WAN Virtualization
In today's fast-paced digital world, seamless connectivity is the key to success for businesses of all sizes. WAN (Wide Area Network) virtualization has emerged as a game-changing technology, revolutionizing the way organizations connect their geographically dispersed branches and remote employees. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of WAN virtualization, its benefits, implementation considerations, and its potential impact on businesses.
WAN virtualization is a technology that abstracts the physical network infrastructure, allowing multiple logical networks to operate independently over a shared physical infrastructure. It enables organizations to combine various types of connectivity, such as MPLS, broadband, and cellular, into a single virtual network. By doing so, WAN virtualization enhances network performance, scalability, and flexibility.
Increased Flexibility and Scalability: WAN virtualization allows businesses to scale their network resources on-demand, facilitating seamless expansion or contraction based on their requirements. It provides flexibility to dynamically allocate bandwidth, prioritize critical applications, and adapt to changing network conditions.
Improved Performance and Reliability:By leveraging intelligent traffic management techniques and load balancing algorithms, WAN virtualization optimizes network performance. It intelligently routes traffic across multiple network paths, avoiding congestion and reducing latency. Additionally, it enables automatic failover and redundancy, ensuring high network availability.
Simplified Network Management:Traditional WAN architectures often involve complex configurations and manual provisioning. WAN virtualization simplifies network management by centralizing control and automating tasks. Administrators can easily set policies, monitor network performance, and make changes from a single management interface, saving time and reducing human errors.
Multi-Site Connectivity: For organizations with multiple remote sites, WAN virtualization offers a cost-effective solution. It enables seamless connectivity between sites, allowing efficient data transfer, collaboration, and resource sharing. With centralized management, network administrators can ensure consistent policies and security across all sites. Cloud Connectivity:
As more businesses adopt cloud-based applications and services, WAN virtualization becomes an essential component. It provides reliable and secure connectivity between on-premises infrastructure and public or private cloud environments. By prioritizing critical cloud traffic and optimizing routing, WAN virtualization ensures optimal performance for cloud-based applications.Matt Conran
Highlights: WAN Virtualization
Understanding Virtualization
Virtualization is a technology that allows for the creation of virtual versions of various IT resources, such as servers, networks, and storage devices. These virtual resources operate independently from physical hardware, enabling multiple operating systems and applications to run simultaneously on a single physical machine. Virtualization opens up a world of possibilities by breaking the traditional one-to-one relationship between hardware and software. Now, virtualization has moved to the WAN.
WAN Virtualization and SD-WAN
Organizations constantly seek innovative solutions in modern networking to enhance their network infrastructure and optimize connectivity. One such solution that has gained significant attention is WAN virtualization. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of WAN virtualization, its benefits, and how it revolutionizes how businesses connect and communicate.
WAN virtualization, also known as Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN), is a technology that enables organizations to abstract their wide area network (WAN) connections from the underlying physical infrastructure. It leverages software-defined networking (SDN) principles to decouple network control and data forwarding, providing a more flexible, scalable, and efficient network solution.
SD-WAN Highlights
SD-WAN, in essence, is a virtualized approach to wide-area networking. It leverages software-defined networking principles to simplify managing and operating a wide area network, connecting geographically dispersed locations. Unlike traditional networks, SD-WAN offers centralized control, automated traffic management, and enhanced security.
VPN and SDN Components
So, what is WAN virtualization? WAN virtualization is an essential technology in the modern business world. It creates virtualized versions of wide area networks (WANs) – networks spanning a wide geographic area. The virtualized WANs can then manage and secure a company’s data, applications, and services.
Regarding implementation, WAN virtualization requires using a virtual private network (VPN), a secure private network accessible only by authorized personnel. This ensures that only those with proper credentials can access the data. WAN virtualization also requires software-defined networking (SDN) to manage the network and its components.
Related: Before you proceed, you may find the following posts helpful:
- SD WAN Overlay
- Generic Routing Encapsulation
- WAN Monitoring
- SD WAN Security
- Container Based Virtualization
- SD WAN and Nuage Networks
WAN Virtualization Key WAN Virtualization Discussion Points: |
|
Back to Basics: WAN virtualization.
WAN Challenges
Deploying and managing the Wide Area Network (WAN) has become more challenging. Engineers face several design challenges, such as traffic flow decentralizing, inefficient WAN link utilization, routing protocol convergence, and application performance issues with active-active WAN edge designs. Active-active WAN designs that spray and pray over multiple active links present technical and business challenges.
To do this efficiently, you have to understand application flows. There may also be performance problems. When packets get to the other end, there may be out-of-order packets as each link propagates at different speeds. The remote end has to be reassembled and put back together, causing jitter and delay. Both high jitter and delay are bad for network performance. To recap on WAN virtualization, including the drivers for SD-WAN, you may follow this SD WAN tutorial.
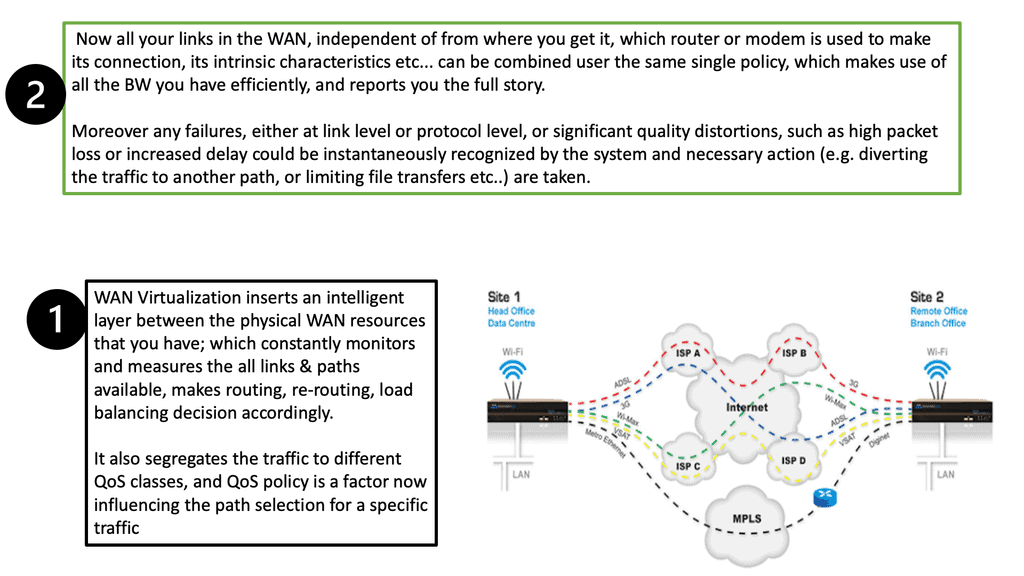
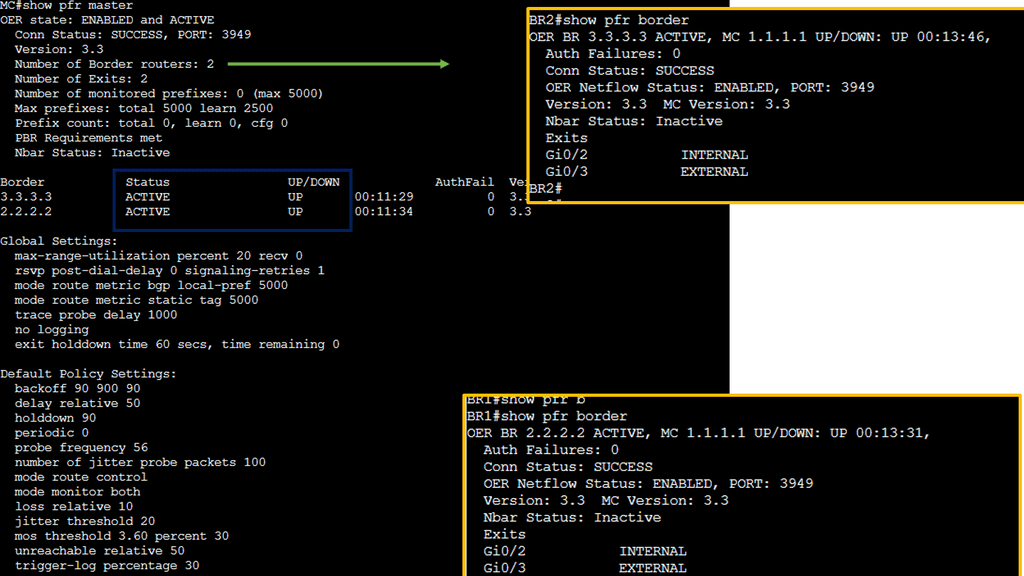
Knowledge Check: Cisco PfR
Cisco PfR is an intelligent routing solution that dynamically optimizes traffic flow within a network. Unlike traditional routing protocols, PfR makes real-time decisions based on network conditions, application requirements, and business policies. By monitoring various metrics such as delay, packet loss, and link utilization, PfR intelligently determines the best path for traffic.
Key Features and Functionalities
PfR offers many features and functionalities that significantly enhance network performance. Some notable features include:
1. Intelligent Path Control: PfR selects the optimal traffic path based on performance metrics, ensuring efficient utilization of network resources.
2. Application-Aware Routing: PfR considers the specific requirements of different applications and dynamically adjusts routing to provide the best user experience.
3. Load Balancing: By distributing traffic across multiple paths, PfR improves network efficiency and avoids bottlenecks.
Knowledge Check: Control and Data Plane
Understanding the Control Plane
The control plane can be likened to a network’s brain. It is responsible for making high-level decisions and managing network-wide operations. From routing protocols to network management systems, the control plane ensures data is directed along the most optimal paths. By analyzing network topology, the control plane determines the best routes to reach a destination and establishes the necessary rules for data transmission.
Unveiling the Data Plane
In contrast to the control plane, the data plane focuses on the actual movement of data packets within the network. It can be thought of as the hands and feet executing the control plane’s instructions. The data plane handles packet forwarding, traffic classification, and Quality of Service (QoS) enforcement tasks. It ensures that data packets are correctly encapsulated, forwarded to their intended destinations, and delivered with the necessary priority and reliability.
Use Cases and Deployment Scenarios
Distributed Enterprises
For organizations with multiple branch locations, WAN virtualization offers a cost-effective solution for connecting remote sites to the central network. It allows for secure and efficient data transfer between branches, enabling seamless collaboration and resource sharing.
Cloud Connectivity
WAN virtualization is ideal for enterprises adopting cloud-based services. It provides a secure and optimized connection to public and private cloud environments, ensuring reliable access to critical applications and data hosted in the cloud.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
WAN virtualization plays a vital role in disaster recovery strategies. Organizations can ensure business continuity during a natural disaster or system failure by replicating data and applications across geographically dispersed sites.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing WAN virtualization requires careful planning and consideration. Factors such as network security, bandwidth requirements, and compatibility with existing infrastructure need to be evaluated. It is essential to choose a solution that aligns with the specific needs and goals of the organization.
SD-WAN vs. DMVPN
Two popular WAN solutions are DMVPN and SD-WAN.
DMVPN (Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network) and SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) are popular solutions to improve connectivity between distributed branch offices. DMVPN is a Cisco-specific solution, and SD-WAN is a software-based solution that can be used with any router. Both solutions provide several advantages, but there are some differences between them.
DMVPN is a secure, cost-effective, and scalable network solution that combines underlying technologies and DMVVPN phases (for example, the traditional DMVPN phase 1 ) to connect multiple sites. It allows the customer to use existing infrastructure and provides easy deployment and management. This solution is an excellent choice for businesses with many branch offices because it allows for secure communication and the ability to deploy new sites quickly.
SD-WAN is a software-based solution that is gaining popularity in the enterprise market. It provides improved application performance, security, and network reliability. SD-WAN is an excellent choice for businesses that require high-performance applications across multiple sites. It provides an easy-to-use centralized management console that allows companies to deploy new sites and manage the network quickly.
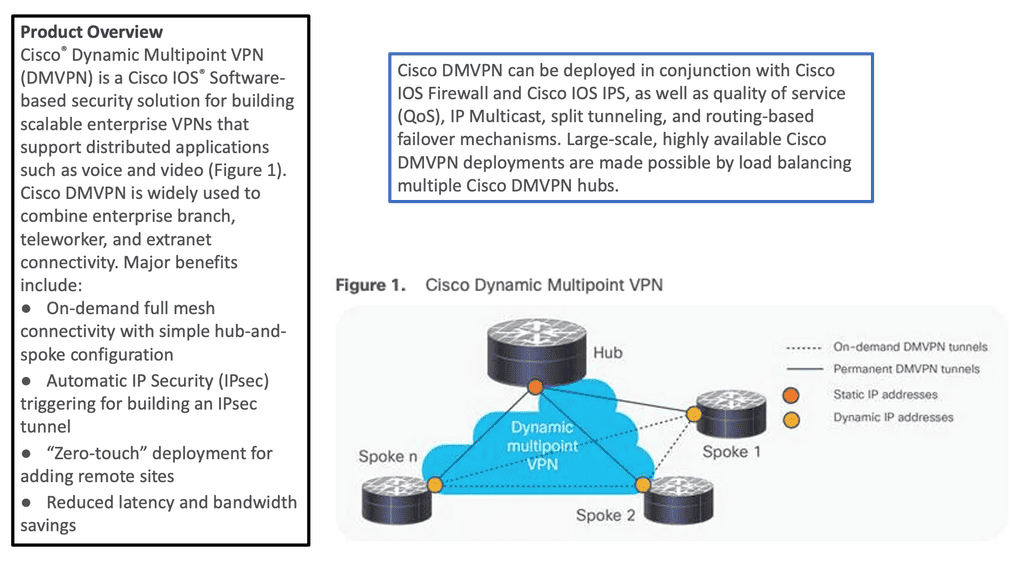
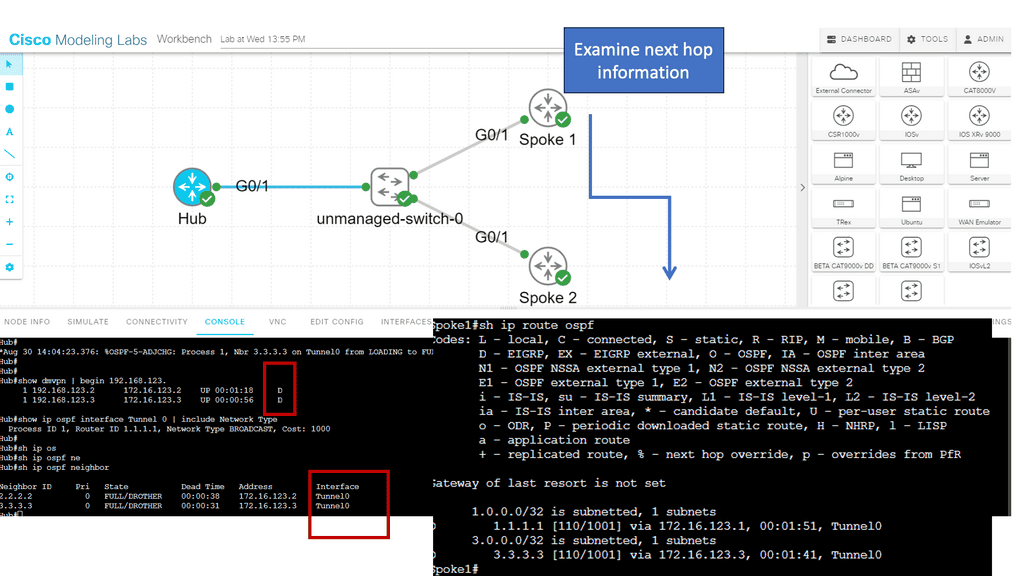
1st Lab Guide: DMVPN operating over the WAN
The following shows DMVPN operating over the WAN. The SP node represents the WAN network. Then we have R11 as the hub and R2, R3 as the spokes. Several protocols make the DMVPM network over the WAN possible. We have GRE; in this case, the tunnel destination is specified as a point-to-point GRE tunnel instead of a mGRE tunnel.
Then we have NHRP, which is used to help create a mapping as this is a nonbroadcast network; we can not use ARP. So, we need to manually set this up on the spokes with the command: ip nhrp NHS 192.168.100.11
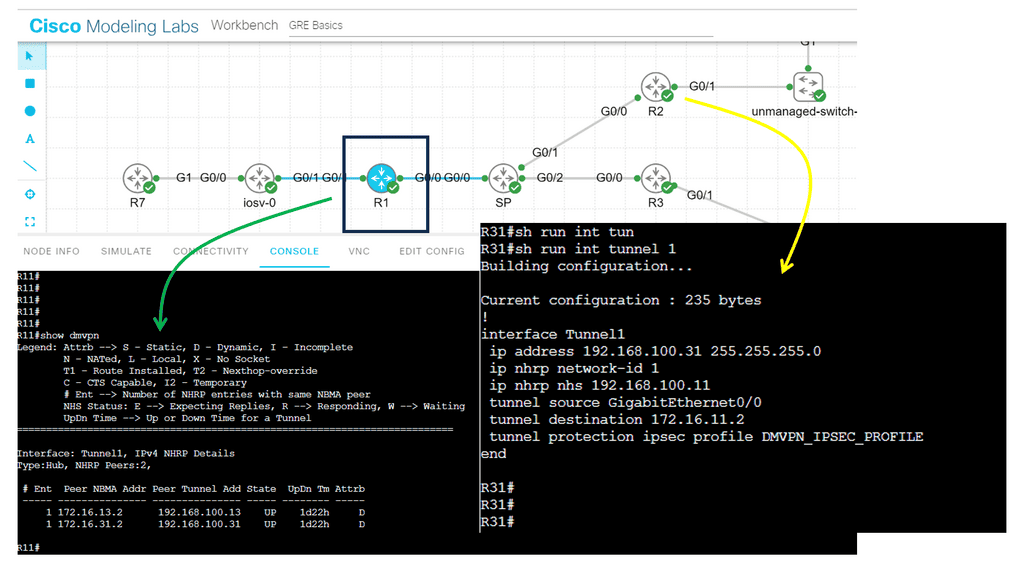
Shift from network-centric to business intent.
The core of WAN virtualization involves shifting focus from a network-centric model to a business intent-based WAN network. So, instead of designing the WAN for the network, we can create the WAN for the application. This way, the WAN architecture can simplify application deployment and management.
First, however, the mindset must shift from a network topology focus to an application services topology. A new application style consumes vast bandwidth and is very susceptible to variations in bandwidth quality. Things such as jitter, loss, and delay impact most applications, which makes it essential to improve the WAN environment for these applications.
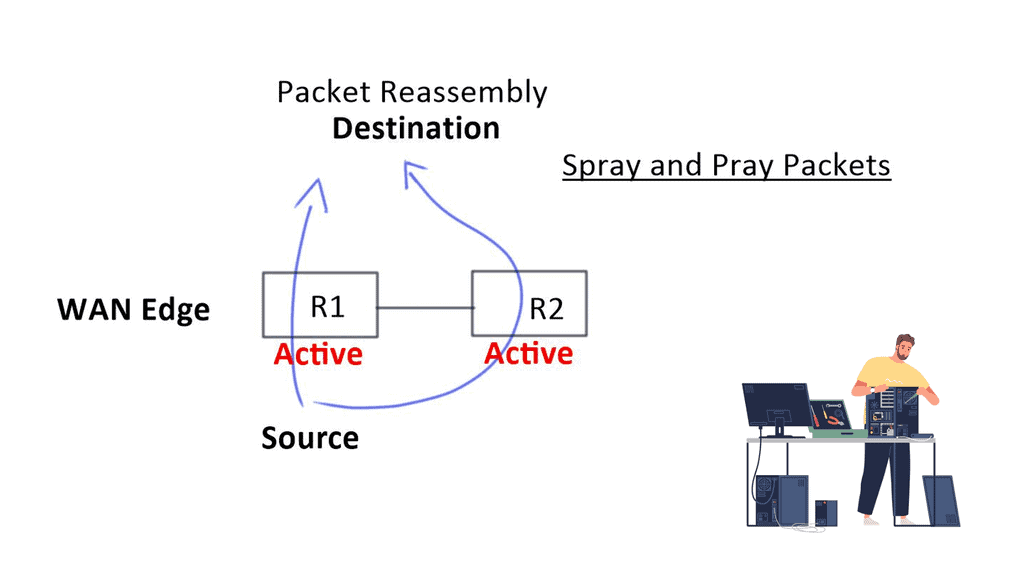
The spray-and-pray method over two links increases bandwidth but decreases “goodput.” It also affects firewalls, as they will see asymmetric routes. When you want an active-active model, you need application session awareness and a design that eliminates asymmetric routing. It would help if you could slice the WAN properly so application flows can work efficiently over either link.
What is WAN Virtualization: Decentralizing Traffic
Decentralizing traffic from the data center to the branch requires more bandwidth to the network’s edges. As a result, we see many high-bandwidth applications running on remote sites. This is what businesses are now trying to accomplish. Traditional branch sites usually rely on hub sites for most services and do not host bandwidth-intensive applications. Today, remote locations require extra bandwidth, which is not cheaper yearly.
Inefficient WAN utilization
Redundant WAN links usually require a dynamic routing protocol for traffic engineering and failover. Routing protocols require complex tuning to load balance traffic between border devices. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the primary protocol for connecting sites to external networks.
It relies on path attributes to choose the best path based on availability and distance. Although these attributes allow granular policy control, they do not cover aspects relating to path performance, such as Round Trip Time (RTT), delay, and jitter.
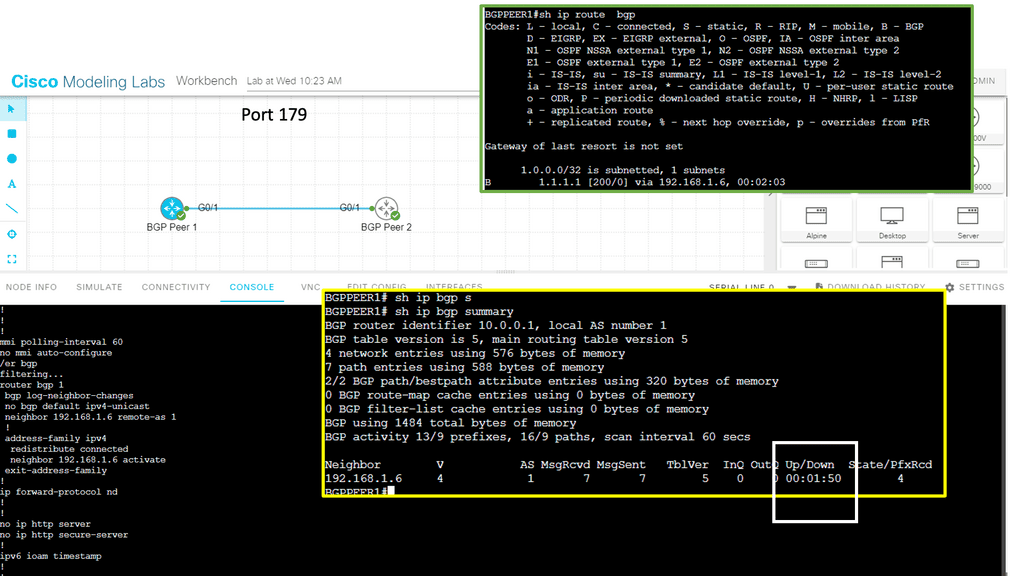
Routing protocol convergence
WAN designs can also be active standby, which requires routing protocol convergence in the event of primary link failure. However, routing convergence is slow, and to speed up, additional features, such as Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD), are implemented that may stress the network’s control plane. Although mechanisms exist to speed up convergence and failure detection, there are still several convergence steps, such as:
Rouitng Convergence | Convergence |
Detect | |
Describe | |
Switch | |
Find |
Branch office security
With traditional network solutions, branches connect back to the data center, which typically provides Internet access. However, the application world has evolved, and branches directly consume applications such as Office 365 in the cloud. This drives a need for branches to access these services over the Internet without going to the data center for Internet access or security scrubbing.
Extending the security diameter into the branches should be possible without requiring onsite firewalls / IPS and other security paradigm changes. A solution must exist that allows you to extend your security domain to the branch sites without costly security appliances at each branch—essentially, building a dynamic security fabric.
WAN Virtualization
The solution to all these problems is SD-WAN ( software-defined WAN ). SD-WAN is a transport-independent overlay software-based networking deployment. It uses software and cloud-based technologies to simplify the delivery of WAN services to branch offices. Similar to Software Defined Networking (SDN), SD-WAN works by abstraction. It abstracts network hardware into a control plane with multiple data planes to make up one large WAN fabric.
SD-WAN in a nutshell
When we consider the Wide Area Network (WAN) environment at a basic level, we connect data centers to several branch offices to deliver packets between those sites, supporting the transport of application transactions and services. The SD-WAN platform allows you to pull Internet connectivity into those sites, becoming part of one large transport-independent WAN fabric.
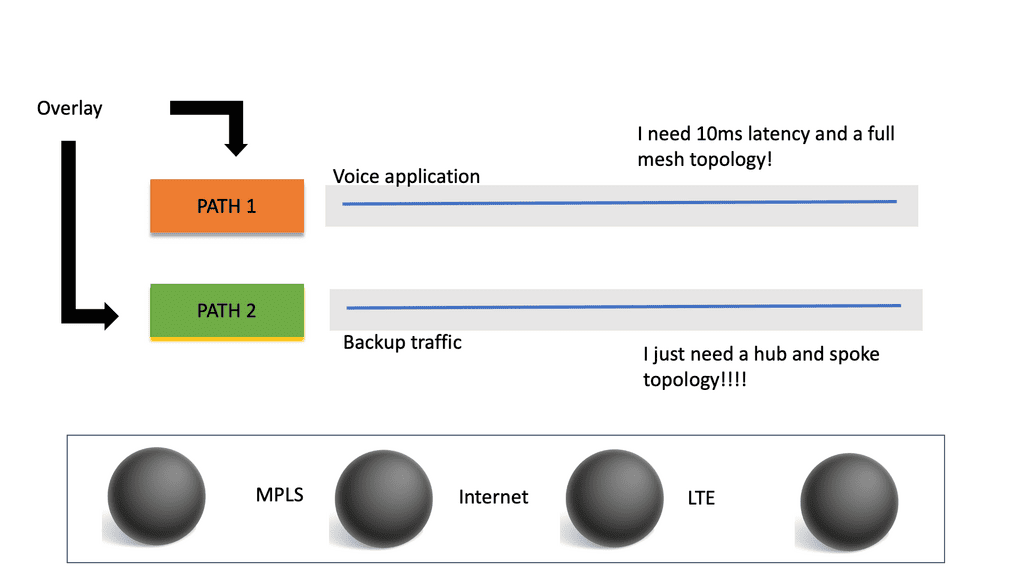
SD-WAN monitors the paths and the application performance on each link (Internet, MPLS, LTE ) and chooses the best path based on performance.
There are many forms of Internet connectivity (cable, DSL, broadband, and Ethernet). They are quick to deploy at a fraction of the cost of private MPLS circuits. SD-WAN provides the benefit of using all these links and monitoring which applications are best for them.
Application performance is continuously monitored across all eligible paths-direct internet, internet VPN, and private WAN. It creates an active-active network and eliminates the need to use and maintain traditional routing protocols for active-standby setups—no reliance on the active-standby model and associated problems.
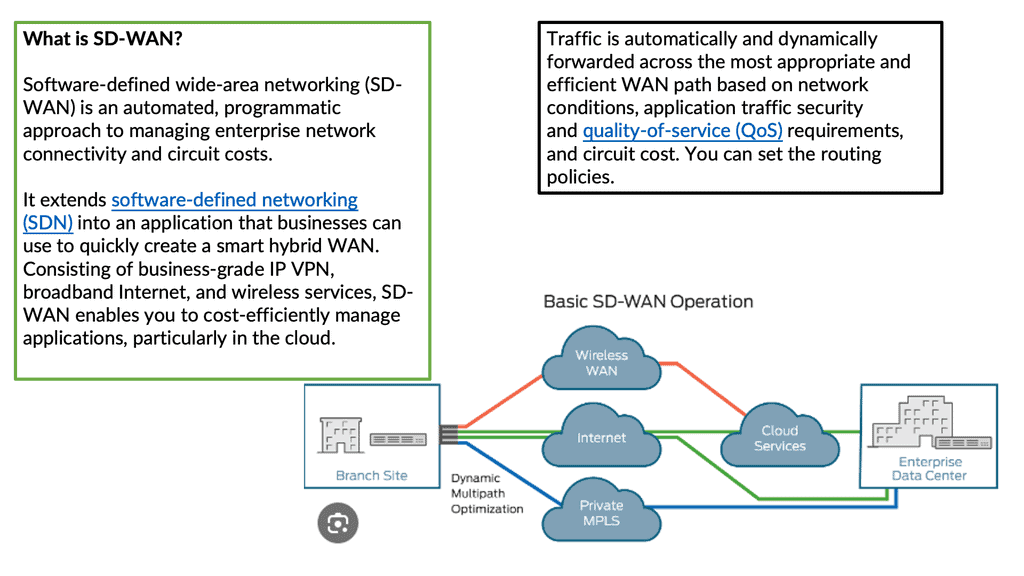
SD-WAN simplifies WAN management
SD-WAN simplifies managing a wide area network by providing a centralized platform for managing and monitoring traffic across the network. This helps reduce the complexity of managing multiple networks, eliminating the need for manual configuration of each site. Instead, all of the sites are configured from a single management console.
SD-WAN also provides advanced security features such as encryption and firewalling, which can be configured to ensure that only authorized traffic is allowed access to the network. Additionally, SD-WAN can optimize network performance by automatically routing traffic over the most efficient paths.
SD-WAN Packet Steering
SD-WAN packet steering is a technology that efficiently routes packets across a wide area network (WAN). It is based on the concept of steering packets so that they can be delivered more quickly and reliably than traditional routing protocols. Packet steering is crucial to SD-WAN technology, allowing organizations to maximize their WAN connections.
SD-WAN packet steering works by analyzing packets sent across the WAN and looking for patterns or trends. Based on these patterns, the SD-WAN can dynamically route the packets to deliver them more quickly and reliably. This can be done in various ways, such as considering latency and packet loss or ensuring the packets are routed over the most reliable connections.
Spraying packets down both links can result in 20% drops or packet reordering. SD-WAN makes packets better utilized, no reorder, and better “goodput.” SD-WAN increases your buying power and results in buying lower bandwidth links and running them more efficiently. Over-provision is unnecessary as you are using the existing WAN bandwidth better.
Knowledge Check: Application-Aware Routing (AAR)
Understanding Application-Aware Routing (AAR)
Application-Aware Routing is a sophisticated networking technique that goes beyond traditional packet-based routing. It considers the unique requirements of different applications, such as video streaming, cloud-based services, or real-time communication, and optimizes the network path accordingly. By prioritizing and steering traffic based on application characteristics, it ensures smooth and efficient data transmission.
Benefits of Application-Aware Routing
2.1 Enhanced Performance: Application-aware routing significantly improves overall performance by dynamically allocating network resources to applications with high bandwidth or low latency requirements. This translates into faster downloads, seamless video streaming, and reduced response times for critical applications.
2.2 Increased Reliability: Traditional routing methods treat all traffic equally, often resulting in congestion and potential bottlenecks. Application Aware Routing intelligently distributes network traffic, avoiding congested paths and ensuring a reliable and consistent user experience. In network failure or congestion, it can dynamically reroute traffic to alternative paths, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
Implementation Strategies
Deep Packet Inspection: A key component of Application-Aware Routing is deep packet inspection (DPI), which analyzes the content of network packets to identify specific applications. DPI enables routers and switches to make informed decisions about handling each packet based on its application, ensuring optimal routing and resource allocation.
3.2 Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration: Implementing QoS parameters alongside Application Aware Routing allows network administrators to allocate bandwidth, prioritize specific applications over others, and enforce policies to ensure the best possible user experience. QoS configurations can be customized based on organizational needs and application requirements.
Future Possibilities
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the potential for Application-Aware Routing is boundless. With emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G networks, the ability to intelligently route traffic based on specific application needs will become even more critical. Application-Aware Routing has the potential to optimize resource utilization, enhance security, and support the seamless integration of diverse applications and services.
Benefits of WAN Virtualization:
1. Enhanced Network Performance: WAN virtualization allows organizations to optimize network performance by intelligently routing traffic across multiple WAN links. Organizations can achieve improved application performance and reduced latency by dynamically selecting the most efficient path based on real-time network conditions.
2. Cost Savings: Traditional WAN solutions often require expensive dedicated circuits for each branch office. With WAN virtualization, organizations can leverage cost-effective internet connections, such as broadband or LTE, while ensuring secure and reliable connectivity. This flexibility in choosing connectivity options can significantly reduce operational costs.
3. Simplified Network Management: WAN virtualization provides centralized management and control of the entire network infrastructure. This simplifies network provisioning, configuration, and monitoring, reducing traditional WAN deployments’ complexity and administrative overhead.
4. Increased Scalability: WAN virtualization offers the scalability to accommodate evolving network requirements as organizations grow and expand their operations. It allows for the seamless integration of new branch offices and additional bandwidth without significant infrastructure changes.
5. Enhanced Security: With the rise in cybersecurity threats, network security is paramount. WAN virtualization enables organizations to implement robust security measures, such as encryption and firewall policies, across the entire network. This helps protect sensitive data and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
- A final note on what is WAN virtualization
Server virtualization and automation in the data center are prevalent, but WANs are stalling in this space. It is the last bastion of hardware models that has complexity. Like hypervisors have transformed data centers, SD-WAN aims to change how WAN networks are built and managed. When server virtualization and hypervisor came along, we did not have to worry about the underlying hardware. Instead, a virtual machine (VM) can be provided and run as an application. Today’s WAN environment requires you to manage details of carrier infrastructure, routing protocols, and encryption.
- SD-WAN pulls all WAN resources together and slices up the WAN to match the applications on them.
The Role of WAN Virtualization in Digital Transformation:
In today’s digital era, where cloud-based applications and remote workforces are becoming the norm, WAN virtualization is critical in enabling digital transformation. It empowers organizations to embrace new technologies, such as cloud computing and unified communications, by providing secure and reliable connectivity to distributed resources.
Summary: WAN Virtualization
In our ever-connected world, seamless network connectivity is necessary for businesses of all sizes. However, traditional Wide Area Networks (WANs) often fall short of meeting the demands of modern data transmission and application performance. This is where the concept of WAN virtualization comes into play, promising to revolutionize network connectivity like never before.
Understanding WAN Virtualization
WAN virtualization, also known as Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN), is a technology that abstracts the physical infrastructure of traditional WANs and allows for centralized control, management, and optimization of network resources. By decoupling the control plane from the underlying hardware, WAN virtualization enables organizations to dynamically allocate bandwidth, prioritize critical applications, and ensure optimal performance across geographically dispersed locations.
The Benefits of WAN Virtualization
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability
With WAN virtualization, organizations can effortlessly scale their network infrastructure to accommodate growing business needs. The virtualized nature of the WAN allows for easy addition or removal of network resources, enabling businesses to adapt to changing requirements without costly hardware upgrades.
Improved Application Performance
WAN virtualization empowers businesses to optimize application performance by intelligently routing network traffic based on application type, quality of service requirements, and network conditions. By dynamically selecting the most efficient path for data transmission, WAN virtualization minimizes latency, improves response times, and enhances overall user experience.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
By leveraging WAN virtualization, organizations can reduce their reliance on expensive Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) connections and embrace more cost-effective broadband links. The ability to intelligently distribute traffic across diverse network paths enhances network redundancy and maximizes bandwidth utilization, providing significant cost savings and improved efficiency.
Implementation Considerations
Network Security
When adopting WAN virtualization, it is crucial to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure network integrity. Encryption protocols, threat detection systems, and secure access controls should be implemented to safeguard against potential security breaches.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Organizations should prioritize critical applications and allocate appropriate bandwidth resources through Quality of Service (QoS) policies to ensure optimal application performance. By adequately configuring QoS settings, businesses can guarantee mission-critical applications receive the necessary network resources, minimizing latency and providing a seamless user experience.
Real-World Use Cases
Global Enterprise Networks
Large multinational corporations with a widespread presence can significantly benefit from WAN virtualization. These organizations can achieve consistent performance across geographically dispersed locations by centralizing network management and leveraging intelligent traffic routing, improving collaboration and productivity.
Branch Office Connectivity
WAN virtualization simplifies connectivity and network management for businesses with multiple branch offices. It enables organizations to establish secure and efficient connections between headquarters and remote locations, ensuring seamless access to critical resources and applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, WAN virtualization represents a paradigm shift in network connectivity, offering enhanced flexibility, improved application performance, and cost savings for businesses. By embracing this transformative technology, organizations can unlock the true potential of their networks, enabling them to thrive in the digital age.