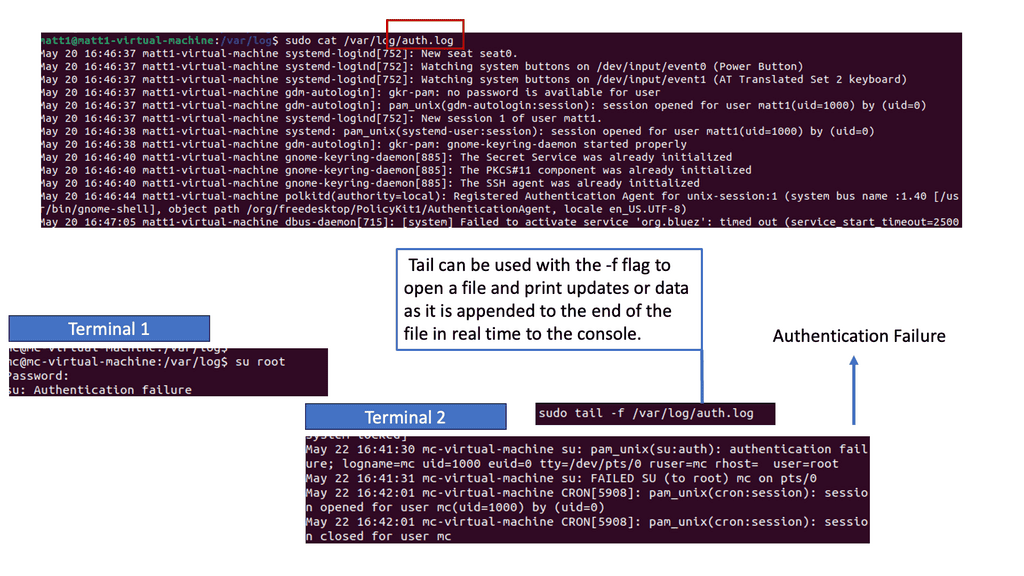
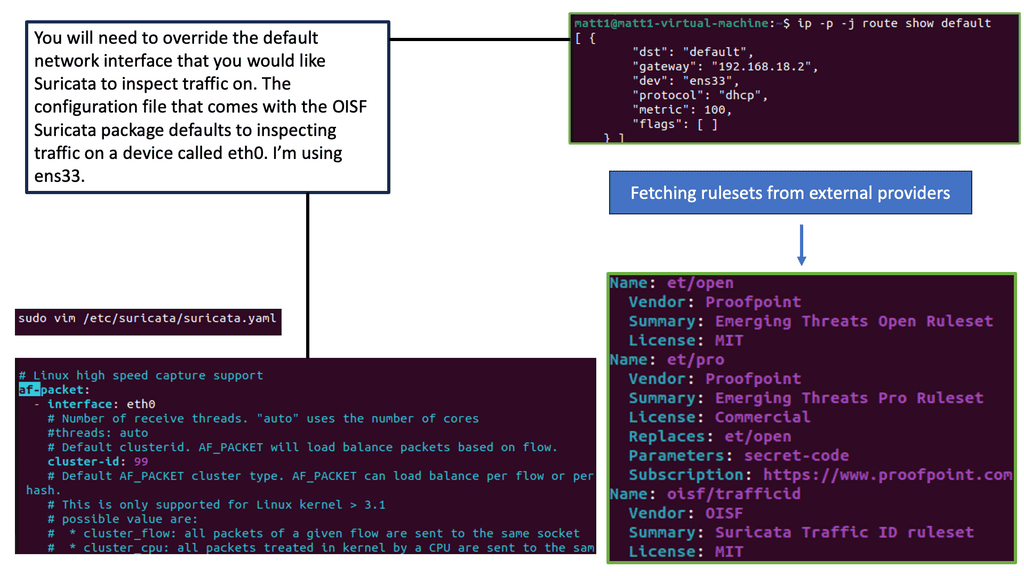
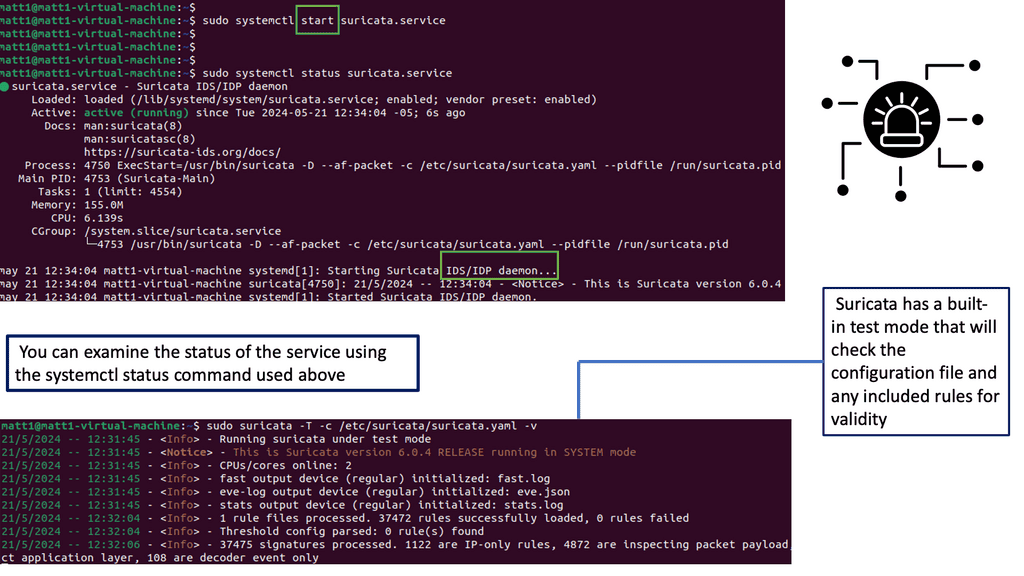
Example IDS Technology: Suricate
API Management Platforms
API Management platforms are used by DevOps teams when they are creating, publishing, and protecting their APIs. DevOps creates an API that is consumed internally and externally to enable their application to rely on these tools. In an enterprise, had everyone been using an effective API management tool, you wouldn’t need a CASB. One of the main reasons for introducing CASBs is that you have a lot of development and test environments that lack good security tools. As a result, you need the 3rd tool to ensure governance and compliance.
Finally, Proxy Management
A proxy monitors all the traffic going in and out of the organization. A standard proxy keeps a tab on the traffic moving internally to the site. A reverse proxy is the opposite, i.e., an external organization looking for internal access to systems. A proxy operates at Layer 5 and Layer 6. It controls and logs what the site users are doing but does not go into layer 7, where all the critical data is.
Closing Points on CASB Tools
The adoption of cloud computing has surged in recent years, providing organizations with scalable and cost-effective solutions. However, this shift has also introduced new security challenges. Traditional security measures often fall short when it comes to protecting data in the cloud. This has led to an increased demand for specialized security solutions like CASB tools, which address the unique threats posed by cloud environments.
CASB tools offer a comprehensive set of features designed to enhance cloud security. These include visibility into cloud usage, data loss prevention, threat protection, and access control. By providing granular control over data and user activities, CASB tools help organizations enforce security policies and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, they offer real-time monitoring and analytics to detect and respond to potential threats swiftly.
Implementing CASB tools requires careful planning and execution. Organizations should start by identifying their specific security needs and selecting a CASB solution that aligns with their goals. It’s essential to integrate CASB tools seamlessly with existing security infrastructure and cloud services. Furthermore, continuous monitoring and regular updates are crucial to maintaining effective protection against evolving threats.
Organizations across various industries have experienced significant benefits from deploying CASB tools. These include improved compliance with regulatory standards, enhanced data protection, and reduced risk of data breaches. By gaining visibility into cloud activities and securing sensitive data, businesses can confidently embrace cloud technologies without compromising security.
Summary: CASB Tools
Cloud computing has become an integral part of modern businesses, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. However, as more organizations embrace the cloud, concerns about data security and compliance arise. This is where Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) tools come into play. In this blog post, we will delve into CASB tools, their features, and the benefits they offer to businesses.
Understanding CASB Tools
CASB tools act as intermediaries between an organization’s on-premises infrastructure and the cloud service provider. They provide visibility and control over data flowing between the organization and the cloud. CASB tools offer a comprehensive suite of security services, including data loss prevention (DLP), access control, threat protection, and compliance monitoring. These tools are designed to address the unique challenges of securing data in the cloud environment.
Key Features of CASB Tools
1. Data Loss Prevention (DLP): CASB tools employ advanced DLP techniques to identify and prevent sensitive data from being leaked or shared inappropriately. They can detect and block data exfiltration attempts, enforce encryption policies, and provide granular control over data access.
2. Access Control: CASB tools offer robust access control mechanisms, allowing organizations to define and enforce fine-grained access policies for cloud resources. They enable secure authentication, single sign-on (SSO), and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure only authorized users can access sensitive data.
3. Threat Protection: CASB tools incorporate threat intelligence and machine learning algorithms to detect and mitigate various cloud-based threats. They can identify malicious activities, such as account hijacking, insider threats, and malware infections, and take proactive measures to prevent them.
Benefits of CASB Tools
1. Enhanced Data Security: By providing visibility and control over cloud data, CASB tools help organizations strengthen their data security posture. They enable proactive monitoring, real-time alerts, and policy enforcement to mitigate data breaches and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
2. Increased Compliance: CASB tools assist organizations in meeting regulatory requirements by monitoring and enforcing compliance policies. They help identify data residency issues, ensure proper encryption, and maintain audit logs for compliance reporting.
3. Improved Visibility: CASB tools offer detailed insights into cloud usage, user activities, and potential risks. They provide comprehensive reports and dashboards, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about their cloud security strategy.
Conclusion:
CASB tools have become indispensable for businesses operating in the cloud era. With their robust features and benefits, they empower organizations to secure their cloud data, maintain compliance, and mitigate risks effectively. By embracing CASB tools, businesses can confidently leverage the advantages of cloud computing while ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their valuable data.