CASB Tools
Cloud computing has become an integral part of modern businesses, offering unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, the reliance on the cloud also brings forth new security challenges. Companies must ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data, even when it resides outside their traditional network perimeters. This is where Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) tools come into play. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of CASB tools and how they help organizations enhance their cloud security.
CASB tools act as a crucial intermediary layer between an organization’s on-premises network and the cloud service providers they utilize. These tools provide a range of security capabilities, including visibility, control, and threat protection. By implementing CASB tools, businesses gain granular visibility into their cloud usage, allowing them to identify potential risks, enforce security policies, and protect sensitive data.
Highlights: CASB Tools
- Network Security Components
Recently, when I spoke to Sorell Slaymaker, we agreed that every technology has its own time and place. Often a specific product set is forcefully molded to perform all tasks. This carries along with its problems. For example, no matter how modified the Next-Gen firewall is, it cannot provide total security. As you know, we need other products for implementing network security, such as a proxy or a cloud access security broker (CASB API) to work alongside the Next-Gen firewall and zero trust technologies, such as single packet authorization to complete the whole picture.
Before you proceed, you may find the following posts helpful
- SASE Definition.
- Zero Trust SASE
- Full Proxy
- Cisco Umbrella CASB
- OpenStack Architecture
- Linux Networking Subsystem
- Cisco CloudLock
- Network Configuration Automation
- A key point: Video on Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB).
In the following video, we will discuss cloud access security brokers. CSB are subject matter experts in the middle, assisting with a wide range of cloud enablement challenges. The CASB API consists of a broker relationship between the cloud and the consumer and applies to public and private clouds serving all cloud service models – IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Back to basics with CASB
A cloud access security broker (CASB) allows you to move to the cloud safely. It protects your cloud users, data, and apps that can enable identity security. With a CASB, you can more quickly combat data breaches while meeting compliance regulations.
For example, Cisco has a CASB in its SASE Umbrella solution that exposes shadow IT by supplying the ability to detect and report on cloud applications in use across your organization. For discovered apps, you can view details on the risk level and block or control usage to manage cloud adoption better and reduce risk.
Key Features and Benefits:
1. Visibility and Control:
CASB tools offer comprehensive visibility into cloud applications and services being used within an organization. They provide detailed insights into user activities, data transfers, and application dependencies, allowing businesses to monitor and manage their cloud environment effectively. With this information, organizations can create and enforce access policies, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access critical data and applications.
2. Data Loss Prevention:
CASB tools help prevent data leakage by monitoring and controlling the movement of data within the cloud. They employ advanced techniques such as encryption, tokenization, and data classification to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Additionally, CASB tools enable businesses to set up policies that detect and prevent data exfiltration, ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
3. Threat Protection:
CASB tools play a vital role in identifying and mitigating cloud-based threats. They leverage machine learning algorithms and behavioral analytics to detect anomalous user behavior, potential data breaches, and malware infiltration. By continuously monitoring cloud activities, CASB tools can quickly detect and respond to security incidents, thereby minimizing the impact of potential breaches.
4. Compliance and Governance:
Maintaining compliance with industry regulations is a top priority for organizations across various sectors. CASB tools provide the necessary controls and monitoring capabilities to help businesses meet compliance requirements. They assist in data governance, ensuring that data is stored, accessed, and transmitted securely according to applicable regulations.
CASB Tools: Introducing CASB API Security
Network security components are essential for safeguarding business data. As most data exchange is commonplace in business, APIs are also widely leveraged. An application programming interface (API) is a standard way of exchanging data between systems, typically over an HTTP/S connection. An API call is a predefined way of obtaining access to specific types of information kept in the data fields.
However, with the acceleration of API communication in the digital world, API security, and CASB API marks a critical moment as the data is being passed everywhere. The rapid growth of API communication has resulted in many teams being unprepared. Although there is an ease in performing the API integrations, along with that comes the challenging part of ensuring proper authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA).
When you initiate an API, there is a potential to open up calls to over 200 data fields. Certain external partners may need access to some, while others may require access to all.
That means a clear and concise understanding of data patterns and access is critical for data loss prevention. Essentially, bad actors are more sophisticated than ever, and simply understanding data authorization is not enough to guard the castle of your data. Business management and finances can face a massive loss due to a lack of data security.
CASB Tools: The challenge
Many enterprise security groups struggle to control the shadow IT; managing all Amazon web services (AWS) accounts is one example where AWS employs tools, such as Macie, that are used for API management. However, these tools work well for only AWS accounts that Macie is turned on for. Enterprises can have hundreds of test and development accounts with a high risk of data leakage, which the security teams are unaware of.
Also, containers and microservices often use transport layer security (TLS) connections to establish secure connectivity, but this falls short in several ways. Examining the world of API security poses the biggest challenge that needs to be solved in the years to come. So what’s the solution?
CASB Tools and CASB API: The way forward
Let’s face it! The digital economy is run by APIs, which permit an exchange of the data that needs to be managed. API security tools have become a top priority with the acceleration of API communication. We don’t want private, confidential, and/or regulated data to leave that is not supposed to leave, and we need to account for data that does leave. If you don’t have something in the middle and encrypt just the connections, data can flow in and out without any governance and compliance.
Ideally, a turnkey product to manage API security in real-time independent of the platform: in the cloud, hybrid, or on-premise, is the next technological evolution of the API security tool market. Authentically, having an API platform across the entire environment, and enforcing real-time security with analytics, empowers the administrators to control the movements and access of data. Currently, API security tools fall into three different types of markets.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers: The CASB API security is between an enterprise and the cloud-hosted services, such as O365, SFDC, ADP, or another enterprise
- API Management Platforms: They focus on creating, publishing, and protecting an API. Development teams that create APIs consumed internally and externally rely on these tools as they write applications. You can check out the Royal Cyber blog to learn about API management platforms like IMB API Connect, MuleSoft, Apigee API, and MS Azure API.
- Proxy Management: They focus on decrypting all the enterprise traffic, scanning, and reporting anomalies. Different solutions are typically used for different types of traffic – web and email. Chat is an example.
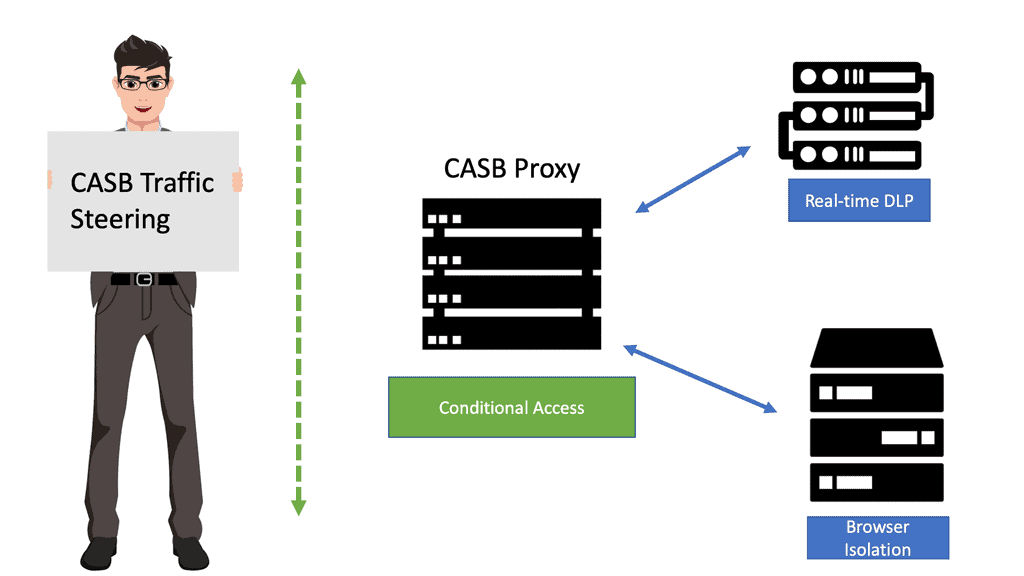
Cloud Access Security Brokers
The rise of CASB occurred due to inadequacies of the traditional WAF, Web Security Gateway, and Next-Gen Firewalls product ranges. The challenge with these traditional products is that they work more as a service than at the data level.
They operate at the HTTP/S layer, usually not classifying and parsing the data. Their protection target is different from that of a CASB. Let’s understand it more closely. If you parse the data, you can classify it. Then you have rules to define the policy, access, and the ability to carry out analytics. As the CASB solutions mature, they will become more automated.
They can automatically do the API discovery, mapping, classifying, and intelligent learning. The CASBs provide a central location for policy and governance. The CASBs sit as a boundary between the entities. It is backed by the prerequisite to be able to decrypt the traffic, be it a TLS or IPSec. After decrypting, it reads, parses, and then re-encrypts the traffic to send it on its way.
Tokenization
When you are in the middle, you need to decrypt the traffic and then parse it to examine and classify all the data. Once it is classified, if there are specific data that is highly sensitive, be it private, confidential, or regulated, you can tokenize it or redact it at a field and file level. Many organizations previously would create a TLS or IPsec connection between themselves and the cloud provider or 3rd party network.
However, they didn’t have strict governance or compliance capabilities to control and track the data going in and out of the organization. TLS or IPsec is the only point-to-point encryption; the traffic is decrypted once you reach the end location. As a result, sensitive data is then available, which could be in an unsecured network.
Additional security controls are needed so that when the connections are complete, the data has an additional level of encryption. TLS or IPSec is for the data in motion, and tokenization is for the data at rest. We have several ways to secure data, and tokenization is one of them. Others include encryption with either provider-managed keys or customer BYOK.
We also have different application-layer encryption. Tokenization substitutes the sensitive data element with a non-sensitive equivalent. The non-sensitive equivalent is referred to as a token. As a result, the 3rd party needs additional credentials to see that data.
However, when you send the data out to a 3rd party, you add another layer of encryption by putting in a token instead of a specific number like the social security number. Redact means that the data is not allowed to leave the enterprise.
CASB API Security
For API security, AAA is at an API layer. This differs from the well-known AAA model used for traditional network access control (NAC). Typically, you allow IP addresses and port numbers in the network world. In an API world, we are at the server and service layer.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a common add-on feature for CSBs. Once you parse and classify the data, you can then govern it. Here, what is of primary concern is what the data is allowed to leave, who is allowed to access it, and when. The DLP is an entire market, whereas the CASB will be specific for specific APIs.
More often than, you need a different DLP solution, for example, to scan your word documents. Some vendors bundle in DLP and CASB. We see this with the Cisco Umbrella, where the CASB and DLP engines are on the same platform.
Presently, the next-generation CASBs are becoming more application-specific. They now have the specific capability for Office 365 and SalesForce. The market is constantly evolving; it will integrate with metadata management over time.
API Management Platforms
API Management platforms are used by DevOps teams when they are creating, publishing, and protecting their APIs. DevOps create an API that is consumed internally and externally to enable their application to rely on these tools. In an enterprise, had everyone been using an effective API management tool, you wouldn’t need a CASB. One of the main reasons for introducing CASBs is that you have a lot of development and test environments that lack good security tools. As a result, you need the 3rd tool to ensure governance and compliance.
-
- Finally, Proxy Management
A proxy monitors all the traffic going in and out of the organization. A standard proxy keeps a tab on the traffic moving internally to the site. A reverse proxy is the opposite, i.e. an external organization looking for internal access to systems. A proxy operates at layer 5 and layer 6. It controls and logs what the site users are doing but does not go into layer 7, where the all-important data is.



