ICMPv6
In the vast realm of networking protocols, one that stands out is ICMPv6. As the successor to ICMPv4, ICMPv6 plays a crucial role in the efficient functioning of the Internet. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of ICMPv6 and explore its significance in modern networking.
ICMPv6, or Internet Control Message Protocol version 6, is an integral component of the Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) suite. It is a vital communication protocol within IPv6 networks, facilitating the exchange of control and error messages between network devices.
ICMPv6, as the name suggests, is the successor to ICMPv4 and is specifically designed for IPv6 networks. It plays a crucial role in maintaining network health, facilitating communication, and providing error reporting and diagnostic capabilities. ICMPv6 messages are an integral part of IPv6 and are used for various purposes.
Addressing and Autoconfiguration: One of the primary functions of ICMPv6 is addressing. It allows hosts to configure their IPv6 addresses dynamically through stateless autoconfiguration or stateful configuration methods. ICMPv6 Router Solicitation and Advertisement messages are used to facilitate this process.
Neighbor Discovery: ICMPv6 neighbor discovery is a vital mechanism that enables hosts to discover other devices on the same link, resolve their IP addresses to link-layer addresses, and detect any changes in the network topology. Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbor Advertisement messages are used for neighbor discovery.
Error Reporting: ICMPv6 is responsible for reporting errors related to IPv6 packet processing. It allows nodes to communicate error conditions to the source of the packet, enabling efficient troubleshooting and network management. ICMPv6 error messages include Destination Unreachable, Packet Too Big, Time Exceeded, and Parameter Problem.
ICMPv6 and Path MTU Discovery: Path Maximum Transmission Unit (PMTU) is an important aspect of efficient data transmission. ICMPv6 plays a vital role in PMTU discovery, allowing hosts to determine the maximum size of packets that can be transmitted without fragmentation. ICMPv6 Packet Too Big messages are used to adjust the packet sizes.Matt Conran
Highlights: ICMPv6
### The Limitations of IPv4
IPv4, the fourth version of the Internet Protocol, has been the backbone of the internet since its inception in the 1980s. However, with the explosion of internet-enabled devices, the 32-bit address space of IPv4, providing approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses, is no longer sufficient. The exhaustion of IPv4 addresses has led to the adoption of Network Address Translation (NAT), which, while a temporary solution, complicates network configurations and can hinder performance.
### IPv6: A New Era of Connectivity
IPv6 was developed to address the limitations of IPv4, offering a robust 128-bit address space. This translates to approximately 340 undecillion unique addresses, enough to assign a unique IP to every grain of sand on Earth. Beyond an expanded address space, IPv6 introduces features such as simplified header format, improved support for extensions and options, and enhanced security through IPsec, which is mandatory in IPv6 implementations.
### Understanding ICMPv6
A critical component of IPv6 is ICMPv6 (Internet Control Message Protocol for IPv6), which is integral for error reporting and diagnostic functions. ICMPv6 is more advanced than its IPv4 counterpart, supporting Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) for address resolution and router discovery. It also facilitates Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD), which is essential for efficient multicast group management. These features enhance network robustness and efficiency, making ICMPv6 a cornerstone of IPv6 networking.
Understanding ICMPv6
1- ) ICMPv6 stands for Internet Control Message Protocol version 6. It is an essential part of the IPv6 suite of protocols and serves as the successor to ICMPv4, which is used in IPv4 networks. ICMPv6 is primarily responsible for error reporting, network diagnostics, and neighbor discovery in IPv6 networks. It operates at the network layer of the TCP/IP model and works closely with the IPv6 protocol.
2 – ) ICMPv6 plays a vital role in ensuring seamless communication across IPv6 networks. Its error reporting and diagnostic capabilities help maintain the integrity of data transmission, minimizing disruptions and optimizing network performance. Additionally, ICMPv6’s neighbor discovery mechanisms enable efficient routing and address resolution, contributing to enhanced connectivity.
3 – ) ICMPv6, as an integral part of IPv6, serves various purposes in network communication. It facilitates the exchange of control and error messages between network devices, ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission. By providing feedback on network conditions, ICMPv6 helps to optimize network performance and troubleshoot connectivity issues. Let’s explore some of the fundamental aspects of ICMPv6.
Note: ICMPv6 Key Considerations
One of the standout features of ICMPv6 is its support for Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). NDP is crucial for address resolution, router discovery, and maintaining reachability information. ICMPv6 also supports multicast listener discovery, which optimizes the use of network resources by allowing devices to join and leave multicast groups dynamically.
While ICMPv6 offers many benefits, it is not without its challenges, particularly in the realm of security. ICMPv6 can be exploited for network reconnaissance and denial-of-service attacks. Therefore, network administrators must implement appropriate security measures, such as using firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to mitigate potential risks.
Additionally, ICMPv6 is invaluable for network troubleshooting. Tools like traceroute and ping rely on ICMPv6 messages to diagnose connectivity issues. By understanding ICMPv6 message types and codes, network professionals can effectively identify and resolve network anomalies, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
**Functions of ICMPv6**
Error Reporting and Diagnostic Messages:
One of the primary functions of ICMPv6 is to report errors and provide diagnostic information to network devices. When an error occurs during the transmission of IPv6 packets, ICMPv6 sends error messages back to the source, informing it about the issue. These error messages include details such as time exceeded, destination unreachable, and packet too big, enabling efficient troubleshooting and network performance optimization.
Neighbor Discovery:
ICMPv6 plays a crucial role in facilitating neighbor discovery in IPv6 networks. Through neighbor solicitation and advertisement messages, ICMPv6 allows devices to identify and communicate with neighboring devices on the same network segment. This process is vital for efficient routing, address resolution, and maintaining network connectivity.
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD):
ICMPv6 also supports Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD), a protocol essential for managing multicast group memberships on IPv6 networks. MLD allows routers to discover which devices are interested in receiving multicast traffic, optimizing network bandwidth by ensuring that multicast data is only sent to devices that request it. This function is particularly important for applications like video streaming and real-time data feeds, where efficient bandwidth utilization is critical.
**Benefits of ICMPv6**
1: Efficient Network Troubleshooting:
ICMPv6 provides valuable diagnostic information, allowing network administrators to quickly identify and resolve issues. By receiving error messages and diagnostic feedback from ICMPv6, administrators can efficiently troubleshoot network problems, minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal performance.
2: Enhanced Network Security:
ICMPv6 assists in network security by providing features like Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD) and Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 Neighbor Discovery (ND) Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND). PMTUD helps prevent packet fragmentation issues, while SEND enhances the security of neighbor discovery processes, mitigating potential security threats.
3: Neighbor Discovery Protocol
One of the primary functions of ICMPv6 is the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). NDP assists in the identification and location of devices within a network. With address resolution, neighbor unreachability detection, and router discovery, NDP enables smooth communication and seamless mobility in IPv6 networks. We will delve into the workings of NDP and its significance in modern networking.
4: Efficient Path MTU Discovery:
ICMPv6 for Path MTU Discovery eliminates the need to configure MTU sizes manually. This dynamic adjustment of packet sizes optimizes network performance by avoiding unnecessary fragmentation.
**ICMPv6 Message Types and Error Reporting**
ICMPv6 encompasses many message types, each serving a specific purpose. From echo requests and replies to router solicitations and advertisements, these messages facilitate network diagnostics, path MTU discovery, and more. Additionally, ICMPv6 plays a vital role in reporting errors such as unreachable destinations and time-exceeded conditions. Explore these message types and understand how they contribute to network troubleshooting.
Security Considerations and ICMPv6
As with any network protocol, security considerations are paramount. ICMPv6 introduces new challenges and opportunities for network administrators to protect against potential vulnerabilities and attacks. We will discuss some of the critical security aspects of ICMPv6 and explore best practices to mitigate risks and ensure network resilience.
While ICMPv6 is crucial for network functionality, it lacks vulnerabilities. Attackers can exploit weaknesses in ICMPv6 to launch various attacks, including ICMPv6 flood attacks, ICMPv6 redirect attacks, and ICMPv6 neighbor discovery exploits. Understanding these vulnerabilities is paramount to implementing effective security measures.
**Security Issues with ICMPv6**
When discussing IPv6 security issues, why concern ourselves about layer 2 security? IPv6 is IP and operates at Layer 3. Here, we need to address IPv6 security risks with ICMPv6 security and keep a close eye on the security issues related to fragmentation in IPv6. While ICMPv6 offers several advantages, it is essential to consider potential security implications.
Malicious actors can exploit ICMPv6 messages for various attacks, such as flooding, spoofing, or surveillance. Network administrators must implement appropriate security measures to mitigate these risks, including packet filtering and intrusion detection.
**Mitigation Strategies for ICMPv6 Security Risks**
To mitigate the security risks associated with ICMPv6, a multi-layered approach is recommended. This includes the implementation of strong access control lists (ACLs) to filter ICMPv6 traffic, the deployment of network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) to monitor suspicious activities, and the use of secure neighbor discovery (SEND) to authenticate NDP messages. By combining these strategies, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to ICMPv6-related threats.
Related: For pre-information, you may find the following posts helpful:
Highlights: ICMPv6
IP Datagrams
Data transmitted over the internetwork using IP is carried in messages called IP datagrams. IP, as with all network protocol messages, uses a specific format for its datagrams. For example, we have an IPv4 datagram format and an IPv6 format.
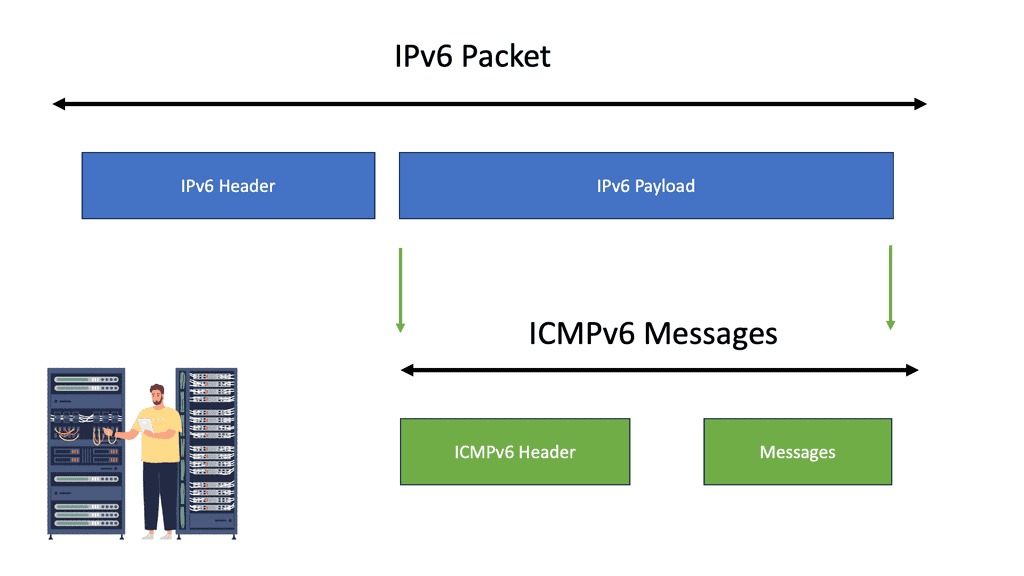
The IPv6 datagram is conceptually divided into the header and the payload. The header contains all the addressing and control fields, while the payload carries the data. If you examine an IPv6 datagram more closely, it is a packet composed of the base header ( 40 bytes) and payload (up to 65,536). In addition, the payload has an optional extension header and data packet.
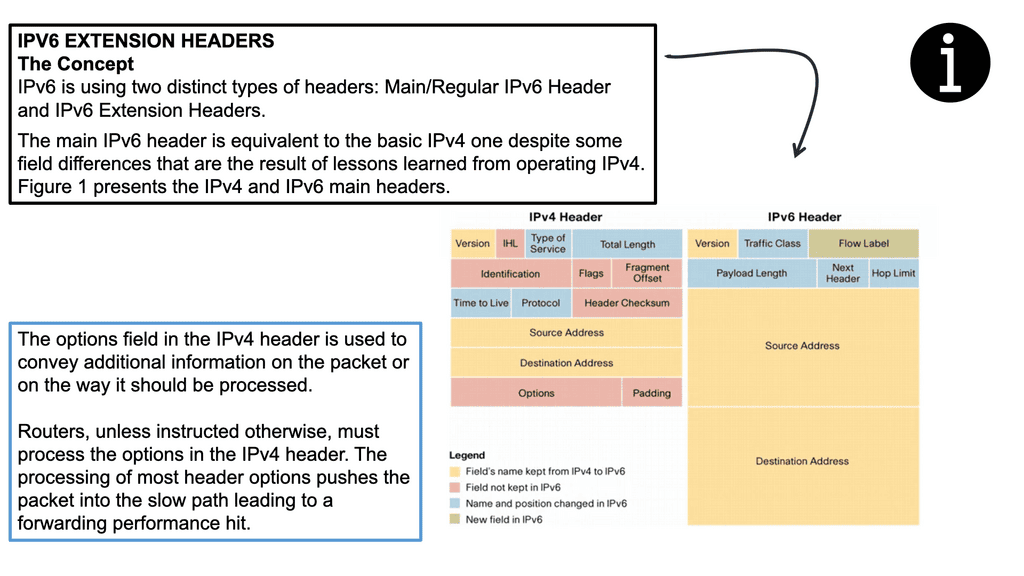
The IPv6 header is the starting point of any IPv6 packet. Unlike its predecessor, IPv4, which uses a 32-bit address, IPv6 employs a 128-bit format, allowing for an almost unlimited number of unique IP addresses. The IPv6 header consists of several fields that provide essential information about the packet’s source and destination and other crucial details required for proper routing and delivery.
Guide: ICMPv6
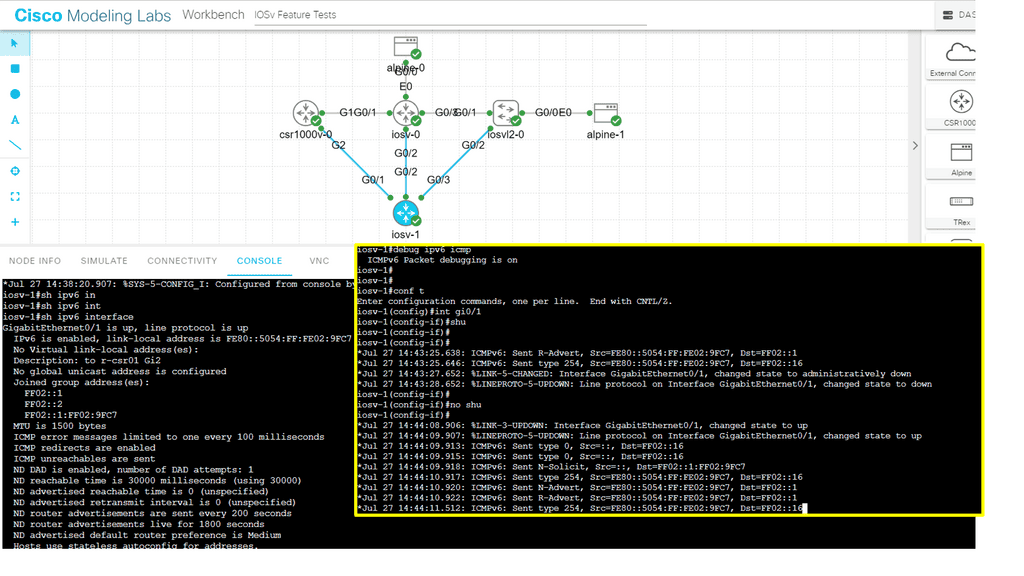
In the following lab, I enabled IPv6 on the G0/1 interface of the device labeled IOSv-1. By default, several events occurred. IPv6 Link-Local addresses, and a base configuration for IPv6 were assigned, which you can see in the screenshot.
As a test, I did an admin shut and no shit on the interface to see what messages would be sent. You can see that ICMPv6 R-Advertisement and type 254 were sent.CMPv6 R-Advertisement, also known as Router Advertisement, is a fundamental component of the IPv6 protocol suite.
It enables routers to inform neighboring devices about their presence and network configuration, facilitating the auto-configuration of IPv6 addresses on the network. Routers periodically send R-Advertisement messages to the local link, providing essential information to connected devices. Notice that no ICMPv6 messages have been received, as I did not enable IPv6 anywhere else on the network.
ICMPv6 offers equivalent functions to IPv4 ARP.
IPv6 has to discover other adjacent IPv6 nodes over layer 2. It uses Neighbor Discovery Protocol ( NDP ) to find IPv6 neighbors, and NDP operates over ICMPv6, not directly over Ethernet, unlike Address Resolution Protocol ( ARP ) for IPv4.
ICMPv6 offers functions equivalent to IPv4 ARP and additional functions such as SEND ( Secure Neighbor Discovery ) and MLD ( Multicast Listener Discovery ). If you expand layer 2 and adjacent IPv6, hosts connect via layer 2 switches, not layer 3 routers. You will face IPv6 layer 2 first-hop security problems.
Of course, if you “properly” configured the network and used layer 2 it should only be used for adjacent node discovery. The first hop could then be a layer 3 switch, which removes IPv6 layer 2 vulnerabilities. For example, the layer 3 switch cannot listen to IPv6 RA messages and could also provide uRFP to verify the source of IPv6, mitigating IPv6 spoofing.
One of the differences between IPv4 and IPv6 is that we no longer use ARP (Address Resolution Protocol). ND (Neighbor Discovery Protocol) replaces its functionality. In this lesson, we’ll examine how ND works.
ND uses ICMP and solicited-node multicast addresses to discover the layer two address of other IPv6 hosts on the same network (local link). It uses two messages to accomplish this:
- Neighbor solicitation message
- Neighbor advertisement message
IPv6 Neighbor Solicitation Message
The Neighbor Solicitation (NS) message is integral to the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) in IPv6. A node uses it to determine the link-layer address of a neighboring node or to check the reachability of a specific IP address within the local network. The NS message is typically sent to the solicited-node multicast address, allowing the intended recipient to respond accordingly.
The destination address will be the solicited-node multicast address of the remote host. This message also includes the layer two address of the host sending it. In the ICMP header of this packet, you will find a type value of 135.
Neighbor Advertisement Message
The primary function of the Neighbor Advertisement Message is to facilitate address resolution. When a device needs to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends an IPv6 packet with the target device’s IPv6 address. The receiving device then responds with a Neighbor Advertisement Message, providing its link-layer address. This enables the sender to establish a direct communication link with the target device.
The most crucial part is that this message includes the host’s layer two address. The neighbor advertisement message uses type 136 in the ICMPv6 packet header.
Guide: IPv6 Neighbor Solicitation and Advertisement
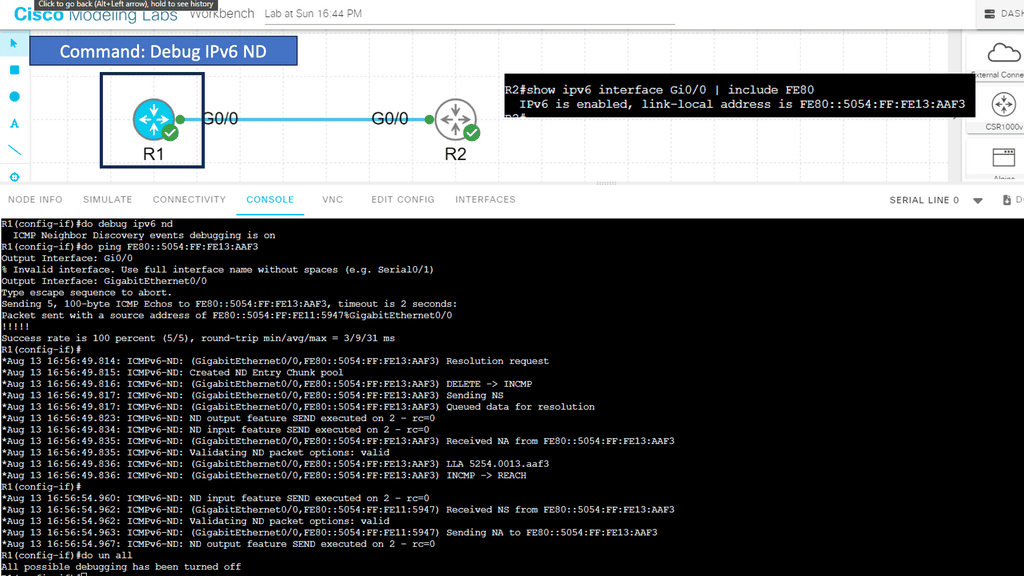
In the following guide, I have two routers directly connected. My only configuration is that I have enabled IPv6 with the IPv6 enable command under the connecting interfaces. I then ran a ping from the R1 to the R2 link-local address. Notice the output from the debug ipv6 nd command.
First, we see a line that includes INCMP. This indicates that the address resolution is in progress. Next, we see that R1 sends the NS (neighbor solicitation) and receives the NA (neighbor advertisement). In the neighbor advertisement, it finds the layer two address of R2.
Then, the status jumps from INCMP to REACH since R1 can reach R2. Also, notice that R1 receives a neighbor solicitation from R2 and replies with the neighbor advertisement.
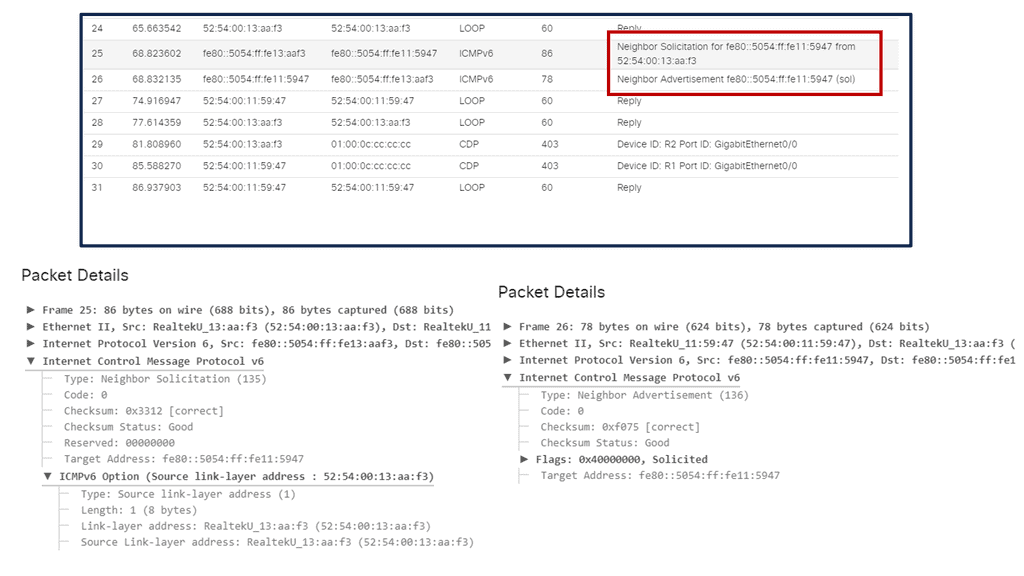
I also run a Packet Capture on the Gigabit link. Notice the neighborhood solicitation and neighbor advertisement addresses in the output below.
ICMPv6 and ICMP
Initially, Internet Control Messaging Protocol ( ICMP ) was introduced to aid network troubleshooting by providing tools used to verify end-to-end reachability. ICMP also reports back errors on hosts. Unfortunately, due to its nature and lack of built-in security, it quickly became a target for many attacks.
For example, ICMP REQUESTS are used by an attacker for network reconnaissance. ICMP’s lack of inherent security opened it up to several vulnerabilities and IPv6 security risks. Security teams block all ICMP message types, adversely affecting functional ICMP features such as Path MTU.
ICMP for v4 and v6 are entirely different. Unlike ICMP for IPv4, ICMPv6 is an integral part of IPv6 communication, and ICMPv6 has features required for IPv6 operation. For this reason, blocking ICMPv6 and all its message types is impossible. Instead, ICMPv6 is a legitimate part of V6; you must select what you can filter.
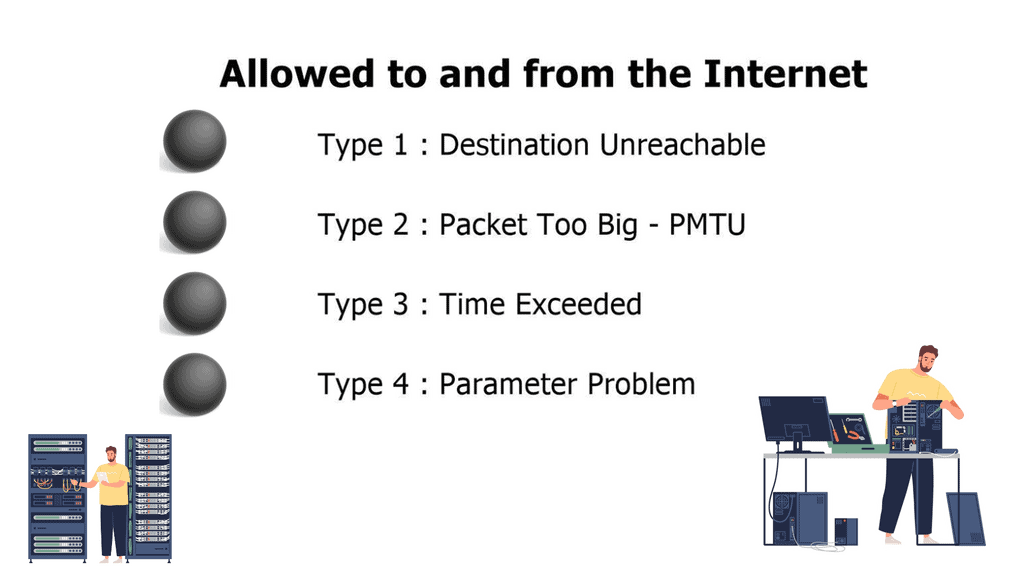
These ICMPv6 error messages are similar to ICMPv4 error messages:
- Destination Unreachable
- Packet Too Big
- Time Exceeded
- Parameter Problem
The following ICMPv6 informational messages used by ping are also similar to those in ICMPv4:
- Echo Request
- Echo Reply
ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery, which includes address resolution (similar to ARP in IPv4), Duplicate Address Detection (DAD), and Neighbor Unreachability Detection (NUD). Neighbor Discovery uses the following ICMPv6 informational messages (see RFC 4861):
- Router Solicitation
- Router Advertisement
- Neighbor Solicitation
- Neighbor Advertisement
- Redirect
ICMPv6 Security: ICMPv6 and Hop Count
Most ICMPv6 messages have their hop count set to 255, exempt from PMTU and ICMPv6 error messages. Any device that receives an ICMPv6 message with a max hop count of less than 255 should drop the packet as an illegal source could craft it. By default, ICMPv6, with a hop count of 255 messages, is dropped at layer 3 boundaries, which are used as a loop prevention mechanism.
The default behavior can cause security concerns. For example, if a firewall receives an ICMPv6 packet with a hop count of 1, it decrees the hop count and sends back an ICMPv6 time exceeded. If a firewall follows default behavior, the attacker could overwhelm packets containing Time-To-Live ( TTL ) 1. Potential DoS are attacking firewall devices.
Try to harden devices by limiting the ICMPv6 error message rate. This will prevent DoS attacks by attackers sending a barrage of malformed packets requiring many ICMPv6 error messages. Use command—ipv6 ICMP error-interval to limit the error return rate.
ICMPv6 Security: Prevent ICMPv6 address spoofing
The best practice is to check the source and destination address in an ICMPv6 packet. For example, in MLD ( Multicast Listener Discovery ), the source should always be a link-local address. If not, the packet likely originated from an illegal source and should be dropped. You may also block any ICMPV6 address that the IANA has not assigned. However, this is a manual process, and ACL adjustments are made whenever IANA changes the list.
Recap: ICMPv6 Features and Functions:
ICMPv6 encompasses many features and functions that enhance network communications’ efficiency and reliability. Some critical aspects of ICMPv6 include:
Neighbor Discovery:
ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is pivotal in identifying and locating neighboring devices on an IPv6 network. It enables automatic configuration, duplicate address detection, and router discovery, ensuring seamless device communication.
In IPv6, neighbor discovery is essential for identifying neighboring devices on the same network. ICMPv6 facilitates this process using Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbor Advertisement messages for address resolution, duplicate address detection, and router discovery. These functions enable devices to learn about their neighbors and maintain efficient communication.
Packet Error Reporting:
ICMPv6 incorporates error reporting mechanisms, enabling devices to report errors encountered during packet transmission. This feature assists network administrators in diagnosing and troubleshooting network issues promptly.
ICMPv6 plays a crucial role in reporting network connectivity and packet delivery errors. When a destination host or router encounters an issue, it generates an ICMPv6 error message and sends it back to the source to inform about the problem. This feedback mechanism helps diagnose and troubleshoot network issues.
Path MTU Discovery:
Path Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) discovery is an essential function of ICMPv6. It enables efficient transmission of IPv6 packets by determining the maximum packet size that can be transmitted without fragmentation. This feature helps avoid unnecessary packet fragmentation, reducing network overhead.
Path Maximum Transmission Unit (PMTU) is the maximum packet size transmitted over a network path without fragmentation. ICMPv6 Path MTU Discovery allows devices to dynamically determine the path MTU and adjust packet sizes accordingly.
Multicast Listener Discovery:
ICMPv6 Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) allows IPv6 hosts to join or leave multicast groups. MLD enables efficient multicast communication and facilitates the deployment of various multicast applications.
As IPv6 supports multicast communication, ICMPv6 provides mechanisms for devices to discover and join multicast groups. Through Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) messages, devices can indicate their interest in receiving multicast traffic and efficiently manage group membership.
Router Advertisement and Solicitation:
ICMPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) and Router Solicitation (RS) messages are crucial in IPv6 network configuration. RAs enable routers to advertise their presence and provide essential network information to hosts, while RS messages facilitate the discovery of neighboring routers.
ICMPv6: Closing Points
IPv6 ICMPv6 plays a crucial role in enhancing the functionality and reliability of IPv6 networks. Its error reporting capabilities, neighbor discovery mechanisms, path MTU discovery, and multicast listener discovery functions make it an essential component of the next-generation Internet Protocol.
As the world transitions towards IPv6, understanding ICMPv6 becomes paramount for network administrators and engineers to effectively manage and troubleshoot IPv6 networks. Embracing the power of IPv6 ICMPv6 will ensure seamless connectivity and pave the way for a more advanced and efficient networking landscape.
Remember, ICMPv6 is not just an upgrade from ICMPv4; it is a protocol that caters specifically to the needs of IPv6 networks. By understanding its features and advantages, network professionals can optimize their infrastructure and embrace the future of Internet communication.
ICMPv6 is more than just a protocol; it’s a vital component that supports the modern internet’s infrastructure. By offering enhanced diagnostic capabilities, robust error messaging, and improved security features, ICMPv6 ensures the reliable and efficient operation of IPv6 networks. As we continue to transition to a world dominated by IPv6, understanding and leveraging ICMPv6 will be crucial for both network administrators and businesses aiming to stay ahead in the digital age.
Summary: ICMPv6
ICMPv6, or Internet Control Message Protocol version 6, is crucial in networking. In this blog post, we delved into the depths of ICMPv6, uncovering its significance, functions, and how it enhances the performance of Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) networks.
Section 1: Understanding ICMPv6
ICMPv6, the successor to ICMPv4, is an integral part of the IPv6 suite. It serves as a vital communication protocol, facilitating the exchange of control and error messages between network devices. Unlike its predecessor, ICMPv6 is designed specifically for IPv6 networks, addressing this advanced protocol’s unique requirements and features.
Section 2: ICMPv6 Functions and Features
Within the world of IPv6, ICMPv6 carries out various essential functions. It provides diagnostic and error reporting capabilities, enabling network devices to communicate issues and errors encountered during packet transmission efficiently. Additionally, ICMPv6 supports the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), which plays a pivotal role in maintaining the network topology, addressing, and link-state information.
Section 3: ICMPv6 Message Types
ICMPv6 encompasses a range of message types, each serving a specific purpose in network communication. From Router Solicitation (RS) and Router Advertisement (RA) messages that facilitate the autoconfiguration of IPv6 addresses to Echo Request and Echo Reply messages used in network diagnostics, these ICMPv6 messages play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and performance of IPv6 networks.
Section 4: Security Considerations and ICMPv6
While ICMPv6 provides valuable functionality, it is essential to address potential security concerns. Network administrators must implement appropriate measures to protect against ICMPv6-based attacks, such as Neighbor Discovery Protocol attacks or ICMPv6 flooding. The network’s security can be enhanced effectively by employing techniques like ingress filtering and implementing strict firewall rules.
Conclusion
ICMPv6 serves as the backbone of IPv6 networks, enabling efficient communication and diagnostics. Understanding its functions and features is vital for network administrators and enthusiasts alike. By grasping the significance of ICMPv6 and implementing necessary security measures, we can harness the power of this protocol to build robust and secure network infrastructures in the age of IPv6.